Abstract
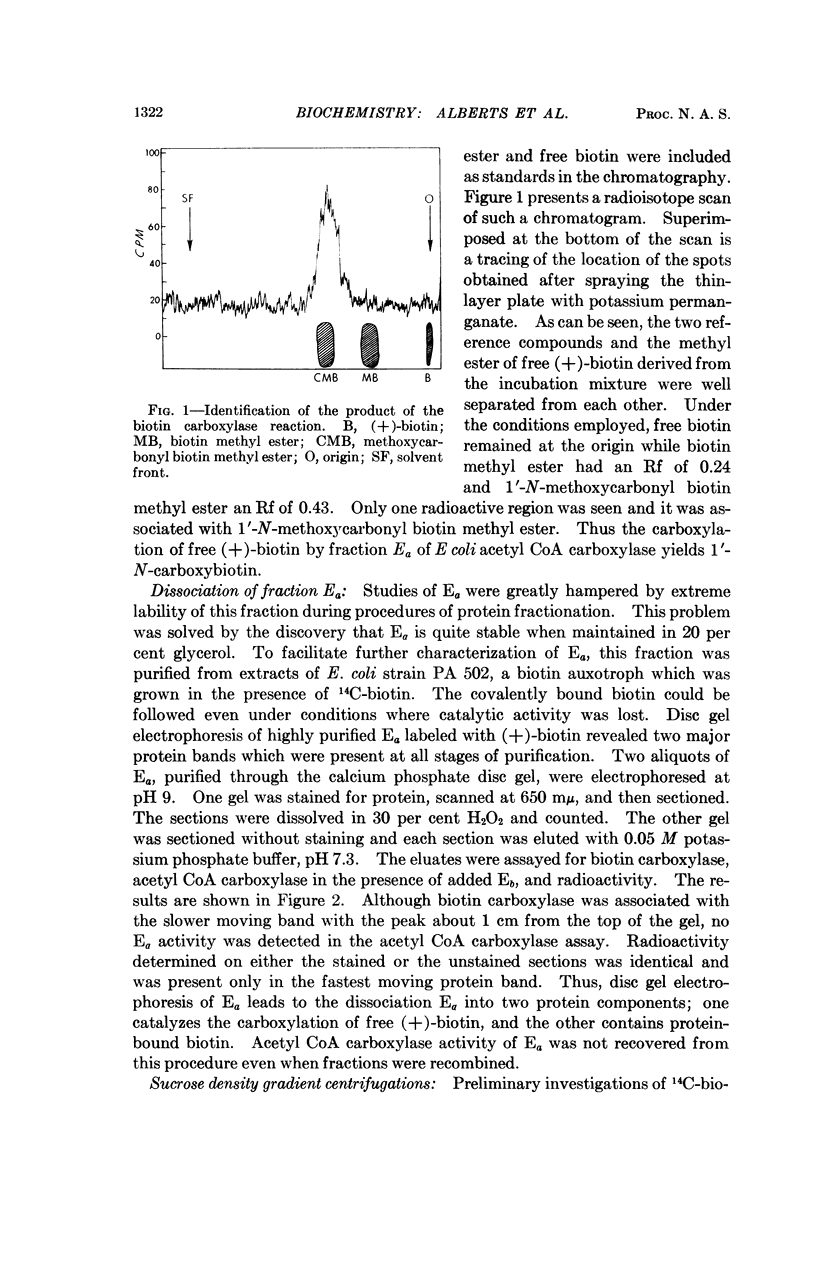
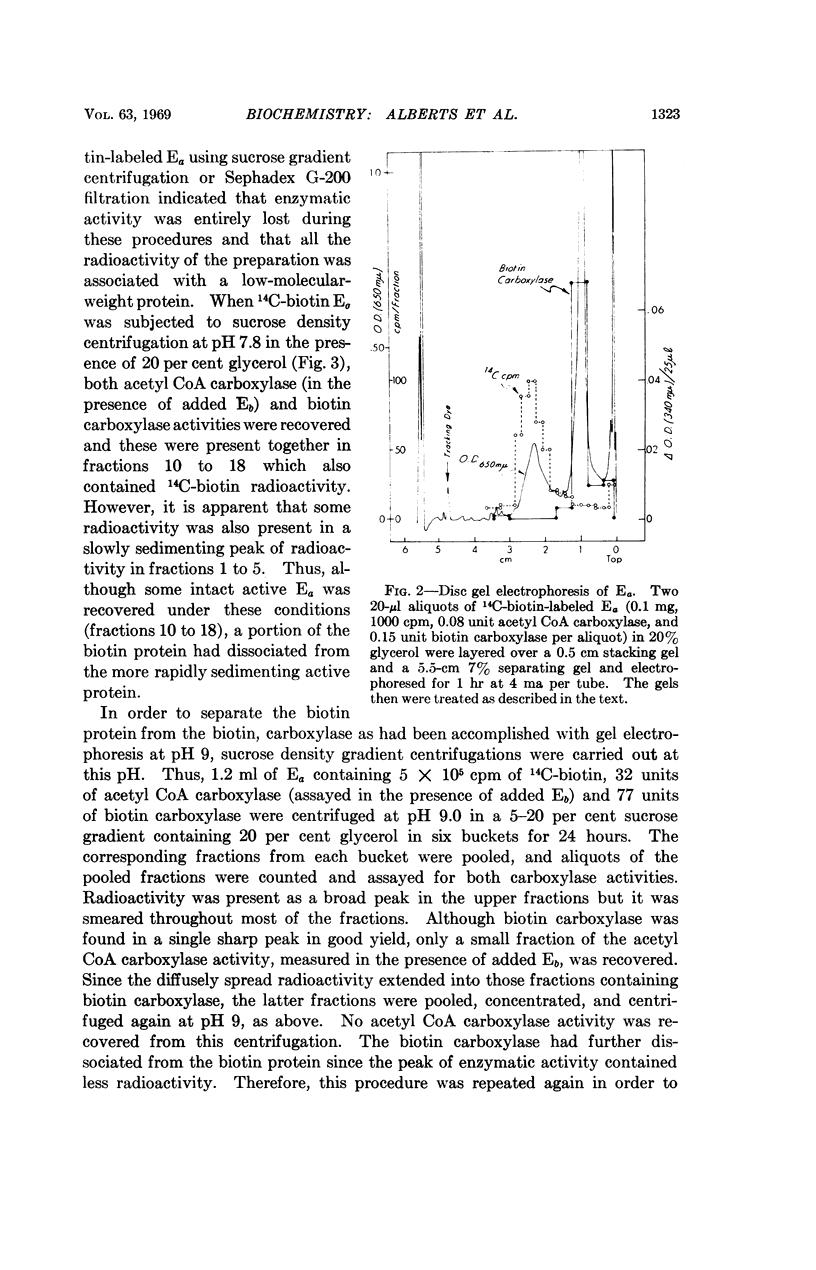
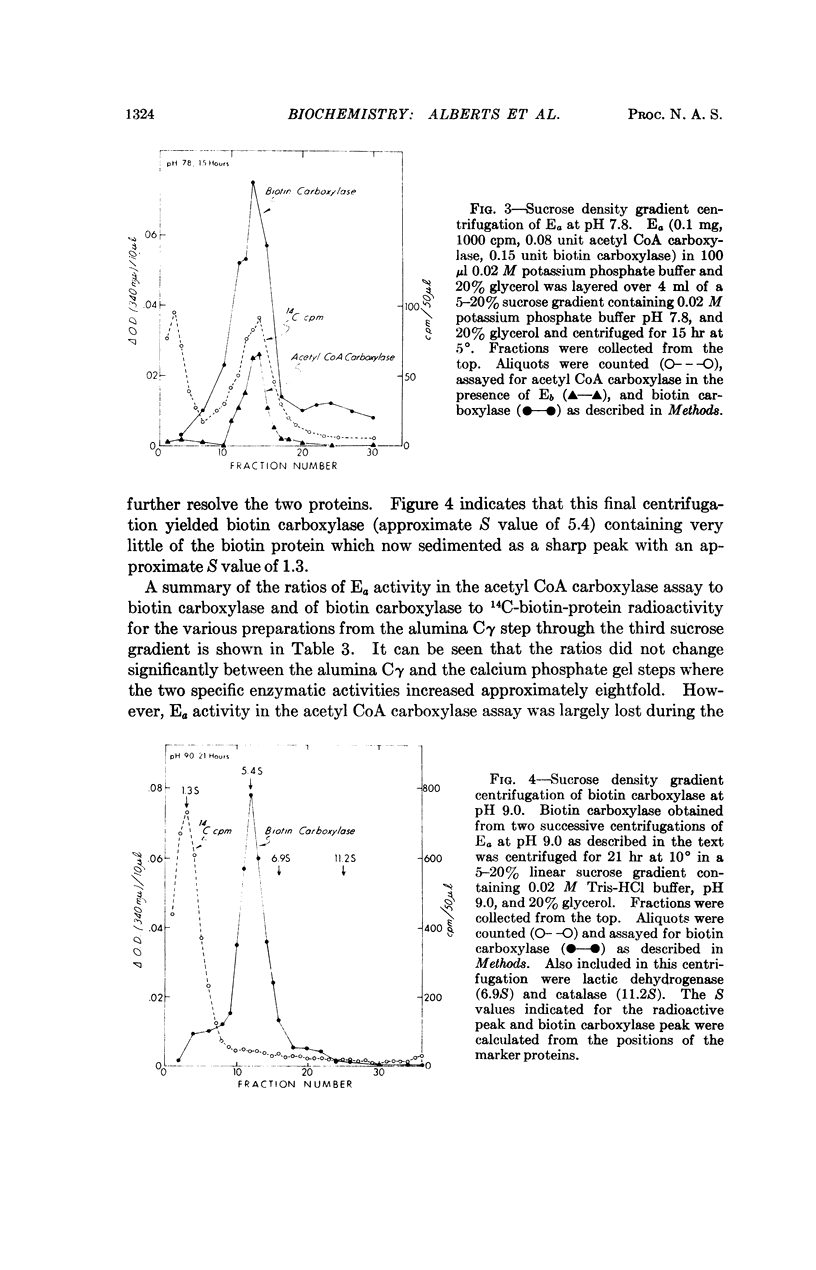
Previous work has shown that Escherichia coli acetyl CoA carboxylase is composed of two dissimilar protein components, Ea which contains covalently bound biotin and forms Ea-CO2-from HCO3- and ATP, and Eb which is involved in the transfer of the carboxyl group from Ea-CO2- to acetyl CoA, forming malonyl CoA. Ea has been dissociated into two subunits at pH 9. One subunit, designated biotin carboxylase, catalyzes a model reaction, the ATP-dependent carboxylation of free (+)-biotin. The other subunit contains covalently bound which is carboxylated by the biotin carboxylase in the course of acetyl CoA carboxylation.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberts A. W., Vagelos P. R. Acetyl CoA carboxylase. I. Requirement for two protein fractions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Feb;59(2):561–568. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.2.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LYNEN F., KNAPPE J., LORCH E., JUETTING G., RINGELMANN E., LACHANCE J. P. [On the biochemical function of biotin. II. Purification and mode of action of beta-methyl-crotonyl-carboxylase]. Biochem Z. 1961;335:123–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUNKRES K. D., RICHARDS F. M. THE PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF NEUROSPORA MALATE DEHYDROGENASE. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1965 Mar;109:466–479. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(65)90391-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll E., Ryder E., Edwards J. B., Lane M. D. Liver acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase: activation of model partial reactions by tricarboxylic acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jul;60(3):986–991. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.3.986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vagelos P. R., Majerus P. W., Alberts A. W., Larrabee A. R., Ailhaud G. P. Structure and function of the acyl carrier protein. Fed Proc. 1966 Sep-Oct;25(5):1485–1494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


