Abstract
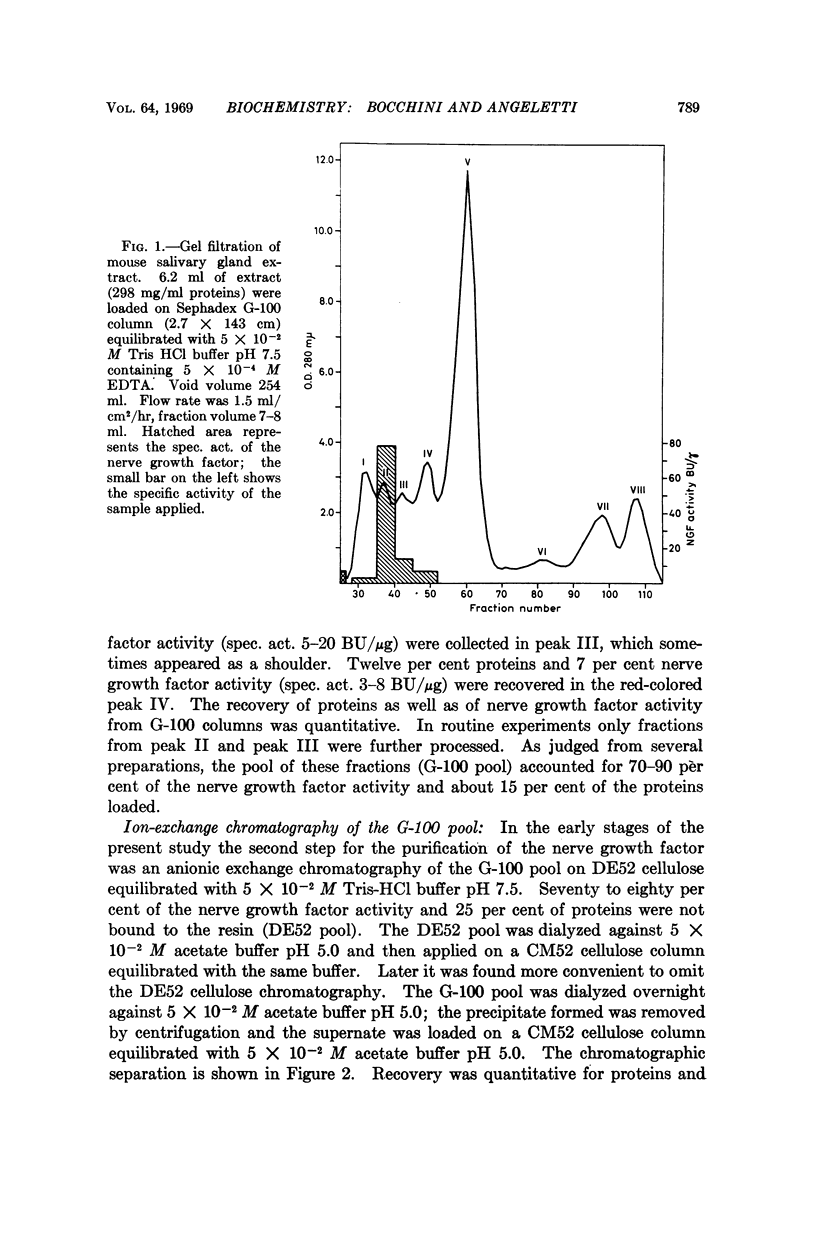
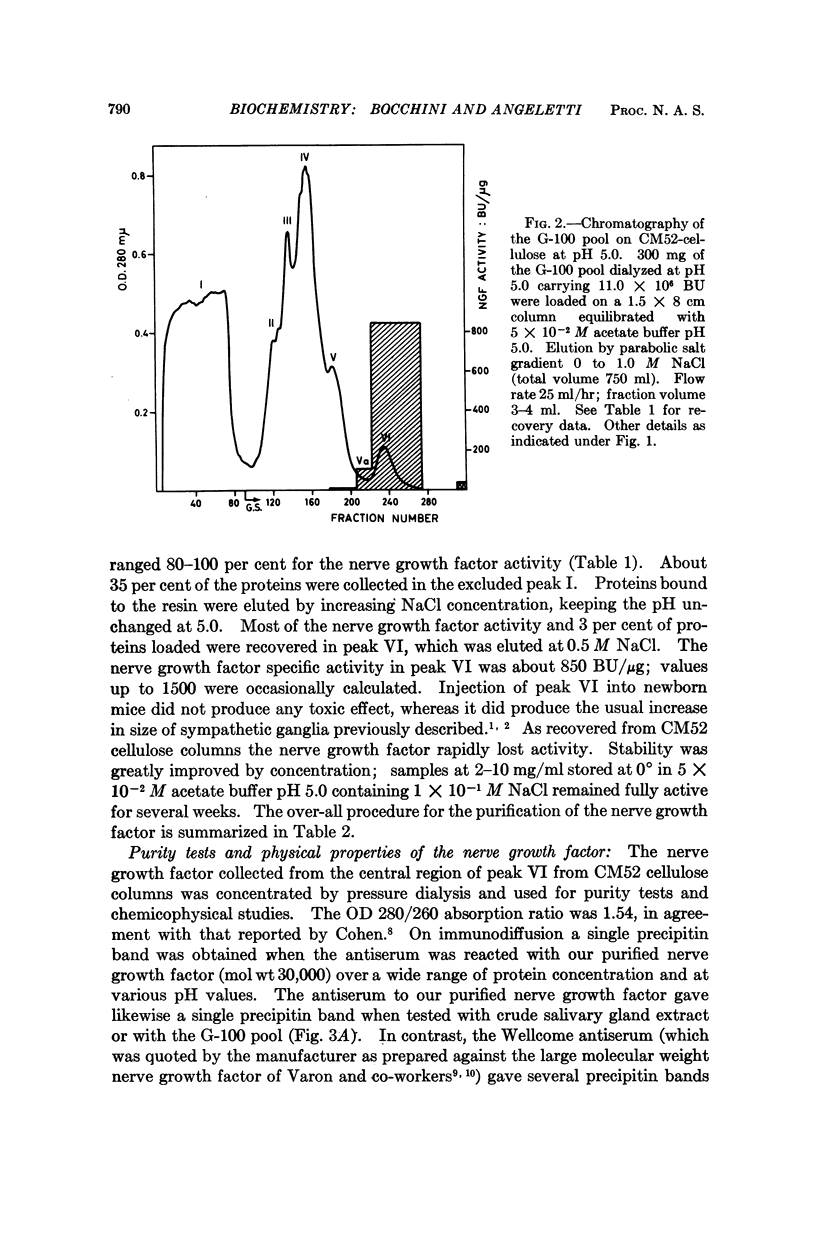
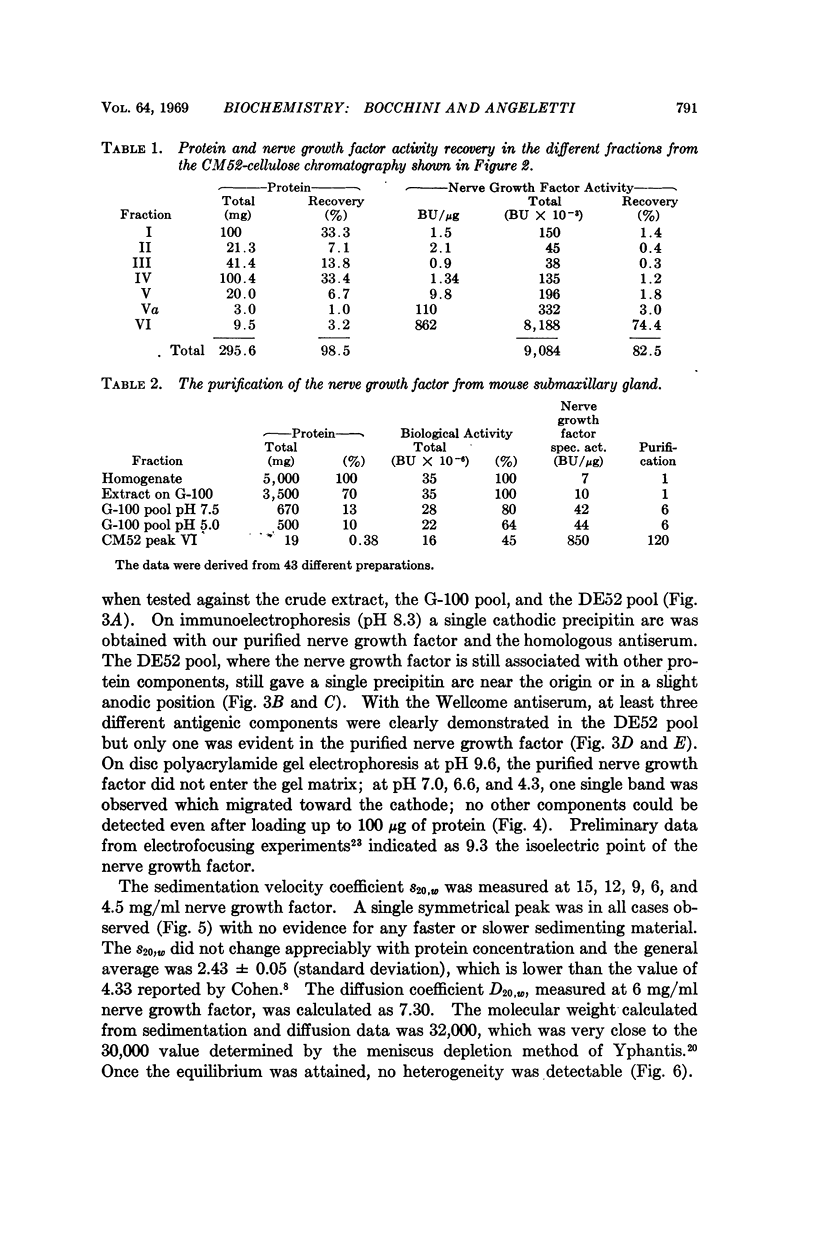
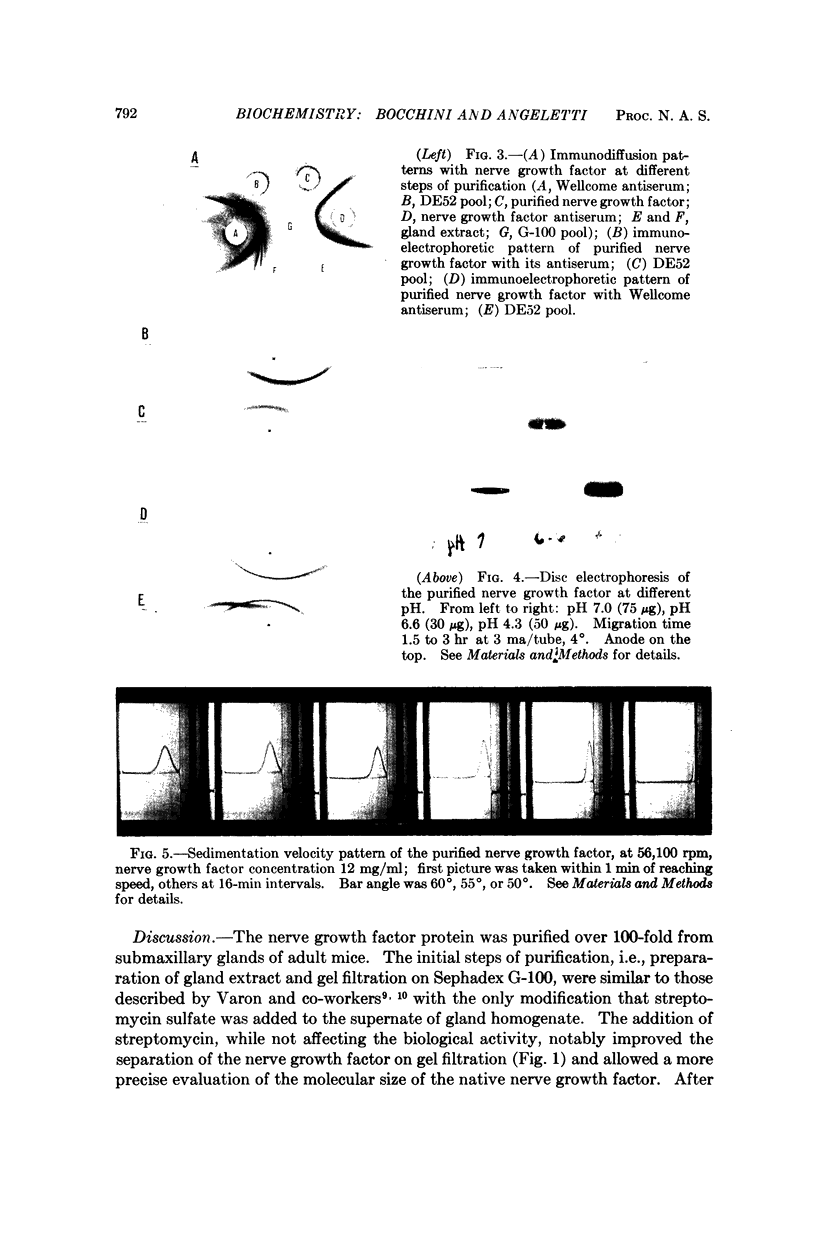
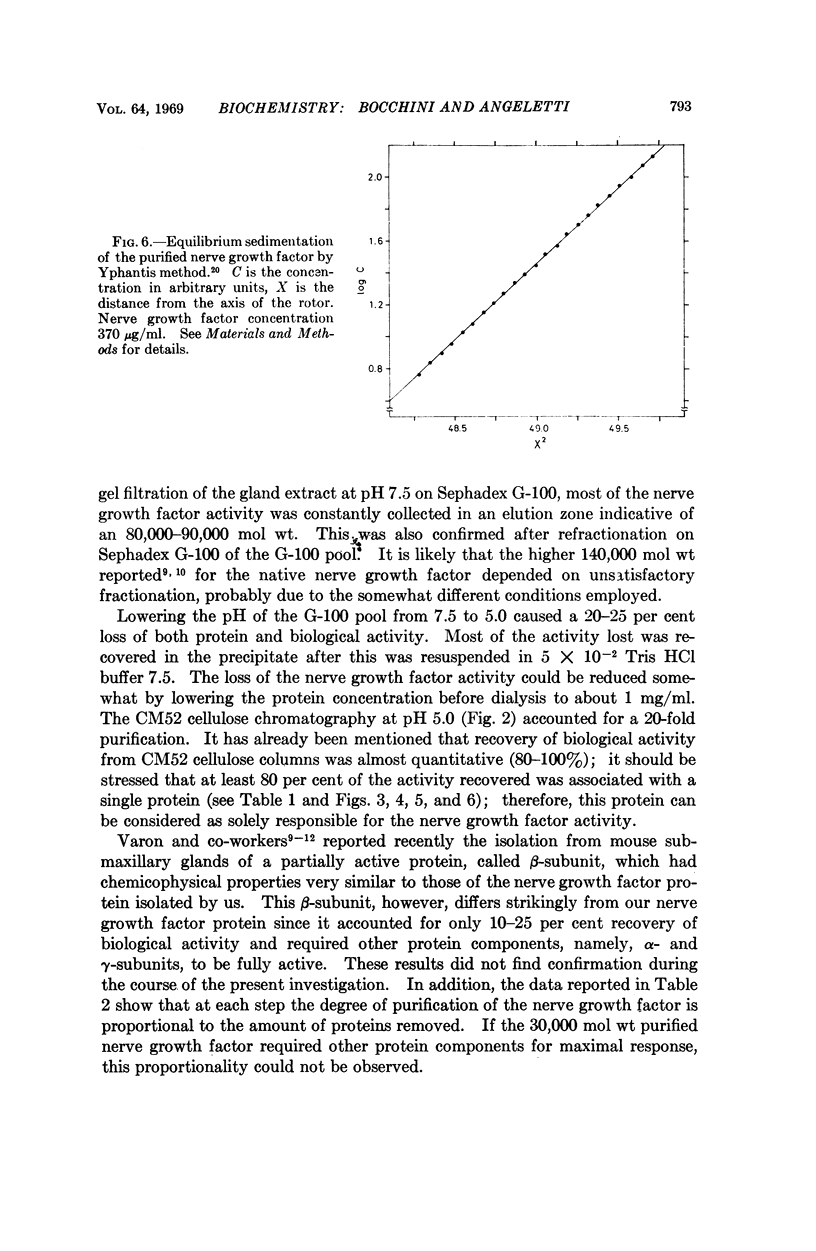
The nerve growth factor protein was purified over 100-fold from adult mouse salivary glands. The first step was a gel filtration on Sephadex G-100 at pH 7.5 of the aqueous gland extract. After gel filtration, most of the NGF activity was eluted in the 80,000-90,000-molecular-weight region (G-100 pool). The G-100 pool was dialyzed at pH 5.0 and fractionated by CM52 cellulose chromatography at pH 5.0. Recovery from CM52 cellulose columns was quantitative for protein and ranged 80-100 per cent for the nerve growth factor activity; the latter was almost completely carried by a protein which did not show any heterogeneity when examined by several analytical tests. The purified nerve growth factor showed an S20,w = 2.43, a D20,w = 7.30 and a 30,000 molecular weight. The over-all recovery was about 45 per cent.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. Estimation of the molecular weights of proteins by Sephadex gel-filtration. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):222–233. doi: 10.1042/bj0910222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angeletti P., Calissano P., Chen J. S., Levi-Montalcini R. Multiple molecular forms of the nerve growth factor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Sep 19;147(1):180–182. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(67)90104-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN S. Purification and metabolic effects of a nerve growth-promoting protein from snake venom. J Biol Chem. 1959 May;234(5):1129–1137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Levi-Montalcini R. A NERVE GROWTH-STIMULATING FACTOR ISOLATED FROM SNAKE VENOM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1956 Sep;42(9):571–574. doi: 10.1073/pnas.42.9.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. PURIFICATION OF A NERVE-GROWTH PROMOTING PROTEIN FROM THE MOUSE SALIVARY GLAND AND ITS NEURO-CYTOTOXIC ANTISERUM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Mar;46(3):302–311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.3.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVI-MONTALCINI R., COHEN S. Effects of the extract of the mouse submaxillary salivary glands on the sympathetic system of mammals. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Mar 29;85:324–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb49963.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVI-MONTALCINI R., MEYER H., HAMBURGER V. In vitro experiments on the effects of mouse sarcomas 180 and 37 on the spinal and sympathetic ganglia of the chick embryo. Cancer Res. 1954 Jan;14(1):49–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R., Angeletti P. U. Nerve growth factor. Physiol Rev. 1968 Jul;48(3):534–569. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1968.48.3.534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R., Booker B. EXCESSIVE GROWTH OF THE SYMPATHETIC GANGLIA EVOKED BY A PROTEIN ISOLATED FROM MOUSE SALIVARY GLANDS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Mar;46(3):373–384. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.3.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R. The nerve growth factor: its mode of action on sensory and sympathetic nerve cells. Harvey Lect. 1966;60:217–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REISFELD R. A., LEWIS U. J., WILLIAMS D. E. Disk electrophoresis of basic proteins and peptides on polyacrylamide gels. Nature. 1962 Jul 21;195:281–283. doi: 10.1038/195281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. P., Varon S., Shooter E. M. Multiple forms of the nerve growth factor protein and its subunits. Biochemistry. 1968 Sep;7(9):3259–3268. doi: 10.1021/bi00849a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varon S., Nomura J., Shooter E. M. Subunit structure of a high-molecular-weight form of the nerve growth factor from mouse submaxillary gland. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jun;57(6):1782–1789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.6.1782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varon S., Nomura J., Shooter E. M. The isolation of the mouse nerve growth factor protein in a high molecular weight form. Biochemistry. 1967 Jul;6(7):2202–2209. doi: 10.1021/bi00859a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesterberg O., Svensson H. Isoelectric fractionation, analysis, and characterization of ampholytes in natural pH gradients. IV. Further studies on the resolving power in connection with separation of myoglobins. Acta Chem Scand. 1966;20(3):820–834. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.20-0820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YPHANTIS D. A. EQUILIBRIUM ULTRACENTRIFUGATION OF DILUTE SOLUTIONS. Biochemistry. 1964 Mar;3:297–317. doi: 10.1021/bi00891a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]