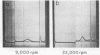
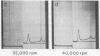
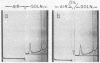
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- GILL S. J., GLOGOVSKY R. L. INFLUENCE OF PRESSURE ON THE REVERSIBLE UNFOLDING OR RIBONUCLEASE AND POLY-GAMMA-L-GLUTAMATE. J Phys Chem. 1965 May;69:1515–1519. doi: 10.1021/j100889a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes F., Steiner R. F. Effects of pressure on the helix-coil transitions of the poly A-poly U system. Biopolymers. 1966 Dec;4(10):1081–1090. doi: 10.1002/bip.1966.360041005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikkai T., Ooi T. The effects of pressure on F-G transformation of actin. Biochemistry. 1966 May;5(5):1551–1560. doi: 10.1021/bi00869a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
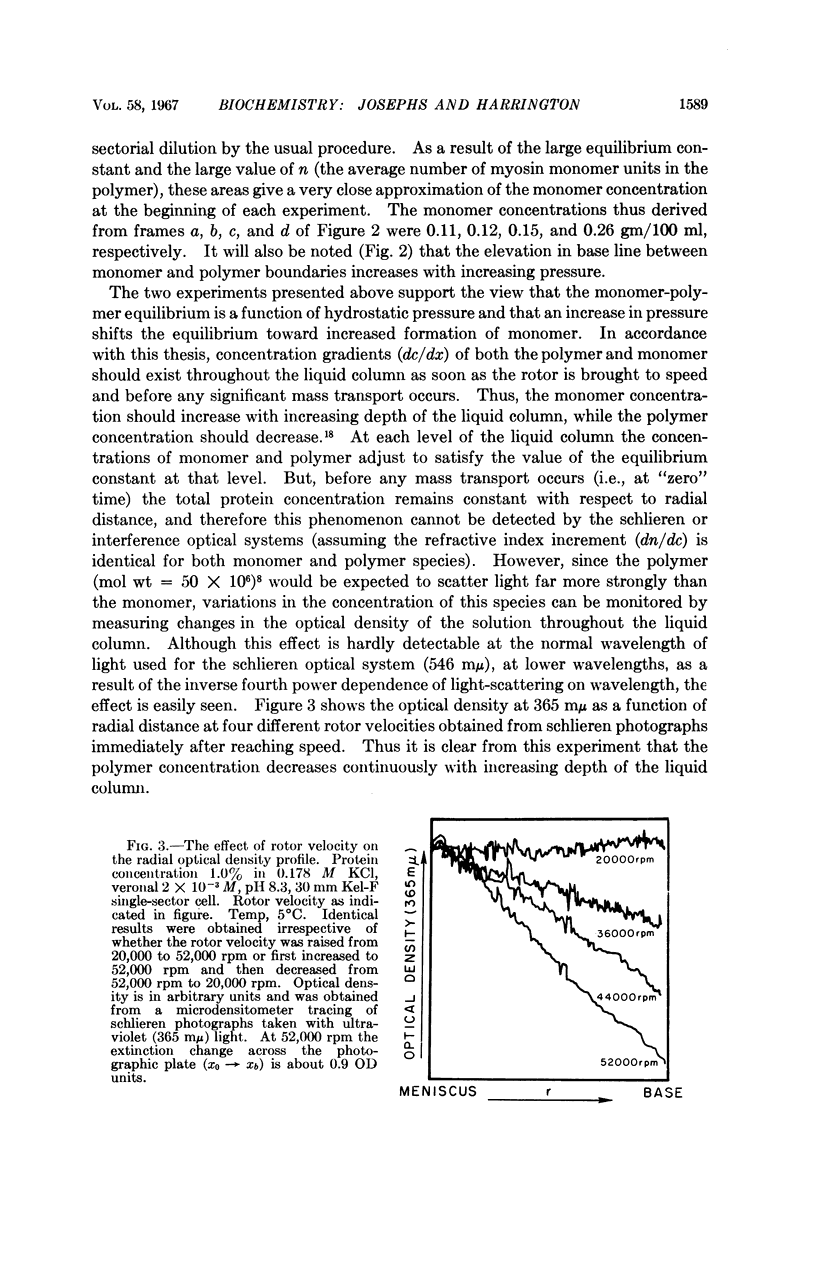
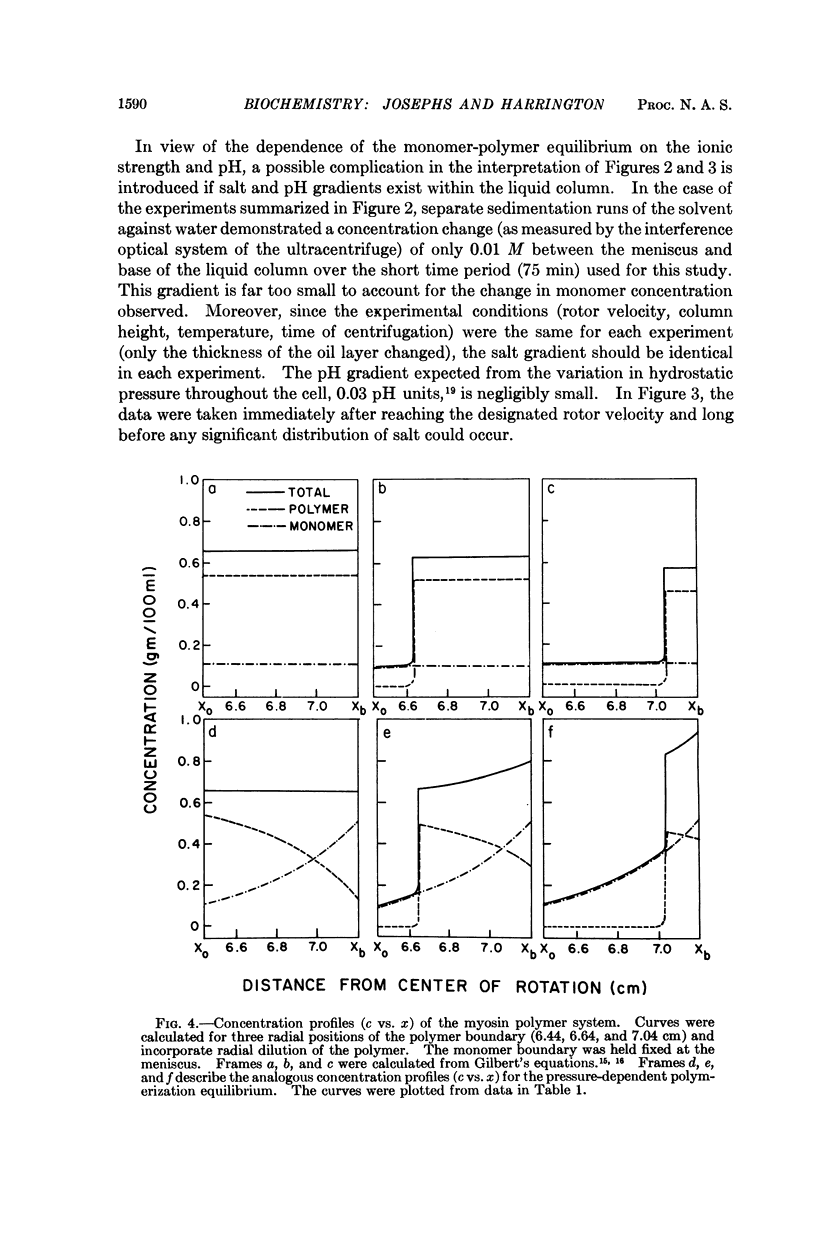
- Josephs R., Harrington W. F. Studies on the formation and physical chemical properties of synthetic myosin filaments. Biochemistry. 1966 Nov;5(11):3474–3487. doi: 10.1021/bi00875a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaminer B., Bell A. L. Myosin filamentogenesis: effects of pH and ionic concentration. J Mol Biol. 1966 Sep;20(2):391–401. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90070-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaminer B., Bell A. L. Synthetic myosin filaments. Science. 1966 Jan 21;151(3708):323–324. doi: 10.1126/science.151.3708.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kegeles G., Rhodes L., Bethune J. L. Sedimentation behavior of chemically reacting systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jul;58(1):45–51. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettman M. S., Nishikawa A. H., Morita R. Y., Becker R. R. Effect of hydrostatic pressure on the aggregation reaction of poly-L-valyl-ribonuclease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Feb 3;22(3):262–267. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90475-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIYAGAWA K. STUDIES ON TAKA-AMYLASE A UNDER HIGH PRESSURE. 3. SOME PHYSIOCHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF PRESSURE-DENATURED AMYLASE A. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1965 May;110:381–387. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(65)90138-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NODA H., EBASHI S. Aggregation of myosin A. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Jul 15;41:386–392. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90035-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teneyck L. F., Kauzmann W. Pressure and hydration effects on chemically reacting systems in the ultracentrifuge. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Sep;58(3):888–894. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.3.888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vournakis J. N., Poland D., Scheraga H. A. Anti-cooperative interactions in single-strand oligomers of deoxyriboadenylic acid. Biopolymers. 1967 Jun;5(5):403–422. doi: 10.1002/bip.1967.360050502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]