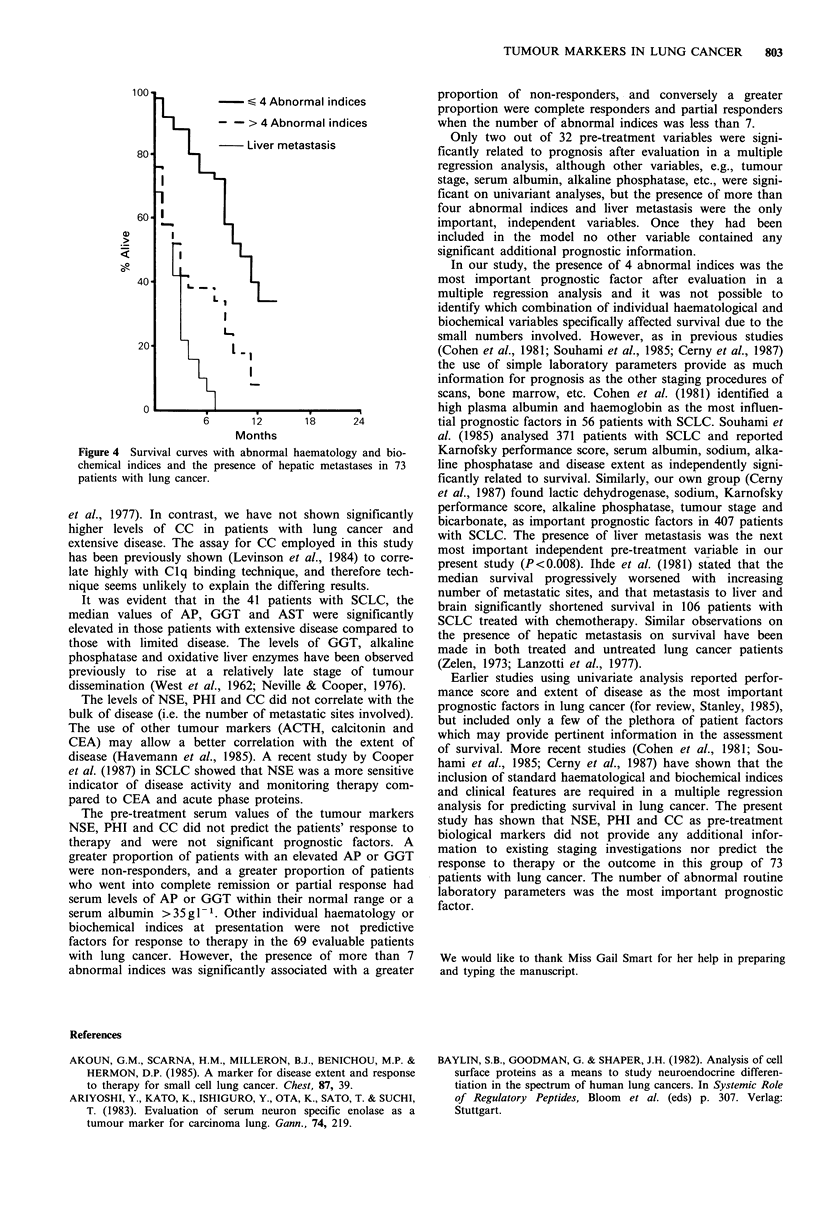
Abstract
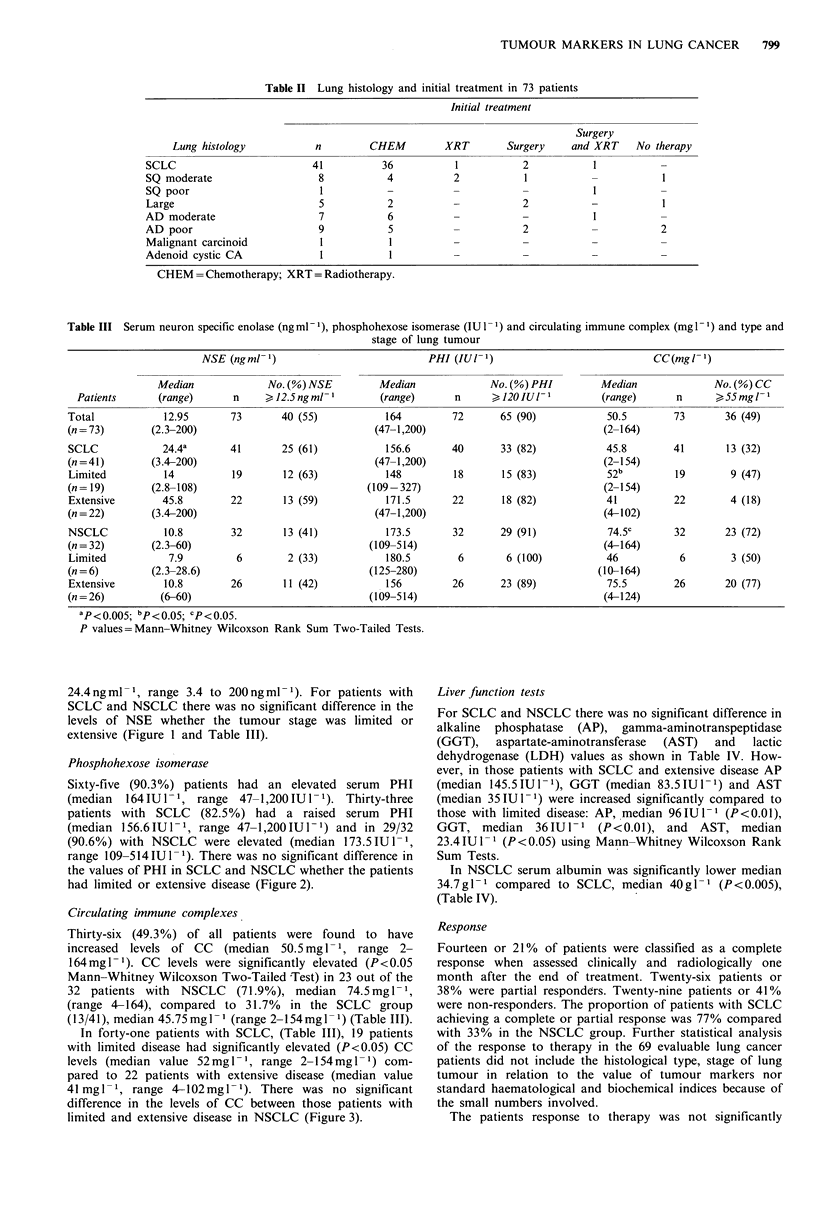
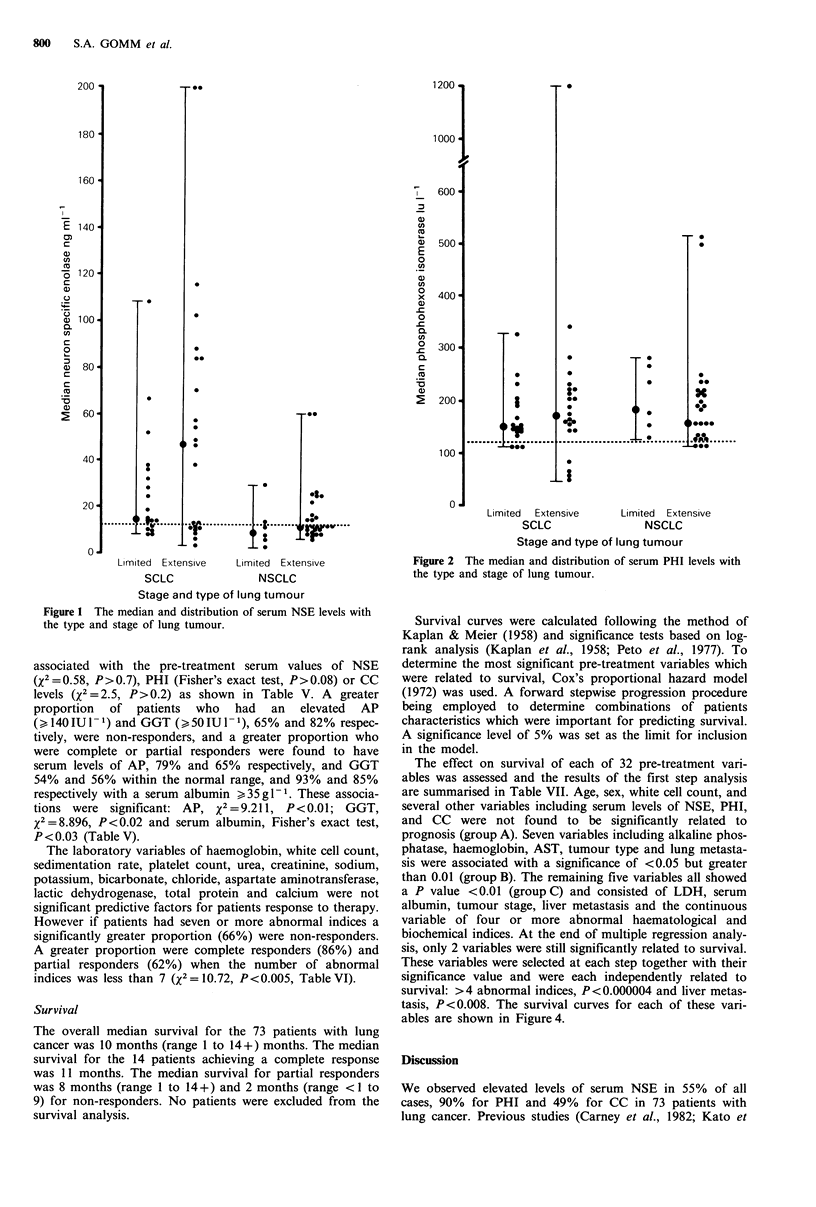
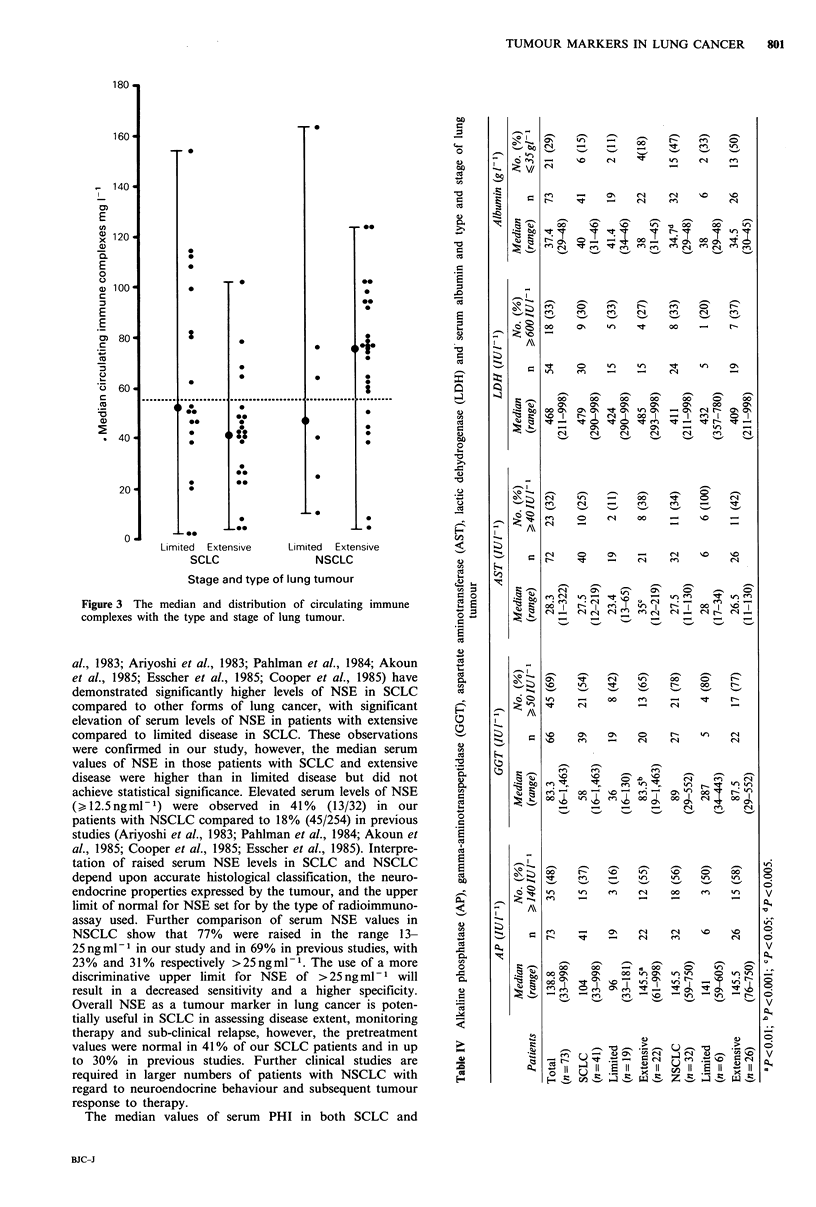
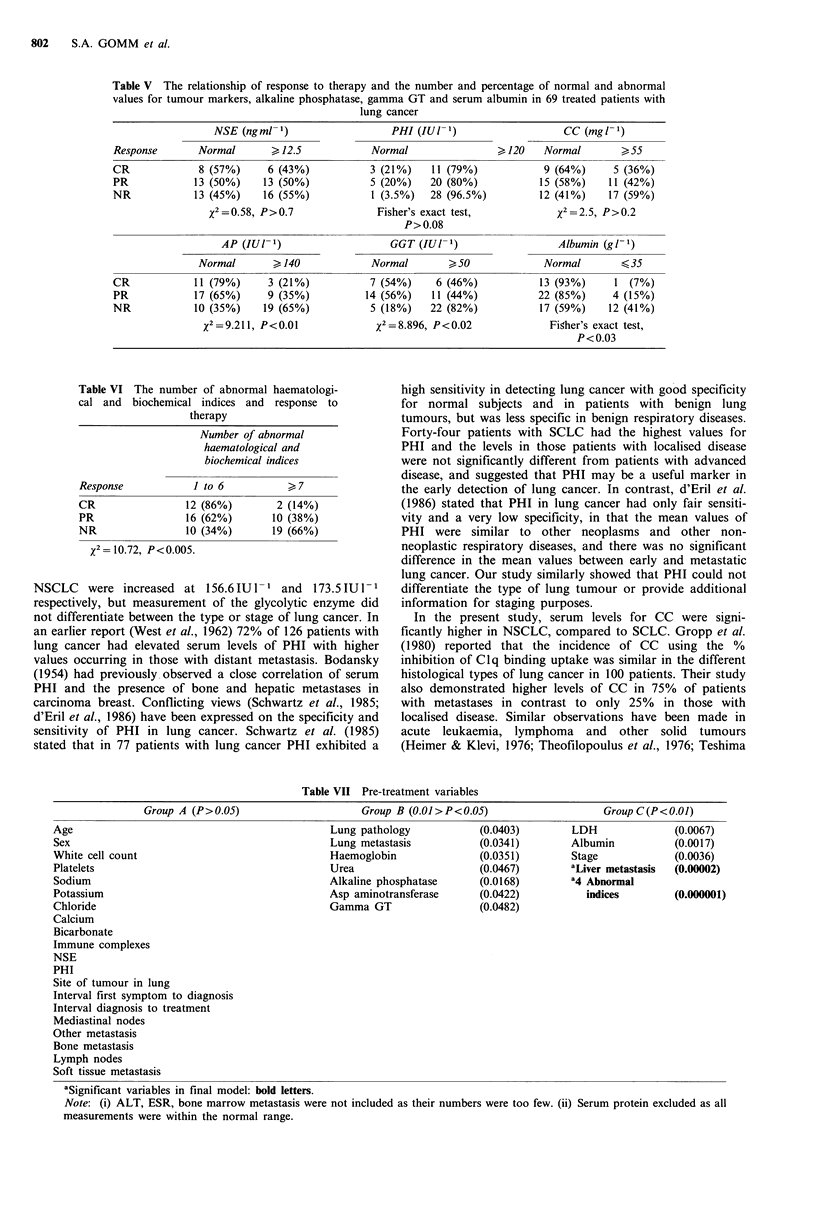
The pre-treatment serum levels of neuron-specific enolase (NSE), phosphohexose isomerase (PHI) and circulating immune complexes (CC) as tumour markers were compared to measurements of standard haematology and biochemical indices in 73 patients with lung cancer, as an aid to differentiation of tumour type, estimating disease extent, predicting response to therapy and prognosis. Elevated NSE greater than or equal to 12.5 ng ml-1, PHI greater than or equal to 55 mgl-1 levels were observed in 55% of cases for NSE, 90% for PHI and 49% for CC. NSE was significantly elevated in 61% (25/41) of patients with SCLC (P less than 0.005) compared to 41% (13/32) with NSCLC. CC levels were significantly raised in 72% (23/32) of patients with NSCLC (P less than 0.05) compared to 32% with SCLC. The levels of NSE and PHI were not related to tumour stage but CC was significantly raised in limited compared to extensive disease in SCLC (P less than 0.05). Serum albumin was significantly lower in NSCLC compared to SCLC, and median values of alkaline phosphatase, gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase and aminoaspartate transferase were significantly higher in patients with extensive disease. The pre-treatment serum values of NSE, PHI, and CC did not predict the response to therapy or prognosis in the 73 patients with lung cancer. The most important prognostic factor was the number of abnormal routine laboratory parameters (greater than 4) in this group of patients.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akoun G. M., Scarna H. M., Milleron B. J., Bénichou M. P., Herman D. P. Serum neuron-specific enolase. A marker for disease extent and response to therapy for small-cell lung cancer. Chest. 1985 Jan;87(1):39–43. doi: 10.1378/chest.87.1.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ariyoshi Y., Kato K., Ishiguro Y., Ota K., Sato T., Suchi T. Evaluation of serum neuron-specific enolase as a tumor marker for carcinoma of the lung. Gan. 1983 Apr;74(2):219–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BODANSKY O. Serum phosphohexose isomerase in cancer. II. As an index of tumor growth in metastatic carcinoma of the breast. Cancer. 1954 Nov;7(6):1200–1226. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(195411)7:6<1200::aid-cncr2820070612>3.0.co;2-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney D. N., Marangos P. J., Ihde D. C., Bunn P. A., Jr, Cohen M. H., Minna J. D., Gazdar A. F. Serum neuron-specific enolase: a marker for disease extent and response to therapy of small-cell lung cancer. Lancet. 1982 Mar 13;1(8272):583–585. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91748-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerny T., Blair V., Anderson H., Bramwell V., Thatcher N. Pretreatment prognostic factors and scoring system in 407 small-cell lung cancer patients. Int J Cancer. 1987 Feb 15;39(2):146–149. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910390204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. H., Makuch R., Johnston-Early A., Ihde D. C., Bunn P. A., Jr, Fossieck B. E., Jr, Minna J. D. Laboratory parameters as an alternative to performance status in prognostic stratification of patients with small cell lung cancer. Cancer Treat Rep. 1981 Mar-Apr;65(3-4):187–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhillon A. P., Rode J., Dhillon D. P., Moss E., Thompson R. J., Spiro S. G., Corrin B. Neural markers in carcinoma of the lung. Br J Cancer. 1985 May;51(5):645–652. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1985.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esscher T., Steinholtz L., Bergh J., Nöu E., Nilsson K., Påhlman S. Neurone specific enolase: a useful diagnostic serum marker for small cell carcinoma of the lung. Thorax. 1985 Feb;40(2):85–90. doi: 10.1136/thx.40.2.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazdar A. F., Carney D. N., Minna J. D. The biology of non-small cell lung cancer. Semin Oncol. 1983 Mar;10(1):3–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gropp C., Havemann K., Scherfe T., Ax W. Incidence of circulating immune complexes in patients with lung cancer and their effect on antibody-dependent cytotoxicity. Oncology. 1980;37(2):71–76. doi: 10.1159/000225407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimer R., Klein G. Circulating immune complexes in sera of patients with Burkett's lymphoma and nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 1976 Sep 15;18(3):310–316. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910180307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihde D. C., Makuch R. W., Carney D. N., Bunn P. A., Cohen M. H., Matthews M. J., Minna J. D. Prognostic implications of stage of disease and sites of metastases in patients with small cell carcinoma of the lung treated with intensive combination chemotherapy. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 May;123(5):500–507. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.123.5.500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. H., Marangos P. J., Forbes J. T., Hainsworth J. D., Van Welch R., Hande K. R., Greco F. A. Potential utility of serum neuron-specific enolase levels in small cell carcinoma of the lung. Cancer Res. 1984 Nov;44(11):5409–5414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato K., Asai R., Shimizu A., Suzuki F., Ariyoshi Y. Immunoassay of three enolase isozymes in human serum and in blood cells. Clin Chim Acta. 1983 Feb 7;127(3):353–363. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(83)90162-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krapf F., Renger D., Schedel I., Leiendecker K., Leyssens H., Deicher H. A PEG-precipitation laser nephelometer technique for detection and characterization of circulating immune complexes in human sera. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Oct 15;54(1):107–117. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90119-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanzotti V. J., Thomas D. R., Boyle L. E., Smith T. L., Gehan E. A., Samuels M. L. Survival with inoperable lung cancer: an integration of prognostic variables based on simple clinical criteria. Cancer. 1977 Jan;39(1):303–313. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197701)39:1<303::aid-cncr2820390147>3.0.co;2-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson S. S., Goldman J. O., Feldkamp C. S. Anti-IgG binding test to assay circulating IgG-containing immune complexes from polyethylene glycol precipitates. Clin Chem. 1984 Sep;30(9):1502–1506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDowell E. M., Trump B. F. Pulmonary smell cell carcinoma showing tripartite differentiation in individual cells. Hum Pathol. 1981 Mar;12(3):286–294. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(81)80133-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melzi d'Eril G. V., Pavesi F., Lotzniker M., Moratti R. More on phosphohexose isomerase as a tumor marker. Clin Chem. 1986 Jun;32(6):1242–1243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville A. M., Cooper E. H. Biochemical monitoring of cancer. A review. Ann Clin Biochem. 1976 Jan;13(1):283–305. doi: 10.1177/000456327601300101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Påhlman S., Esscher T., Bergh J., Steinholtz L., Nöu E., Nilsson K. Neuron-specific enolase as a marker for neuroblastoma and small-cell carcinoma of the lung. Tumour Biol. 1984;5(2):119–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowan R. M. The assay of phosphoglucose isomerase in human serum. Med Lab Sci. 1978 Apr;35(2):155–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel A. T., Bokisch V. A., Müller-Eberhard H. J. C1q deviation test for the detection of immune complexes, aggregates of IgG, and bacterial products in human serum. J Exp Med. 1975 Jul 1;142(1):139–150. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.1.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souhami R. L., Bradbury I., Geddes D. M., Spiro S. G., Harper P. G., Tobias J. S. Prognostic significance of laboratory parameters measured at diagnosis in small cell carcinoma of the lung. Cancer Res. 1985 Jun;45(6):2878–2882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapia F. J., Polak J. M., Barbosa A. J., Bloom S. R., Marangos P. J., Dermody C., Pearse A. G. Neuron-specific enolase is produced by neuroendocrine tumours. Lancet. 1981 Apr 11;1(8224):808–811. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92682-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teshima H., Wanebo H., Pinsky C., Day N. K. Circulating immune complexes detected by 125I-Clq deviation test in sera of cancer patients. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jun;59(6):1134–1142. doi: 10.1172/JCI108737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEST M., SCHWARTZ M. A., WALSH W. S., ZIMMERMAN H. J. Serum enzymes in disease. XI. Glycolytic and oxidative enzymes and transaminases in patients with cancer of the lung. Cancer. 1962 Sep-Oct;15:931–935. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196209/10)15:5<931::aid-cncr2820150508>3.0.co;2-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zelen M. Keynote address on biostatistics and data retrieval. Cancer Chemother Rep 3. 1973 Mar;4(2):31–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


