Abstract
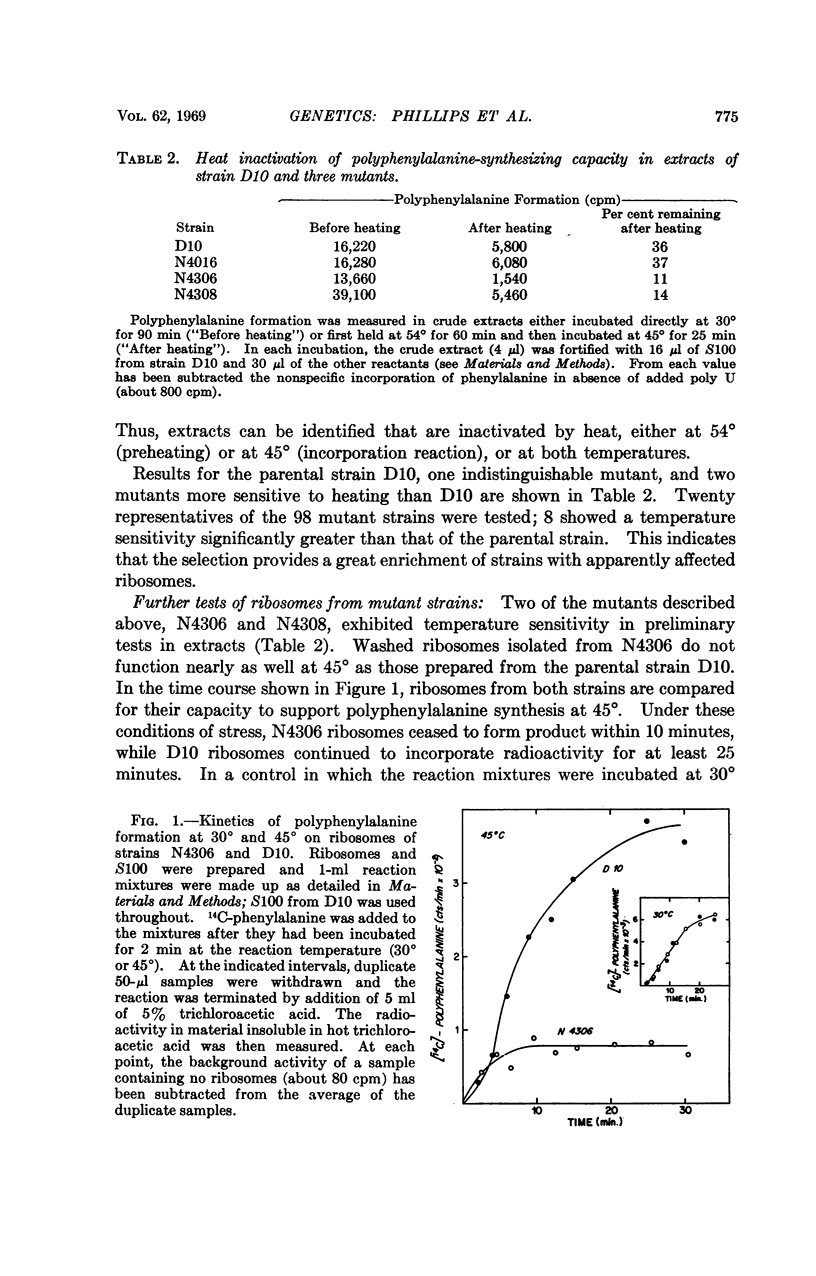
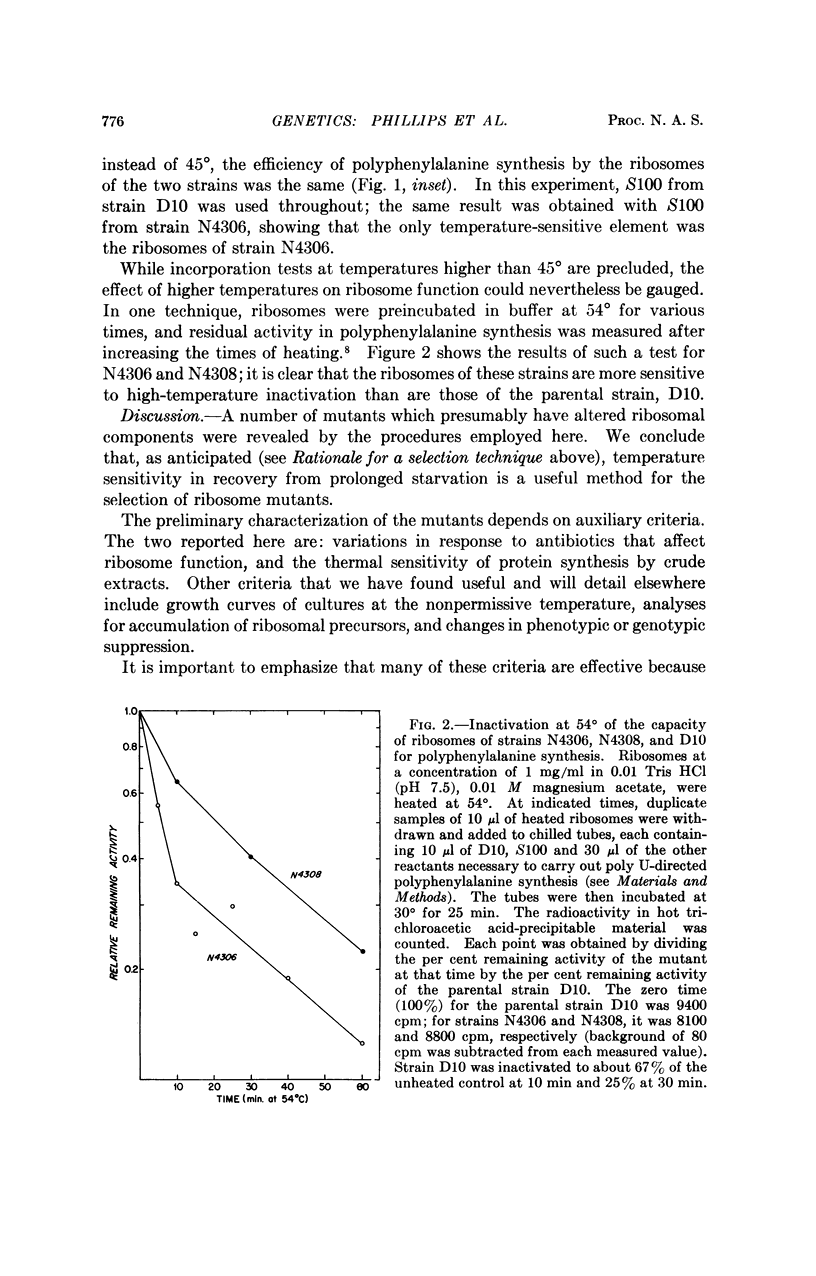
Only a few ribosome genes have been identified. Increasing the available kinds of ribosome mutants would thus facilitate the analysis of specification and function of the organelle. In an attempt to reveal a number of ribosome genes, we sought mutants that could not form functional ribosomes at a nonpermissive temperature (43°). Cells were depleted of ribosomes by nutrient starvation at 43°, and 98 strains that could not recover from the starvation were then isolated. Of these 98, many satisfied auxiliary criteria for ribosome mutants; 23 showed increased sensitivity to antibiotics that affect ribosome function; and 8 of 20 representative strains had crude extracts more temperature sensitive than that of the parental strain when assayed for polyphenylalanine formation in the presence of excess soluble enzymes (S100) of the parental strain. In further tests with two of these strains, the temperature sensitivity of the washed ribosomes, compared to that of the parental strain, was confirmed.
The variety of phenotypes among the mutants suggests that this selection is capable of revealing mutants in many ribosome genes.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apirion D. Altered ribosomes in a suppressor strain of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1966 Apr;16(2):285–301. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80173-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apirion D., Schlessinger D. Coresistance to neomycin and kanamycin by mutations in an Escherichia coli locus that affects ribosomes. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):768–776. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.768-776.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apirion D. Three genes that affect Escherichia coli ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1967 Dec 14;30(2):255–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Anderson P., Davis B. D. Inhibition of protein synthesis by spectinomycin. Science. 1965 Sep 3;149(3688):1096–1098. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3688.1096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLAKS J. G., COX E. C., WITTING M. L., WHITE J. R. Polypeptide synthesis with ribosomes from streptomycin-resistant and dependent E. coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 May 11;7:390–393. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90321-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flaks J. G., Leboy P. S., Birge E. A., Kurland C. G. Mutations and genetics concerned with the ribosome. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1966;31:623–631. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1966.031.01.081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gesteland R. F. Isolation and characterization of ribonuclease I mutants of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1966 Mar;16(1):67–84. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80263-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTHAEI J. H., NIRENBERG M. W. Characteristics and stabilization of DNAase-sensitive protein synthesis in E. coli extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Oct 15;47:1580–1588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.10.1580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangiarotti G., Apirion D., Schlessinger D., Silengo L. Biosynthetic precursors of 30S and 50S ribosomal particles in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1968 Jan;7(1):456–472. doi: 10.1021/bi00841a058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPEYER J. F., LENGYEL P., BASILIO C. Ribosomal localization of streptomycin sensitivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Apr 15;48:684–686. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.4.684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tocchini-Valentini G. P., Mattoccia E. A mutant of E. coli with an altered supernatant factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Sep;61(1):146–151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.1.146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


