Abstract
Despite vast improvements in our understanding of cancer genetics, a large percentage of cancer cases present without knowledge of the causative genetic events. Tyrosine kinases are frequently implicated in the pathogenesis of numerous types of cancer, but identification and validation of tyrosine kinase targets in cancer can be a time-consuming process. We report the establishment of an efficient, functional screening assay using RNAi technology to directly assess and compare the effect of individually targeting each member of the tyrosine kinase family. We demonstrate that siRNA screening can identify tyrosine kinase targets containing activating mutations in Janus kinase (JAK) 3 (A572V) in CMK cells and c-KIT (V560G) in HMC1.1 cells. In addition, this assay identifies targets that do not contain mutations, such as JAK1 and the focal adhesion kinases (FAK), that are crucial to the survival of the cancer cells. This technique, with additional development, might eventually offer the potential to match specific therapies with individual patients based on a functional assay.
Introduction
The recent success of monoclonal antibodies and small-molecule inhibitors of tyrosine kinases in numerous malignancies have highlighted the potential of targeted therapy for the treatment of cancer.1–4 However, broad application of this strategy will require a more detailed understanding of the principal genetic targets involved in cancer pathogenesis in each individual patient. Tyrosine kinases constitute a gene family of 91 members that have an integral role in signal transduction of mammalian cells, including critical cellular processes as diverse as proliferation, apoptosis, differentiation, and cell motililty. Aberrant regulation of any of these processes might contribute to oncogenesis, thus it is not surprising that dysregulation of tyrosine kinase activity has been observed in numerous types of malignancy.5
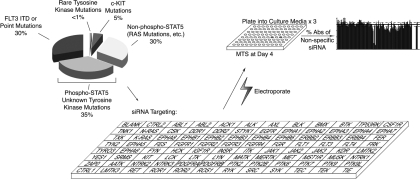
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) represents one malignancy in which tyrosine kinases are abnormally regulated. Previous studies have shown that phosphorylation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 (STAT5) is present in blast cells from at least 70% of patients with AML.6–8 Because STAT5 phosphorylation is tightly controlled by tyrosine kinase signaling networks, this suggests the presence of constitutively active, mutated tyrosine kinases in these patients. To date, the only known activating mutations in tyrosine kinases in AML are point mutations in c-KIT (5%), mutations or internal tandem duplications in FLT3 (30%), and rare mutations observed in JAK2, JAK3, and PDGFR (Figure 1).9–19 These known abnormalities in tyrosine kinases give mechanistic insight into the genetics underlying approximately half of the cases of AML with phospho-STAT5. Of the remaining cases with unknown genetic etiology, the presence of phosphorylated STAT5 suggests that the tyrosine kinase family is one likely source of unknown oncogenic mutations (Figure 1).
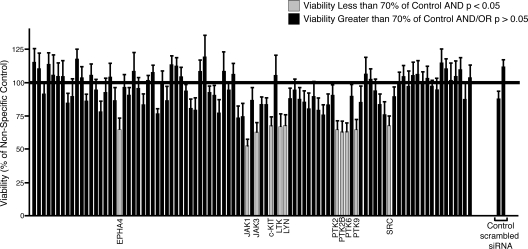
Figure 1.
Scheme for RNAi functional profiling of AML cells. Thirty-five percent of AML cases exhibit phosphorylated STAT5 without knowledge of specific tyrosine kinases that are dysregulated. To better understand which tyrosine kinases contribute to this disease, we administered siRNA individually targeting each member of the tyrosine kinase family as well as N-RAS, K-RAS and 2 controls (CTRL) into AML cell lines. Cells were plated into culture media and subjected to an MTS assay at day 4 after electroporation for determination of cell viability and proliferation. All absorbance values were normalized to the absorbance values of 2 nonspecific control siRNA molecules.
To determine the identity of novel mutant genes in cancer, numerous approaches have been used. One strategy involves large-scale sequencing of selected or entire cancer genomes. While this process has uncovered numerous mutations, the functional role of many of these genetic abnormalities remains unclear.20,21 We have previously reported an alternate strategy that employs phospho-proteomic profiling of cells as a means of guiding sequencing studies to likely sources of mutations.17,22–24 Despite the successes of both of these approaches, an alternative strategy that directly delivers functional information about important genes could offer even greater diagnostic potential for AML as well as other malignancies. RNAi technology allows functional data to be obtained by selectively reducing the expression of individual genes, thus allowing the necessity of those genes for cancer cell viability to be assessed.25,26 Indeed, numerous studies have used individual and multiplexed RNAi screens to better understand radiation and DNA damage susceptibility, mitotic progression, angiogenesis, tumor suppression, genomic stability, as well as to better define numerous signaling pathways in mammalian, Caenorhabditis elegans, and Drosophila melanogaster cells.27–39 With this approach, modified to selectively analyze the tyrosine kinase family, a rapid screen can identify genes that are crucial for cancer cell growth and viability, regardless of their mutational status. These genes can subsequently form the basis for targeted, therapeutic intervention.
To better understand the role of aberrant tyrosine kinase signaling in AML, we developed a high-throughput functional profiling assay that uses RNAi technology. In particular, we used an siRNA library that targets the entire tyrosine kinase gene family to construct functional profiles of AML cell lines, revealing targets critical for the proliferation and viability of these cells. These profiles revealed expected targets based on previously known activating mutations harbored by the CMK and HMC1.1 cell lines. In addition, they revealed unexpected targets that were informative about previously undefined signaling mechanisms of the primary targets. Taken together, this technique has the possibility of offering an efficient and cost-effective alternative to large-scale sequencing projects, and with further development it might provide a useful clinical service for molecular genetic diagnosis of the unique targeted therapy profile of malignancies.
Methods
Cell culture
K562 cells were obtained from American Type Culture Collection (Manassas, VA). CMK and HEL cells were obtained from the German Resource Centre for Biological Material (DSMZ; Braunschweig, Germany). HMC1.1 cells were provided by Dr Michael Heinrich. All cells were maintained in RPMI-1640 medium supplemented with 10% FBS (Atlanta Biologicals, Lawrenceville, GA), l-glutamine, and penicillin/streptomycin (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA). For proliferation assays, cells were incubated for 72 hours in the presence of JAK Inhibitor I, JAK3 inhibitor III, AG-490, PP2, or Src Kinase Inhibitor I (EMD Biosciences, San Diego, CA), and the number of viable cells was determined with the CellTiter 96 AQueous One solution cell proliferation assay (Promega, Madison, WI). For HMC1.1 cell stimulation, cells were serum starved overnight in RPMI supplemented with 0.1% bovine serum albumin, l-glutamine, and penicillin/streptomycin. The following day, cells were stimulated for 5 minutes with 100 ng/mL recombinant stem-cell factor (Peprotech, Rocky Hill, NJ).
Optimization of electroporation conditions
CMK cells (1.5 × 105) were washed one time in OptiMEM (Invitrogen) and resuspended in 75 μL siPORT buffer (Ambion, Austin, TX). Cells were incubated with Block-It Fluorescent Oligo (Invitrogen) at a 1:100 dilution and transferred to a 1-mm cuvette (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA). Electroporation was carried out at 0 V, 100 V, 200 V, 300 V, and 400 V (all 100 μsec, 1 pulse) for determination of optimal voltage. This procedure was repeated at the optimal voltage for 100 μsec, 150 μsec, 200 μsec, and 250 μsec for 1 pulse or 2 pulses for determination of optimal pulse length. All samples were washed in PBS, stained with propidium iodide (PI; Guava viability reagent) for viability analysis (Guava Technologies, Hayward, CA), and analyzed by flow cytometry for fluorescent shift induced by the fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-labeled oligo (FACSAria; BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA). For evaluation of gene knockdown, the above procedure was repeated at the optimal conditions using siRNA targeting GAPDH (Dharmacon, Lafayette, CO) at 500 or 1000 nM. Glyceraldhyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) gene silencing was determined at 48 hours after electroporation by immunoblot analysis for GAPDH and β-actin as a loading control.
siRNA knockdown using tyrosine kinase library
CMK or HMC1.1 cells (107) were washed one time in OptiMEM (Invitrogen) and resuspended in 4.2 mL of siPORT buffer (Ambion). Cells were aliquoted at 42 μL per well onto a 96-well electroporator (Ambion) and 2 μL of siRNA at 20 μM was added to each well. The tyrosine kinase library used in this study contains 4 siRNA targeting constructs per well (purchased from Dharmacon), and we manually added single and pooled nonspecific siRNA as well as siRNA pools (4 constructs per target) against ephrin type-A receptor (EPHA)5, EPHA6, src-related kinase lacking C-terminal regulatory tyrosine and N-terminal myristylation (SRMS), apoptosis-associated tyrosine kinase (AATK), lemur tyrosine kinase (LMTK)3, N-RAS, K-RAS (all from Dharmacon). These were added separately because they are not included in the standard tyrosine kinase library. Cells were electroporated at 2220 V (equivalent of 300 V per well), 100 μsec, 2 pulses and 15 000 cells per well were replated using a Hydra 96-channel automated pipettor (Matrix Technologies, Hudson, NH) into triplicate plates containing 100 μL per well of standard culture media. For determination of cell viability and proliferation, cells were subjected to the CellTiter 96 AQueous One solution cell-proliferation assay (MTS; Promega). All values were normalized to the mean of the 2 nonspecific siRNA control wells.
Confirmation of RNAi silencing
For confirmation of efficient knockdown in HMC1.1 cells, siRNA targeting JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, EPHA4, PTK2, PTK2B, PTK6, PTK9, LTK, LYN, SRC, and c-KIT, was transfected at 300 V, 100 μsec, 2 pulses and whole cell lysates (see “Immunoblotting”) or total cellular RNA (Qiagen, Valencia, CA) were harvested after 48 hours using standard procedures. Total RNA was used to synthesize cDNA (Invitrogen SuperScript III) and quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) against each respective gene (primers listed in Document S1, available on the Blood website; see the Supplemental Materials link at the top of the online article) as well as GAPDH40 was performed on each sample using SYBR Green qPCR SuperMix (Invitrogen) and a DNA Engine Opticon 2 system for real-time PCR (Bio-Rad). Quantitative PCR cycle values were converted to arbitrary qPCR units based on a standard curve for each gene or GAPDH, each value was normalized to its respective GAPDH value, and percent knockdown was calculated based on the following formula: (nonspecific − gene-specific)/nonspecific × 100. Whole cell lysates were separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and analyzed by immunoblotting using antibodies against JAK1 (BD Biosciences), JAK2, EPHA4, LYN, SRC (Millipore, Billerica, MA), JAK3, PTK6, LTK (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA), PTK2, PTK2B (Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA), and β-actin (Millipore). Densitometry was performed and the value for each band was normalized to its respective β-actin loading control and the above formula was used to calculate percent knockdown.
Immunoblotting
For direct immunoblots, cells were lysed in sample buffer (75 mM Tris pH 6.8, 3% SDS, 15% glycerol, 8% β-mercaptoethanol, 0.1% bromophenol blue). For immunoprecipitation, cells were lysed in 1 × cell lysis buffer (Cell Signaling Technology) supplemented with tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor cocktail, Aprotinin, and 4-(2-aminoethyl)benzene-sulfonyl fluoride hydrochloride (AEBSF; Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO) and incubated overnight with antibodies specific for c-KIT (EMD Biosciences), JAK1 (BD Biosciences), or JAK3 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology). Immune complexes were precipitated with protein A-sepharose beads (Amersham Biosciences, Piscataway, NJ), washed 3 times in lysis buffer, resuspended in sample buffer, and immunoprecipitations as well as whole cell lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE. Proteins were transferred to polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes (Millipore) and subjected to immunoblot analysis with the above antibodies specific for c-KIT, JAK1, JAK3, as well as phospho-JAK1 (Cell Signaling Technology), GAPDH (Santa Cruz), or β-actin (EMD Biosciences).
Sequencing analysis
JAK1 and JAK3 pseudokinase and activation loop domains were sequenced according to previously described protocols.17,41
Statistical analyses
For tyrosine kinase siRNA library knockdown experiments, a Student t test was carried out for each well in comparison to both single and pooled nonspecific siRNA controls. The mean of the 2-tailed P value was determined for consideration of significance and data points with P value less than .05 and mean value less than 70% of nonspecific controls were considered significant. For cell proliferation assays, a Student t test was carried out for each dose point comparing HMC1.1 to K562 cell viability.
Results
Optimization of electroporation conditions for siRNA transfection
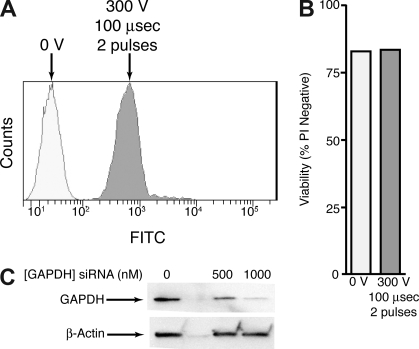
We assessed the optimal conditions for delivery of siRNA molecules into CMK cells. As suspension cells are often recalcitrant to transfection by liposomal delivery methods, we focused instead on electroporation-based delivery. Initially, we incubated FITC-labeled siRNA molecules with CMK cells and delivered an increasing range of voltage to the cells in single pulses and at constant pulse duration. Two days after electroporation, cells were analyzed for viability by propidium iodide exclusion and incorporation of the FITC-labeled siRNA was determined by flow cytometry. The voltage at which cells exhibited maximal incorporation of FITC-labeled siRNA and still exhibited minimal decrease in cell viability was chosen for the second step of optimization. Using this voltage (300 V in the case of CMK cells) cells were again incubated with FITC-labeled siRNA and exposed to single and double pulses of an increasing range of pulse duration. Cells were again analyzed by flow cytometry for viability and FITC incorporation, and we determined that optimal conditions for siRNA delivery into CMK cells was 300 V, 100 μsec, 2 pulses (Figure 2A,B). For final confirmation of efficient siRNA delivery and target reduction, we used the above electroporation conditions to deliver 500 or 1000 nM GAPDH-targeting siRNA into CMK cells. We performed immunoblot analysis at 48 hours after electroporation for GAPDH and β-actin and demonstrated 93% knockdown of GAPDH in CMK cells using 1000 nM siRNA at these parameters (Figure 2C).
Figure 2.
Optimization of electroporation in CMK cells. (A) CMK cells were incubated with a FITC-labeled siRNA molecule and left untreated or electroporated at 300 V, 100 μsec, 2 pulses. After 48 hours cells were analyzed for FITC incorporation by flow cytometry. (B) CMK cells were treated as in panel A and stained with propidium idodide. Viability as measured by PI exclusion was determined by flow cytometry on a Guava Technologies flow cytometer. (C) CMK cells were incubated with 0, 500, or 1000 nM siRNA targeting GAPDH and electroporated as in panel A. After 48 hours cell lysates were subjected to immunoblot analysis for GAPDH and β-actin.
Functional profiling of CMK cells using a tyrosine kinase siRNA library
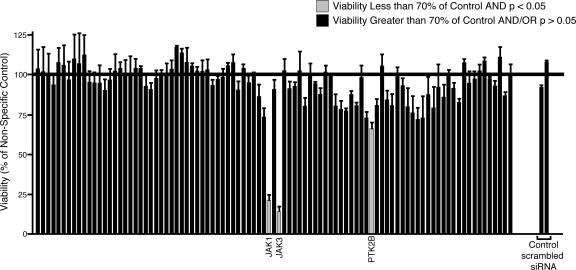
We previously determined that CMK cells harbor an activating mutation in JAK3 (A572V).17 To determine whether functional profiling with a tyrosine kinase siRNA library could be an effective tool for target identification in malignant cells, we tested CMK cells using this tyrosine kinase siRNA library with the expectation that knockdown of JAK3, as well as any other critical components in the JAK3 signaling cascade, would reduce the viability and proliferation of CMK cells. Using the above transfection conditions, we introduced siRNA individually targeting each member of the tyrosine kinase family as well as siRNA targeting the N-RAS and K-RAS oncogenes, and 2 nonspecific siRNA controls into CMK cells. Each siRNA well in this library is composed of a pool of 4 individual siRNA molecules that are each designed against a different region of the target transcript. We assessed cell viability and proliferation 4 days after electroporation (Figure 1). This time point was chosen as a result of numerous pilot studies over a time course from day 2 through day 6 showing peak functional effects at day 4 and a plateau thereafter (data not shown). As expected, siRNA directed against JAK3 significantly reduced the viability of CMK cells (Figure 3). This was consistent with our earlier findings that CMK cells depend on JAK3A572V function and activity for viability and proliferation. We also observed, however, that siRNA targeting JAK1 yielded an equally significant reduction in the viability and proliferation of CMK cells (Figure 3). This was an intriguing result, given that JAK1 had not been detected by phospho-proteomic profiling and did not contain any activating mutations as assessed by sequencing (data not shown). The sequence of the predicted tryptic phosphopeptide containing the JAK1 activation loop phosphorylation site is EY*YTVK. This 6 amino acid peptide is almost certainly too hydrophilic to bind to the C18 resin we had previously used for peptide purification and analysis. Thus, we would not expect to have detected this phosphopeptide in our previous mass spectrophotometric analysis of the CMK cell lysates. However, our current siRNA profiling data suggested that the oncogenic signaling from JAK3A572V in CMK cells depends on JAK1, a finding that is consistent with the known association of JAK1 and JAK3 downstream of numerous cytokine receptors.42 While JAK3 and JAK1-specific siRNA reduced the growth and viability of CMK cells far more significantly than any other siRNA molecules, a few other targets did modulate CMK cell growth to a more subtle extent (a complete list of viability values and significance calculations can be found in Table S1).
Figure 3.
siRNA functional profiling in CMK cells. CMK cells (105) were suspended in siPORT buffer and incubated with 1 μM siRNA from an siRNA library individually targeting each member of the tyrosine kinase family as well as N-RAS, K-RAS, and single and pooled nonspecific siRNA controls. Cells were electroporated on a 96-well electroporation plate at 2220 V (equivalent of 300 V), 100 μsec, 2 pulses. Cells were replated into culture media and cell viability and proliferation was determined by an MTS assay at day 4 after electroporation. Values represent percent mean (normalized to nonspecific control wells) plus or minus SEM (n = 3).
Association of JAK1 and JAK3 in CMK cells
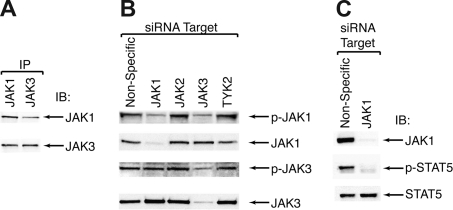
Because siRNA profiling indicated a reliance on JAK1 for the proliferation of CMK cells, we hypothesized that JAK1 is a signaling partner of JAK3 in these cells. To assess whether JAK1 was critical for JAK3 signaling in CMK cells we adopted 3 strategies. First, we looked for association of these 2 proteins by immunoprecipitation of JAK1 or JAK3, followed by immunoblotting for both JAK1 and JAK3. In both circumstances, we observed coimmunoprecipitation of JAK1 and JAK3, indicating that there is interaction between JAK1 and JAK3 in CMK cells (Figure 4A). Second, we used siRNA to individually knockdown each member of the JAK family and then performed immunoblot for JAK1 and JAK3 as well as their phosphorylated, active versions. Using siRNA targeting JAK1, we observed a reduction in total and phospho-JAK1 with no effect on the phosphorylation status of JAK3. Using siRNA targeting JAK3, however, we observed a reduction in total and phopho-JAK3 as well as a reduction in phospho-JAK1, indicating that JAK3 is a critical upstream activator of JAK1 (Figure 4B). Knockdown of JAK2 or tyrosine kinase (TYK)2 showed no effect on JAK1 or JAK3 phosphorylation (Figure 4B). Finally, we tested whether JAK1 was critical for downstream JAK3 signaling events. We previously published that JAK3, but not JAK2 or TYK2, can induce phosphorylation and activation of STAT5 in CMK cells.17 To test whether JAK1 is necessary for this signaling event, we targeted JAK1 using siRNA in CMK cells and assessed phosphorylation of STAT5. Knockdown of JAK1 resulted in a decrease in levels of phosphorylated STAT5, indicating that JAK1 is a necessary component of activated JAK3 signaling in CMK cells (Figure 4C).
Figure 4.
JAK3 signals through JAK1 in CMK cells. (A) CMK cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with antibodies specific for JAK1 or JAK3 and subjected to immunoblot analysis for JAK1 and JAK3. (B) CMK cells were incubated with siRNA targeting JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, and TYK2 and electroporated as in (1A). After 48 hours, cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblot using antibodies specific for total and phospho-JAK1 and JAK3. (C) CMK cells were incubated with siRNA targeting JAK1 and treated as in Figure 1A. After 48 hours, cell lysates were subjected to immunoblot analysis for JAK1 and total and phospho-STAT5.
Functional profiling of HMC1.1 cells using a tyrosine kinase siRNA library
We next tested our siRNA functional profiling approach using a cell line with a known mutation in a receptor tyrosine kinase to determine whether the breadth of targets and extent of functional knockdown is different from cells with an activating mutation in a cytosolic protein such as JAK3. For these experiments, we chose HMC1.1 cells, as they harbor an activating mutation in the stem cell factor (SCF) receptor, c-KIT (V560G).43 Immunoblot analysis confirmed that c-KIT expression could be effectively reduced in HMC1.1 cells using our electroporation parameters (Figure S1). As expected, we observed significant reduction in viability and proliferation of HMC1.1 cells after siRNA targeting of c-KIT, although the extent of the reduction in viability was not as great as that observed with JAK1 or JAK3 in CMK cells (Figure 5). In addition to reduction of HMC1.1 viability after c-KIT knockdown, we also observed equivalent reductions in the viability of cells after targeting of 10 other genes: EPHA4, JAK1, JAK3, leukocyte tyrosine kinase (LTK), LYN, protein tyrosine kinase (PTK)2 (FAK), PTK2B (FAK2), PTK6 (BRK), PTK9, and SRC (a complete list of viability values and significance calculations can be found in Table S2). To confirm expression and efficient target reduction with our siRNA library, we performed quantitative PCR and immunoblot analysis after transfection of each of these 10 siRNAs into HMC1.1 cells. Significant target reduction at both the mRNA and protein levels was seen with each of these siRNAs (Figure S1). With the exception of EPHA4 and LTK, these proteins are all cytosolic tyrosine kinases that are widely implicated in various signaling pathways. In particular, SRC and its family member LYN have been extensively documented as downstream signaling partners of c-KIT.44 The rest of these secondary targets, however, have not been previously documented as critical components of c-KIT signaling.
Figure 5.
siRNA functional profiling in HMC1.1 cells. HMC1.1 cells (105) were suspended in siPORT buffer and incubated with 1 μM siRNA from an siRNA library individually targeting each member of the tyrosine kinase family as well as N-RAS, K-RAS, and single and pooled nonspecific siRNA controls. Cells were electroporated on a 96-well electroporation plate at 2220 V (equivalent of 300 V), 100 μsec, 2 pulses. Cells were replated into culture media and cell viability and proliferation was determined by an MTS assay at day 4 after electroporation. Values represent percent mean (normalized to nonspecific control wells) plus or minus SEM (n = 3).
Confirmation of secondary targets using small-molecule kinase inhibitors
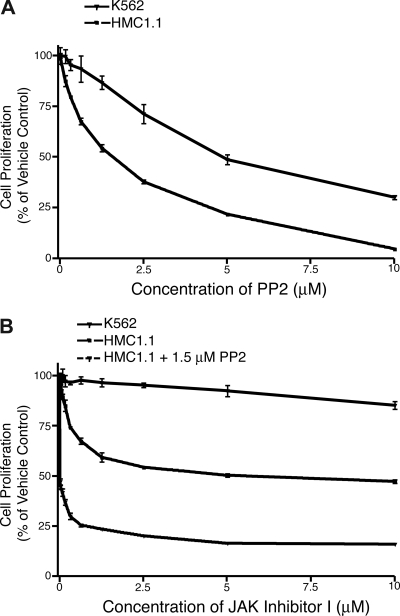
Small-molecule kinase inhibitors exist for several of the secondary targets observed in HMC1.1 cells, notably SRC, LYN, JAK1, and JAK3. To determine whether these targets are important for HMC1.1 growth and viability, as implied by the siRNA library data, we performed proliferation assays with HMC1.1 cells treated with a gradient of concentrations of PP2, SRC kinase inhibitor I, JAK inhibitor I, AG-490, and JAK3 inhibitor III. PP2 and SRC kinase inhibitor I are both small-molecules that exhibit broad activity against the SRC family of tyrosine kinases, with little specificity to any individual SRC family kinase.45,46 JAK inhibitor I potently inhibits all members of the JAK family, while JAK3 inhibitor III specifically inhibits JAK3.47,48 AG-490 has specificity for JAK2 at concentrations below 50 μM, however, it has been shown to inhibit JAK3 at 50 μM and above.49,50 As a control cell line with a different primary oncogenic lesion, we used K562 cells that are transformed by the BCR-ABL fusion oncogene. As has been previously reported, K562 cells show some sensitivity to SRC inhibition by PP2 and other SRC family inhibitors.51,52 Our findings were consistent with these previous observations showing an IC50 of 5 μM for K562 cell proliferation after 3 days in culture. HMC1.1 cells treated under the same conditions exhibited even greater sensitivity to PP2, with an IC50 of 1.5 μM (Figure 6A). Parallel studies with SRC inhibitor I showed equivalent findings with HMC1.1 cells exhibiting greater sensitivity to the inhibitor than K562 cells with an IC50 of 5 μM (Figure S2A). To assess whether JAK1 and JAK3 were viable targets in HMC1.1 cells, we tested the effect of JAK inhibitor I on these cells as well as K562 cells. As we had seen previously, K562 cells are resistant to JAK inhibitor I at concentrations up to and including 10 μM17; however, HMC1.1 cells exhibited sensitivity to this pan-JAK inhibitor, reaching an IC50 at 5 μM (Figure 6B). Because this inhibitor also has activity against JAK2 and TYK2, we additionally tested the JAK3-specific, JAK3 inhibitor III, on HMC1.1 cells and saw an IC50 of 8.5 μM (predicted IC50 of 11 μM) while K562 cells did not reach an IC50 by 20 μM (Figure S2B). As an additional control, we treated HMC1.1 and HEL cells with the JAK2 inhibitor, AG-490. HEL cells depend on a mutated allele of JAK2 (V617F) for viability and, thus, exhibited sensitivity to AG-490 with an IC50 of 45 μM.22,53 HMC1.1 cells showed significantly less sensitivity to AG-490, not reaching an IC50 by 50 μM (Figure S2C).
Figure 6.
HMC1.1 cells are sensitive to inhibitors targeting JAK1, JAK3, and SRC. (A) HMC1.1 and K562 control cells were treated with increasing concentrations of the SRC family inhibitor, PP2. 72 hours later, cells were subjected to an MTS assay for determination of total viable cells. Values represent mean plus or minus SEM. (n = 3). (B) HMC1.1 and K562 control cells were treated with increasing concentrations of the pan-JAK inhibitor, JAK inhibitor I, alone or in combination with 1.5 μM PP2. 72 hours later, cells were subjected to an MTS assay for determination of total viable cells. Values represent mean plus or minus SEM. (n = 3).
Interestingly, the reduction of viability and proliferation of HMC1.1 cells induced by JAK inhibitor I did not exceed much beyond 50% despite increasing concentrations of the drug. This suggests that alternate signaling pathways might be able to rescue these cells in the absence of functional JAK1 and JAK3 signaling. Because these data were consistent with our siRNA library findings, where no single well exhibited less than 50% reduction in viability, we tested whether combining a SRC inhibitor with this JAK kinase inhibitor could achieve an additive effect on reduction of HMC1.1 cell growth and viability. As such, we incubated HMC1.1 cells over the same drug concentrations of JAK inhibitor I, but in combination with an IC50 (1.5 μM) of PP2. The combination yielded lower viability readings at all dose points compared with the JAK inhibitor alone (Figure 6B). These data indicate that HMC1.1 cells depend on JAK and SRC family members for growth and viability and that these 2 signaling pathways might be partially redundant. To further clarify which specific JAK and SRC family members were functioning in this redundant fashion, we transfected HMC1.1 cells with all possible combinations of siRNA targeting JAK1, JAK3, LYN, and SRC. Unexpectedly, we were not able to observe any further decrease in cell viability with any of these combinations than with individual knockdown of these genes (data not shown). This indicates that the additive effect observed with JAK and SRC family inhibition might rely either on off-target effects of these inhibitors or on the functions of other gene family members in addition to JAK1, JAK3, LYN, and SRC.
Association of c-KIT with JAK1 and JAK3 in HMC1.1 cells
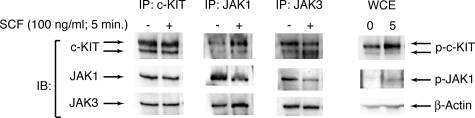
Numerous studies have implicated JAK2 in signaling downstream of c-KIT54–56; however, HMC1.1 cell viability and proliferation was normal after treatment with siRNA targeting JAK2 (Table S2). Instead, siRNA targeting JAK1 and JAK3 as well as small molecule inhibitors targeting these 2 proteins significantly reduced the viability of HMC1.1 cells. Sequence analysis of JAK1 and JAK3 did not reveal genetic abnormalities (data not shown), implicating JAK1 and JAK3 rather than JAK2 in c-KIT signal transduction in this setting. To test this hypothesis, we immunoprecipitated c-KIT, JAK1, and JAK3 from HMC1.1 cells after stimulation with SCF. Immunoblotting for c-KIT, JAK1, and JAK3 indicated that all 3 of these proteins were interacting in HMC1.1 cells both with and without stimulation with SCF, a finding that is consistent with the constitutive kinase activity of the V560G mutation in c-KIT (Figure 7). After stimulation with SCF, we did see additional evidence of JAK1 signaling downstream of c-KIT as we observed increases in the level of phospho-JAK1 in these SCF-stimulated HMC1.1 cells. We did observe coimmuoprecipitation of c-KIT and JAK2 as well as increased phospho-JAK2 after SCF stimulation in HMC1.1 cells; however, our siRNA library findings indicate that this signaling event is not crucial for cell viability. These data indicate that in this setting of a mast cell leukemia line, signaling of c-KIT through JAK1 and JAK3 is crucial for cell growth and viability identifying JAK1 and JAK3 as viable therapeutic targets. In contrast, JAK2 does become activated by SCF-c-KIT signaling in HMC1.1 cells, but it is not necessary for maintenance of cell viability.
Figure 7.
c-KIT signals through JAK1 and JAK3 in HMC1.1 cells. HMC1.1 cells were serum-starved overnight and stimulated with 100 ng/mL SCF for 5 minutes. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated for c-KIT, JAK1, or JAK3. Immunoprecipitates and whole cell extract (WCE) were analyzed by immunoblot for c-KIT, total and phospho JAK1 and JAK3, and β-actin.
Discussion
We demonstrate that high-throughput functional screening with an siRNA library targeting all tyrosine kinases is an efficient and useful approach toward identifying therapeutic targets in malignant cells. With this approach, we could rapidly identify the primary, mutated targets, JAK3 and c-KIT, in 2 AML cell lines. In addition to these 2 genes we were also able to identify numerous secondary targets, some of which were not observed by phospho-proteomic profiling, and all of which would have remained undisclosed by conventional sequencing approaches. These secondary targets serve 2 useful purposes. First, they offer insight into signaling pathways originating from the mutated oncogene, and second, they offer alternative targets for therapeutic intervention in patients.
One cell line that was functionally profiled had an activating mutation in a cytosolic tyrosine kinase and the other had an activating mutation in a receptor tyrosine kinase. The viability profile of these 2 cell lines is suggestive of different levels of redundancy emanating from mutations in these 2 different classes of tyrosine kinases. CMK cells, with an activating mutation in the cytosolic protein, JAK3, exhibit sensitivity to siRNA targeting JAK3 or its critical signaling partner, JAK1. While there are a few other genes whose targeting yields subtle effects on cell growth, there are no other genes whose contribution to growth and viability of CMK cells seems nearly as crucial as these 2 genes. Alternatively, HMC1.1 cells, with an activating mutation in the receptor tyrosine kinase, c-KIT, exhibit 11 genes that all appear equivalent in their contribution to viability of HMC1.1 cells. In addition, the decrease in viability observed with all of these 11 genes in HMC1.1 cells is less dramatic than that observed in CMK cells with siRNA targeting JAK1 or JAK3. This discrepancy could be explained in several ways. From a technical standpoint, it is possible that the extent of target reduction by siRNA is less efficient in HMC1.1 cells than in CMK cells. Indeed, quantitative densitometry of GAPDH immunoblots after siRNA targeting in these 2 cell lines revealed greater than 90% target reduction in CMK cells compared with approximately 70% reduction in HMC1.1 cells (data not shown). A second possibility is that oncogenic signals originating from receptor tyrosine kinases might have more redundancy in downstream signaling cascades making ablation of any one of these targets less detrimental for overall cell growth and viability. Evidence for this concept comes from the fact that combination of inhibitors targeting the SRC and JAK families showed an additive effect in reduction of growth and viability of HMC1.1 cells (Figure 6B). Finally, the possibility remains that HMC1.1 cells could harbor a second activating mutation in another tyrosine kinase or in an oncogene that lies outside the tyrosine kinase family. While no specific evidence exists for this hypothesis, it might warrant further exploration.
These studies offer the potential of functionally analyzing signaling pathways in a larger scale than has previously been conducted. Previous studies have indicated that c-KIT interacts with JAK2. Indeed, stimulation of numerous cell types with SCF results in phosphorylation and kinase activation of JAK2, including in HMC1.1 cells (Figure S3). Our data, however, indicate JAK2 is dispensable for c-KIT signaling in HMC1.1 cells as cell viability was unaffected despite significant knockdown by JAK2 siRNA (Figures 4, S1). This conclusion is bolstered by the relative resistance of HMC1.1 cells to inhibition of JAK2 by AG-490 in comparison to the JAK2-dependent cell line, HEL (Figure S2C). In contrast, siRNA functional profiling clearly indicates that JAK1 and JAK3, previously not known to be associated with c-KIT signaling, are crucial signaling mediators of this pathway in HMC1.1 cells. Using this technology, it might be possible to explore numerous signaling pathways from a new perspective. Here we have applied siRNA functional profiling to cells with constitutively active pathways; however, this analysis could also be performed by treating cells with the growth factor or other ligand of interest after siRNA targeting. Using this approach, we might expect to find data that complement our current biochemical understanding of signaling pathways as we found in CMK cells, or we might uncover new insights into pathways as we found with c-KIT signaling through JAK1 and JAK3 in HMC1.1 cells.
Finally, these data demonstrate the utility of siRNA functional profiling in target identification in malignant cells. Perhaps the most important facet of these findings is the ability of functional profiling to identify a wide range of targets, which is not limited to mutated targets, in malignant cells. Indeed, the ability of c-KIT to signal through JAK1 and JAK3 might prompt an investigation as to the efficacy of new JAK3 inhibitors in c-KIT derived cancer, especially in cases with imatinib-resistant mutations in c-KIT.57 Along similar lines, this assay might also prove useful for the determination of sensitivity profiles of other kinases with drug-resistant mutations, such as BCR-ABL or epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). Additionally, siRNA targeting of the focal adhesion kinases, PTK2 and PTK2B, in both CMK and HMC1.1 cells yielded reduction in cell growth and viability. This might reveal a novel target for therapeutic intervention in malignancies that depend on c-KIT, JAK1, or JAK3 signaling. Thus, siRNA functional profiling might provide an efficient diagnostic tool for identification of molecular targets for therapeutic intervention in malignant cells, such that patients might be matched with a cocktail of small-molecule kinase inhibitors that are individually tailored to their cancer.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society, the T..J. Martell Foundation, and the Doris Duke Charitable Foundation. J.W.T. is supported by a cancer biology training grant from the National Institutes of Health. M.C.H. is supported in part by a VA Merit Review Grant. B.J.D. is an investigator of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Footnotes
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Authorship
Contribution: J.W.T. designed and performed research, analyzed data, and wrote the paper; D.K.W., S.W., M.L., J.O., H.E., and A.S.C. performed research; T.O. and M.L. designed research; and M.C.H., M.W.D., and B.J.D. contributed vital reagents, designed research, and revised the paper.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Brian J. Druker, Basic Science 5390, Mailcode L592, 3181 SW Sam Jackson Park Road, Portland, OR 97239;e-mail: drukerb@ohsu.edu.
References
- 1.Druker BJ, Guilhot F, O'Brien SG, et al. Five-year follow-up of patients receiving imatinib for chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:2408–2417. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa062867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of nonsmall-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2129–2139. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa040938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC, et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 2004;304:1497–1500. doi: 10.1126/science.1099314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Smith I, Procter M, Gelber RD, et al. 2-year follow-up of trastuzumab after adjuvant chemotherapy in HER2-positive breast cancer: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2007;369:29–36. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60028-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Krause DS, Van Etten RA. Tyrosine kinases as targets for cancer therapy. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:172–187. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra044389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Birkenkamp KU, Geugien M, Lemmink HH, Kruijer W, Vellenga E. Regulation of constitutive STAT5 phosphorylation in acute myeloid leukemia blasts. Leukemia. 2001;15:1923–1931. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2402317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hayakawa F, Towatari M, Iida H, et al. Differential constitutive activation between STAT-related proteins and MAP kinase in primary acute myelogenous leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 1998;101:521–528. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2141.1998.00720.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Spiekermann K, Pau M, Schwab R, Schmieja K, Franzrahe S, Hiddemann W. Constitutive activation of STAT3 and STAT5 is induced by leukemic fusion proteins with protein tyrosine kinase activity and is sufficient for transformation of hematopoietic precursor cells. Exp Hematol. 2002;30:262–271. doi: 10.1016/s0301-472x(01)00787-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Fröhling S, Lipka DB, Kayser S, et al. Rare occurrence of the JAK2 V617F mutation in AML subtypes M5, M6, and M7. Blood. 2006;107:1242–1243. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-09-3644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Golub TR, Barker GF, Lovett M, Gilliland DG. Fusion of PDGF receptor beta to a novel ets-like gene, tel, in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia with t(5;12) chromosomal translocation. Cell. 1994;77:307–316. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Illmer T, Schaich M, Ehninger G, Thiede C. Tyrosine kinase mutations of JAK2 are rare events in AML but influence prognosis of patients with CBF-leukemias. Haematologica. 2007;92:137–138. doi: 10.3324/haematol.10489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Jelinek J, Oki Y, Gharibyan V, et al. JAK2 mutation 1849G>T is rare in acute leukemias but can be found in CMML, Philadelphia chromosome-negative CML, and megakaryocytic leukemia. Blood. 2005;106:3370–3373. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-05-1800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lee JW, Kim YG, Soung YH, et al. The JAK2 V617F mutation in de novo acute myelogenous leukemias. Oncogene. 2006;25:1434–1436. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Levine RL, Loriaux M, Huntly BJ, et al. The JAK2V617F activating mutation occurs in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia and acute myeloid leukemia, but not in acute lymphoblastic leukemia or chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 2005;106:3377–3379. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-05-1898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Stirewalt DL, Radich JP. The role of FLT3 in haematopoietic malignancies. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:650–665. doi: 10.1038/nrc1169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Tse KF, Mukherjee G, Small D. Constitutive activation of FLT3 stimulates multiple intracellular signal transducers and results in transformation. Leukemia. 2000;14:1766–1776. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2401905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Walters DK, Mercher T, Gu TL, et al. Activating alleles of JAK3 in acute megakaryoblastic leukemia. Cancer Cell. 2006;10:65–75. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2006.06.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Yamamoto Y, Kiyoi H, Nakano Y, et al. Activating mutation of D835 within the activation loop of FLT3 in human hematologic malignancies. Blood. 2001;97:2434–2439. doi: 10.1182/blood.v97.8.2434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Yokota S, Kiyoi H, Nakao M, et al. Internal tandem duplication of the FLT3 gene is preferentially seen in acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome among various hematological malignancies A study on a large series of patients and cell lines. Leukemia. 1997;11:1605–1609. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2400812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Greenman C, Stephens P, Smith R, et al. Patterns of somatic mutation in human cancer genomes. Nature. 2007;446:153–158. doi: 10.1038/nature05610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sjöblom T, Jones S, Wood LD, et al. The consensus coding sequences of human breast and colorectal cancers. Science. 2006;314:268–274. doi: 10.1126/science.1133427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Walters DK, Goss VL, Stoffregen EP, et al. Phosphoproteomic analysis of AML cell lines identifies leukemic oncogenes. Leuk Res. 2006;30:1097–1104. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2006.01.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Gu TL, Mercher T, Tyner JW, et al. A novel fusion of RBM6 to CSF1R in acute megakaryoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2007;110:323–333. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-10-052282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Gu TL, Goss VL, Reeves C, et al. Phosphotyrosine profiling identifies the KG-1 cell line as a model for the study of FGFR1 fusions in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2006;108:4202–4204. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-06-026666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA, Driver SE, Mello CC. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1998;391:806–811. doi: 10.1038/35888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Mello CC, Conte D., Jr Revealing the world of RNA interference. Nature. 2004;431:338–342. doi: 10.1038/nature02872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Brummelkamp TR, Fabius AW, Mullenders J, et al. An shRNA barcode screen provides insight into cancer cell vulnerability to MDM2 inhibitors. Nat Chem Biol. 2006;2:202–206. doi: 10.1038/nchembio774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kolfschoten IG, van Leeuwen B, Berns K, et al. A genetic screen identifies PITX1 as a suppressor of RAS activity and tumorigenicity. Cell. 2005;121:849–858. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.04.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Korherr C, Gille H, Schafer R, et al. Identification of proangiogenic genes and pathways by high-throughput functional genomics: TBK1 and the IRF3 pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:4240–4245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0511319103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Lum L, Yao S, Mozer B, et al. Identification of Hedgehog pathway components by RNAi in Drosophila cultured cells. Science. 2003;299:2039–2045. doi: 10.1126/science.1081403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.MacKeigan JP, Murphy LO, Blenis J. Sensitized RNAi screen of human kinases and phosphatases identifies new regulators of apoptosis and chemoresistance. Nat Cell Biol. 2005;7:591–600. doi: 10.1038/ncb1258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Martin SE, Jones TL, Thomas CL, et al. Multiplexing siRNAs to compress RNAi-based screen size in human cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35:e57. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Moffat J, Grueneberg DA, Yang X, et al. A lentiviral RNAi library for human and mouse genes applied to an arrayed viral high-content screen. Cell. 2006;124:1283–1298. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.01.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Müller P, Kuttenkeuler D, Gesellchen V, Zeidler MP, Boutros M. Identification of JAK/STAT signalling components by genome-wide RNA interference. Nature. 2005;436:871–875. doi: 10.1038/nature03869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ngo VN, Davis RE, Lamy L, et al. A loss-of-function RNA interference screen for molecular targets in cancer. Nature. 2006;441:106–110. doi: 10.1038/nature04687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Pothof J, van Haaften G, Thijssen K, et al. Identification of genes that protect the C. elegans genome against mutations by genome-wide RNAi. Genes Dev. 2003;17:443–448. doi: 10.1101/gad.1060703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Tsuji AB, Sudo H, Sugyo A, et al. A fast, simple method for screening radiation susceptibility genes by RNA interference. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;333:1370–1377. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.06.047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.van Haaften G, Romeijn R, Pothof J, et al. Identification of conserved pathways of DNA-damage response and radiation protection by genome-wide RNAi. Curr Biol. 2006;16:1344–1350. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2006.05.047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Westbrook TF, Martin ES, Schlabach MR, et al. A genetic screen for candidate tumor suppressors identifies REST. Cell. 2005;121:837–848. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.03.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Kang JX, Liu J, Wang J, He C, Li FP. The extract of huanglian, a medicinal herb, induces cell growth arrest and apoptosis by up-regulation of interferon-beta and TNF-alpha in human breast cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 2005;26:1934–1939. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgi154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Levine RL, Wadleigh M, Cools J, et al. Activating mutation in the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia, and myeloid metaplasia with myelofibrosis. Cancer Cell. 2005;7:387–397. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2005.03.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Yamaoka K, Saharinen P, Pesu M, Holt VE, Silvennoinen O, 3rd, O'Shea JJ. The Janus kinases (Jaks). Genome Biol. 2004;5:253. doi: 10.1186/gb-2004-5-12-253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Furitsu T, Tsujimura T, Tono T, et al. Identification of mutations in the coding sequence of the proto-oncogene c-kit in a human mast cell leukemia cell line causing ligand-independent activation of c-kit product. J Clin Invest. 1993;92:1736–1744. doi: 10.1172/JCI116761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Roskoski R., Jr Signaling by Kit protein-tyrosine kinase–the stem cell factor receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;337:1–13. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.08.055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Hanke JH, Gardner JP, Dow RL, et al. Discovery of a novel, potent, and Src family-selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Study of Lck- and FynT-dependent T cell activation. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:695–701. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.2.695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Tian G, Cory M, Smith AA, Knight WB. Structural determinants for potent, selective dual site inhibition of human pp60c-src by 4-anilinoquinazolines. Biochemistry. 2001;40:7084–7091. doi: 10.1021/bi0100586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Sudbeck EA, Liu XP, Narla RK, et al. Structure-based design of specific inhibitors of Janus kinase 3 as apoptosis-inducing antileukemic agents. Clin Cancer Res. 1999;5:1569–1582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Thompson JE, Cubbon RM, Cummings RT, et al. Photochemical preparation of a pyridone containing tetracycle: a Jak protein kinase inhibitor. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2002;12:1219–1223. doi: 10.1016/s0960-894x(02)00106-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Meydan N, Grunberger T, Dadi H, et al. Inhibition of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia by a Jak-2 inhibitor. Nature. 1996;379:645–648. doi: 10.1038/379645a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Wang LH, Kirken RA, Erwin RA, Yu CR, Farrar WL. JAK3, STAT, and MAPK signaling pathways as novel molecular targets for the tyrphostin AG-490 regulation of IL-2-mediated T cell response. J Immunol. 1999;162:3897–3904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Okutani Y, Kitanaka A, Tanaka T, et al. Src directly tyrosine-phosphorylates STAT5 on its activation site and is involved in erythropoietin-induced signaling pathway. Oncogene. 2001;20:6643–6650. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Wilson MB, Schreiner SJ, Choi HJ, Kamens J, Smithgall TE. Selective pyrrolo-pyrimidine inhibitors reveal a necessary role for Src family kinases in Bcr-Abl signal transduction and oncogenesis. Oncogene. 2002;21:8075–8088. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Quentmeier H, MacLeod RA, Zaborski M, Drexler HG. JAK2 V617F tyrosine kinase mutation in cell lines derived from myeloproliferative disorders. Leukemia. 2006;20:471–476. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2404081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Brizzi MF, Zini MG, Aronica MG, Blechman JM, Yarden Y, Pegoraro L. Convergence of signaling by interleukin-3, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, and mast cell growth factor on JAK2 tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:31680–31684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Linnekin D, Weiler SR, Mou S, et al. JAK2 is constitutively associated with c-Kit and is phosphorylated in response to stem cell factor. Acta Haematol. 1996;95:224–228. doi: 10.1159/000203882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Weiler SR, Mou S, DeBerry CS, et al. JAK2 is associated with the c-kit proto-oncogene product and is phosphorylated in response to stem cell factor. Blood. 1996;87:3688–3693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Changelian PS, Flanagan ME, Ball DJ, et al. Prevention of organ allograft rejection by a specific Janus kinase 3 inhibitor. Science. 2003;302:875–878. doi: 10.1126/science.1087061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.