Abstract
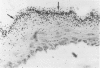
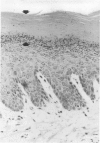
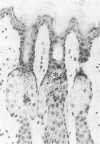
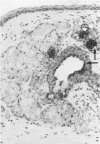
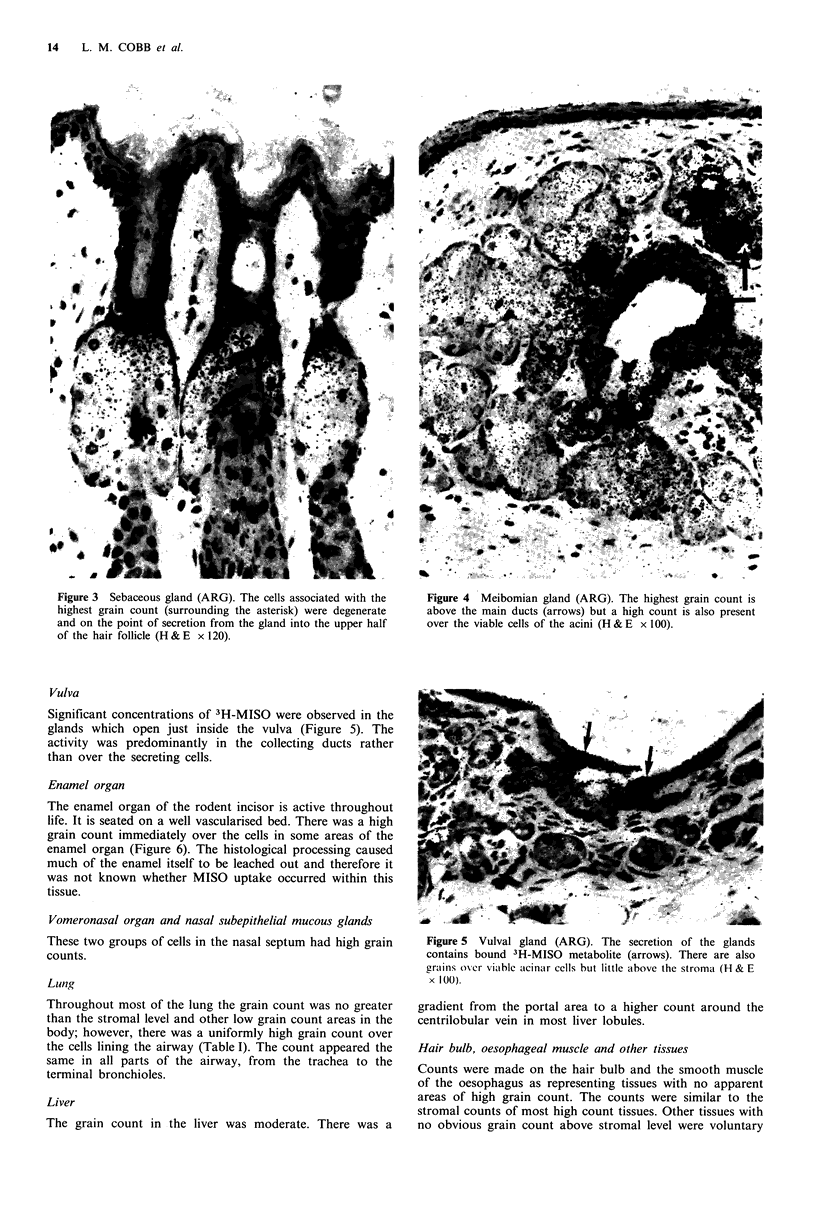
Mice were injected with tritiated misonidazole (750 mg/kg-1), killed after 24h and the excised tissues prepared for autoradiography (ARG) to identify sites of accumulation. The previously reported high grain count associated with bound misonidazole metabolite(s) was observed in the liver. The ratio of grain count in the emulsion above the centrilobular hepatocytes to the count over connective tissue (stroma) was 12. A higher count ratio for 'target' cells to stroma was observed in the following cells/tissues: meibomian gland (ducts 110, acini 65), oesophagus (keratinised layer 60), incisor (enamel organ 17), nasal septum (subepithelial glands 13). For some of these tissues the explanation might appear to lie with localised hypoxia, but for others which were probably normoxic there is as yet no obvious reason for these findings.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akel G., Benard P., Canal P., Soula G. Distribution and tumor penetration properties of a radiosensitizer 2-[14C] misonidazole (Ro 07-0582), in mice and rats as studied by whole-body autoradiography. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1986;17(2):121–126. doi: 10.1007/BF00306739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ash D. V., Smith M. R., Bugden R. D. Distribution of misonidazole in human tumours and normal tissues. Br J Cancer. 1979 May;39(5):503–509. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1979.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohlen H. G. Intestinal tissue PO2 and microvascular responses during glucose exposure. Am J Physiol. 1980 Feb;238(2):H164–H171. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1980.238.2.H164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. M. Selective radiosensitization of the hypoxic cells of mouse tumors with the nitroimidazoles metronidazole and Ro 7-0582. Radiat Res. 1975 Dec;64(3):633–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman J. D., Baer K., Lee J. Characteristics of the metabolism-induced binding of misonidazole to hypoxic mammalian cells. Cancer Res. 1983 Apr;43(4):1523–1528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin J. B., Rauth A. M. The metabolism and pharmacokinetics of the hypoxic cell radiosensitizer and cytotoxic agent, misonidazole, in C3H mice. Radiat Res. 1981 May;86(2):341–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franko A. J., Koch C. J. Binding of misonidazole to V79 spheroids and fragments of Dunning rat prostatic and human colon carcinomas in vitro: diffusion of oxygen and reactive metabolites. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1984 Aug;10(8):1333–1336. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(84)90343-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franko A. J. Misonidazole and other hypoxia markers: metabolism and applications. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1986 Jul;12(7):1195–1202. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(86)90257-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrecht B. M., Chapman J. D. The labelling of EMT-6 tumours in BALB/C mice with 14C-misonidazole. Br J Radiol. 1983 Oct;56(670):745–753. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-56-670-745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall E. J., Roizin-Towle L. Hypoxic sensitizers: radiobiological studies at the cellular level. Radiology. 1975 Nov;117(2):453–457. doi: 10.1148/117.2.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendry J. H. Quantitation of the radiotherapeutic importance of naturally-hypoxic normal tissues from collated experiments with rodents using single doses. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1979 Jul;5(7):971–976. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(79)90602-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langler A. J., Bugden R. D., Gibson P. The penetration of misonidazole into a mature structural cartilage. Br J Cancer. 1982 Feb;45(2):282–285. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1982.44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McManus M. E., Monks A., Collins J. M., White R., Strong J. M. Nonlinear pharmacokinetics of misonidazole and desmethylmisonidazole in the isolated perfused rat liver. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Dec;219(3):669–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. C., Randhawa V., Denekamp J. The effects of melphalan and misonidazole on the vasculature of a murine sarcoma. Br J Cancer. 1987 Mar;55(3):233–238. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1987.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raleigh J. A., Franko A. J., Koch C. J., Born J. L. Binding of misonidazole to hypoxic cells in monolayer and spheroid culture: evidence that a side-chain label is bound as efficiently as a ring label. Br J Cancer. 1985 Feb;51(2):229–235. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1985.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasey J. S., Grunbaum Z., Krohn K., Nelson N., Chin L. Comparison of binding of [3H]misonidazole and [14C]misonidazole in multicell spheroids. Radiat Res. 1985 Mar;101(3):473–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasey J. S., Grunbaum Z., Magee S., Nelson N. J., Olive P. L., Durand R. E., Krohn K. A. Characterization of radiolabeled fluoromisonidazole as a probe for hypoxic cells. Radiat Res. 1987 Aug;111(2):292–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauth A. M. Pharmacology and toxicology of sensitizers: mechanism studies. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1984 Aug;10(8):1293–1300. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(84)90335-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone H. B., Withers H. R. Tumor and normal tissue response to metronidazole and irradiation in mice. Radiology. 1974 Nov;113(2):441–444. doi: 10.1148/113.2.441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urtasun R. C., Chapman J. D., Raleigh J. A., Franko A. J., Koch C. J. Binding of 3H-misonidazole to solid human tumors as a measure of tumor hypoxia. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1986 Jul;12(7):1263–1267. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(86)90273-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Os-Corby D. J., Koch C. J., Chapman J. D. Is misonidazole binding to mouse tissues a measure of cellular pO2? Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Oct 15;36(20):3487–3494. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90330-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varghese A. J., Whitmore G. F. Binding to cellular macromolecules as a possible mechanism for the cytotoxicity of misonidazole. Cancer Res. 1980 Jul;40(7):2165–2169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winterbourn C. C. Cytochrome c reduction by semiquinone radicals can be indirectly inhibited by superoxide dismutase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Jun;209(1):159–167. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90268-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman P. Pharmacokinetics of hypoxic cell radiosensitizers: a review. Cancer Clin Trials. 1980 Fall;3(3):237–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]