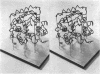
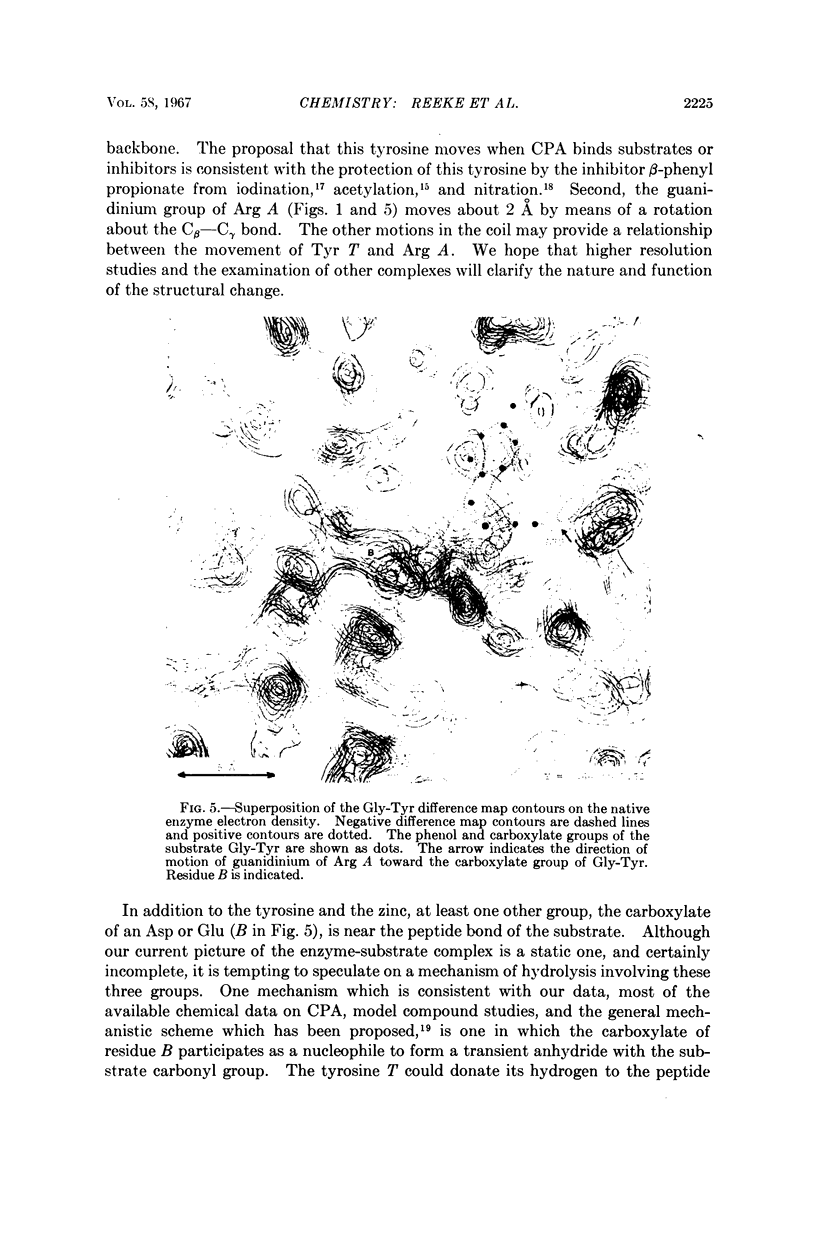
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARGETZI J. P. KUMAR KS, COX DJ, WALSH KA, NEURATH H: THE AMINO ACID COMPOSITION OF BOVINE PANCREATIC CARBOXYPEPTIDASE A. Biochemistry. 1963 Nov-Dec;2:1468–1474. doi: 10.1021/bi00906a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARGETZI J. P., THOMPSON E. O., SAMPATHKUMAR K. S., WALSH K. A., NEURATH H. THE AMINO- AND CARBOXYL-TERMINAL RESIDUES AND THE SELF-DIGESTION OF BOVINE PANCREATIC CARBOXYPEPTIDASE A. J Biol Chem. 1964 Nov;239:3767–3774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUMAR K. S., CLEGG J. B., WALSH K. A. THE N-TERMINAL SEQUENCE OF BOVINE CARBOXYPEPTIDASE A AND ITS RELATION OF ZYMOGEN ACTIVATION. Biochemistry. 1964 Nov;3:1728–1732. doi: 10.1021/bi00899a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEURATH H. MECHANISM OF ZYMOGEN ACTIVATION. Fed Proc. 1964 Jan-Feb;23:1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Némethy G., Phillips D. C., Leach S. J., Scheraga H. A. A second right-handed helical structure with the parameters of the Pauling-Corey alpha-helix. Nature. 1967 Apr 22;214(5086):363–365. doi: 10.1038/214363a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAULING L., COREY R. B., BRANSON H. R. The structure of proteins; two hydrogen-bonded helical configurations of the polypeptide chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1951 Apr;37(4):205–211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.37.4.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauling L., Corey R. B. Configurations of Polypeptide Chains With Favored Orientations Around Single Bonds: Two New Pleated Sheets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1951 Nov;37(11):729–740. doi: 10.1073/pnas.37.11.729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riordan J. F., Sokolovsky M., Vallee B. L. Environmentally sensitive tyrosyl residues. Nitration with tetranitromethane. Biochemistry. 1967 Jan;6(1):358–361. doi: 10.1021/bi00853a053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roholt O. A., Pressman D. The sequence around the active-center tyrosyl residue of bovine pancreatic carboxypeptidase A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jul;58(1):280–285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.1.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMPSON R. T., RIORDAN J. F., VALLEE B. L. FUNCTIONAL TYROSYL RESIDUES IN THE ACTIVE CENTER OF BOVINE PANCREATIC CARBOXYPEPTIDASE A. Biochemistry. 1963 May-Jun;2:616–622. doi: 10.1021/bi00903a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T., Vallee B. L. Iodocarboxypeptidase. Biochemistry. 1966 May;5(5):1760–1767. doi: 10.1021/bi00869a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz T. A., Ludwig M. L., Quiocho F. A., Lipscomb W. N. The structure of carboxypepidase A. V. Studies of enzyme-substrate and enzyme-inhibitor complexes at 6 A resolution. J Biol Chem. 1967 Oct 25;242(20):4662–4668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VALLEE B. L. ACTIVE CENTER OF CARBOXYPEPTIDASE A. Fed Proc. 1964 Jan-Feb;23:8–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALSH K. A., SAMPATH KUMAR K. S., BARGETZI J. P., NEURATH H. Approaches to the selective chemical labeling of the active site of carboxypepticase A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Aug;48:1443–1449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.8.1443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]