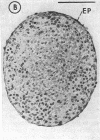
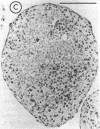
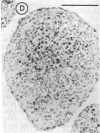
Abstract
Mouse and chick embryonic myocardial cells sort out from each other in aggregates of heart ventricle cells. This result invalidates the generalization that embryonic cells of a given tissue from different warm-blooded vertebrate species possess identical cell-sorting properties.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- GARBER B., MOSCONA A. A. AGGREGATION IN VIVO OF DISSOCIATED CELLS. I. RECONSTRUCTION OF SKIN IN THE CHORIOALLANTOIC MEMBRANE FROM SUSPENSIONS OF EMBRYONIC CHICK AND MOUSE SKIN CELLS. J Exp Zool. 1964 Mar;155:179–201. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401550206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOSCONA A. Development of heterotypic combinations of dissociated embryonic chick cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Jun;92(2):410–416. doi: 10.3181/00379727-92-22495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOSCONA A., MOSCONA H. The dissociation and aggregation of cells from organ rudiments of the early chick embryo. J Anat. 1952 Jul;86(3):287–301. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOSCONA A. Rotation-mediated histogenetic aggregation of dissociated cells. A quantifiable approach to cell interactions in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1961 Jan;22:455–475. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(61)90122-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscona A. THE DEVELOPMENT IN VITRO OF CHIMERIC AGGREGATES OF DISSOCIATED EMBRYONIC CHICK AND MOUSE CELLS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1957 Jan 15;43(1):184–194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.43.1.184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEINBERG M. S. On the mechanism of tissue reconstruction by dissociated cells. I. Population kinetics, differential adhesiveness. and the absence of directed migration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Sep 15;48:1577–1582. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.9.1577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinkaus J. P., Groves P. W. DIFFERENTIATION IN CULTURE OF MIXED AGGREGATES OF DISSOCIATED TISSUE CELLS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1955 Oct 15;41(10):787–795. doi: 10.1073/pnas.41.10.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]