Abstract
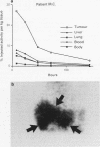
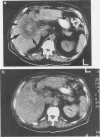
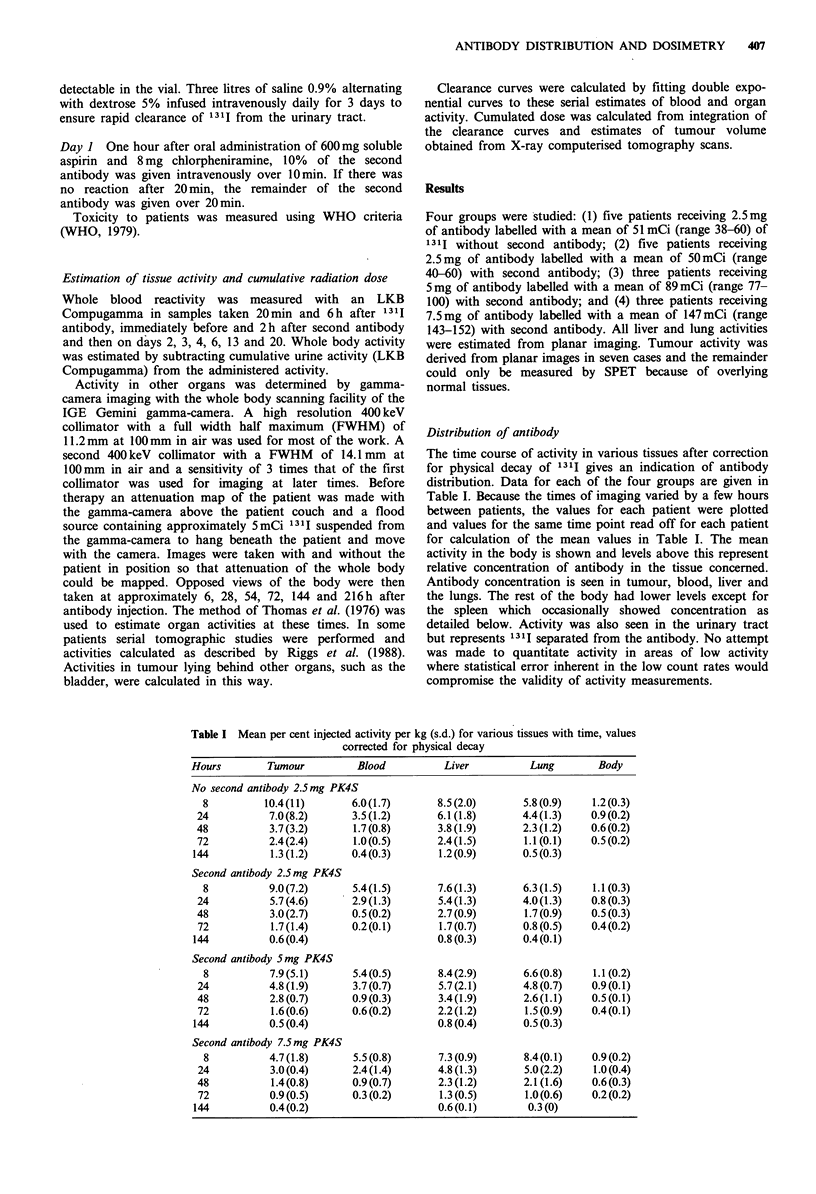
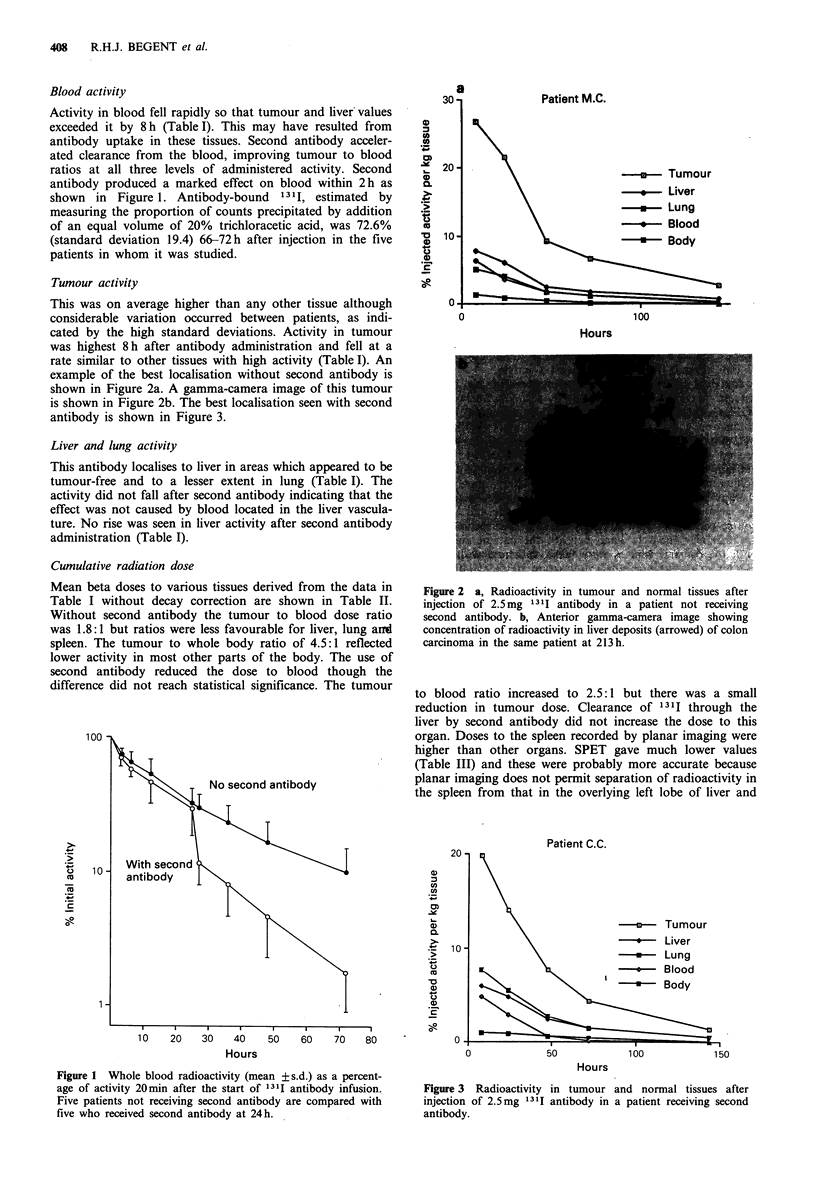
The distribution of iodine-131 (131I) labelled antibody to carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) has been studied in 16 patients with colorectal cancer. Levels of tumour and normal tissue radioactivity were measured by serial gamma-camera imaging and counting of blood and urine. Maximum concentrations were found in tumour 8 h after administration and varied up to 9-fold in different patients. Higher levels were found on average in tumour than in any other tissue. Liver, lung and blood were the other tissues in which antibody was concentrated relative to the rest of the body. Antibody cleared from all these tissues over 1 week. Second antibody directed against the antitumour (first) antibody was given 24 h after first antibody in order to accelerate clearance from the blood. This increased the tumour to blood ratio but had little effect on other tissues. Cumulative radiation dose to tumour and normal tissue was estimated. In patients with the most efficient localisation the tumour to body ratio was 20:1 and tumour to blood ratio 5:1. This may be sufficient for effective therapy of cancer in patients selected for efficient antibody localisation. The data may be used to estimate the effect of different therapeutic strategies. For instance, in the time after second antibody administration the average tumour to blood ratio of radiation dose was 11:1, suggesting that two phase systems in which the therapeutic modality is given after a good tumour to normal tissue ratio is obtained may be effective for the majority of patients.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
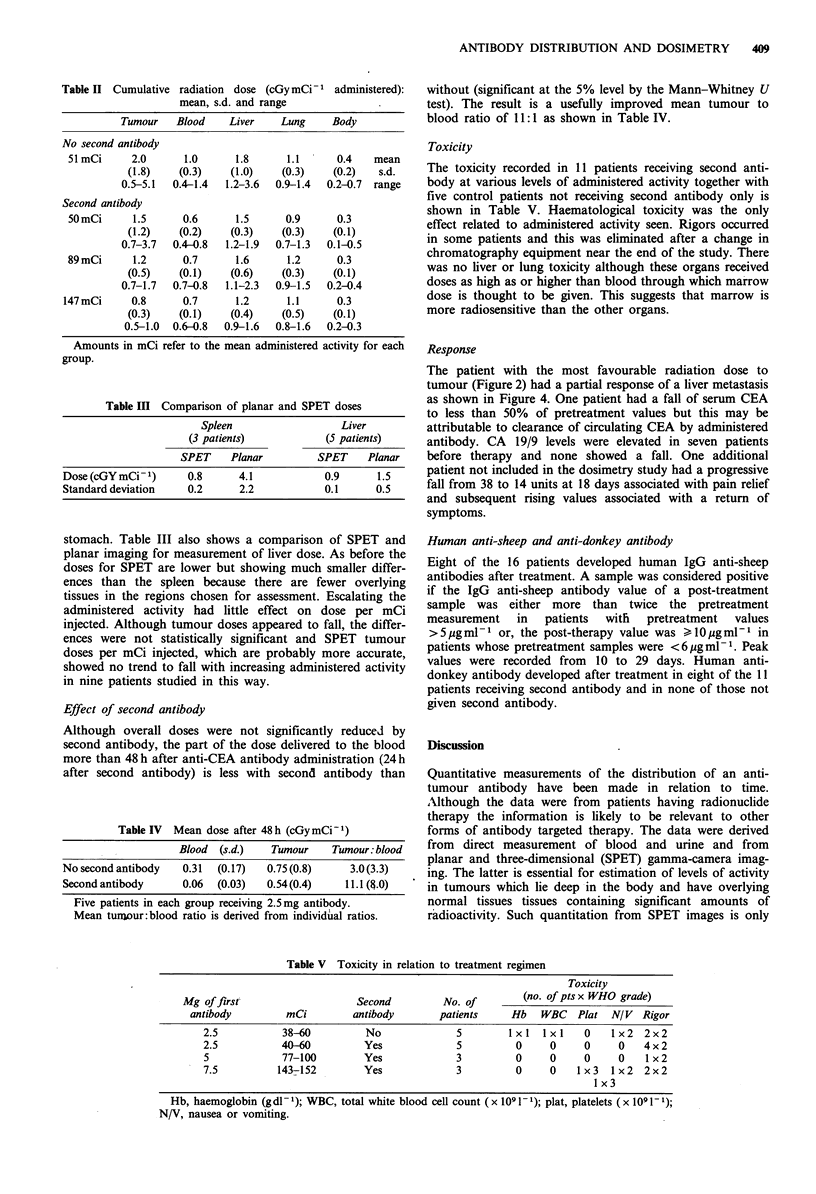
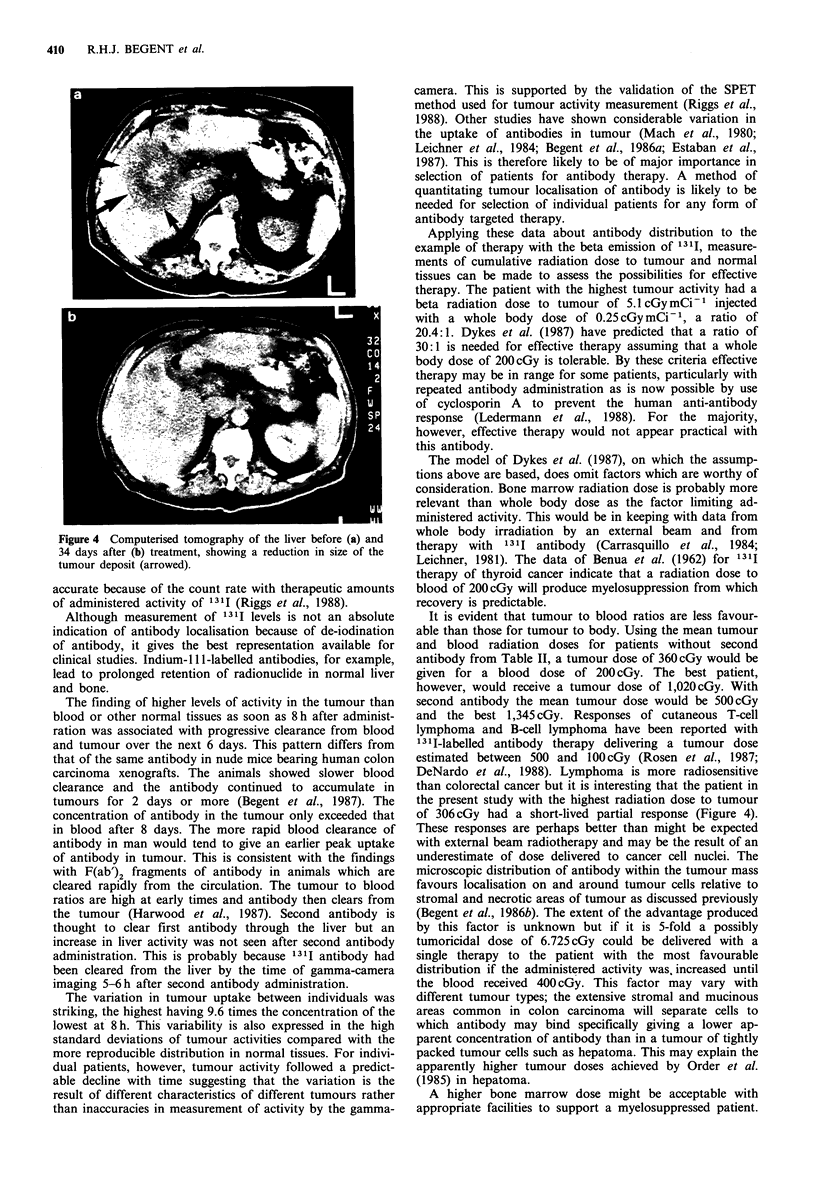
- BENUA R. S., CICALE N. R., SONENBERG M., RAWSON R. W. The relation of radioiodine dosimetry to results and complications in the treatment of metastatic thyroid cancer. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1962 Jan;87:171–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badger C. C., Krohn K. A., Shulman H., Flournoy N., Bernstein I. D. Experimental radioimmunotherapy of murine lymphoma with 131I-labeled anti-T-cell antibodies. Cancer Res. 1986 Dec;46(12 Pt 1):6223–6228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagshawe K. D., Springer C. J., Searle F., Antoniw P., Sharma S. K., Melton R. G., Sherwood R. F. A cytotoxic agent can be generated selectively at cancer sites. Br J Cancer. 1988 Dec;58(6):700–703. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1988.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begent R. H., Keep P. A., Green A. J., Searle F., Bagshawe K. D., Jewkes R. F., Jones B. E., Barratt G. M., Ryman B. E. Liposomally entrapped second antibody improves tumour imaging with radiolabelled (first) antitumour antibody. Lancet. 1982 Oct 2;2(8301):739–742. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90923-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchegger F., Vacca A., Carrel S., Schreyer M., Mach J. P. Radioimmunotherapy of human colon carcinoma by 131I-labelled monoclonal anti-CEA antibodies in a nude mouse model. Int J Cancer. 1988 Jan 15;41(1):127–134. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910410123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasquillo J. A., Krohn K. A., Beaumier P., McGuffin R. W., Brown J. P., Hellström K. E., Hellström I., Larson S. M. Diagnosis of and therapy for solid tumors with radiolabeled antibodies and immune fragments. Cancer Treat Rep. 1984 Jan;68(1):317–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceriani R. L., Blank E. W. Experimental therapy of human breast tumors with 131I-labeled monoclonal antibodies prepared against the human milk fat globule. Cancer Res. 1988 Aug 15;48(16):4664–4672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiou R. K., Vessella R. L., Limas C., Shafer R. B., Elson M. K., Arfman E. W., Lange P. H. Monoclonal antibody-targeted radiotherapy of renal cell carcinoma using a nude mouse model. Cancer. 1988 May 1;61(9):1766–1775. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19880501)61:9<1766::aid-cncr2820610908>3.0.co;2-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covell D. G., Barbet J., Holton O. D., Black C. D., Parker R. J., Weinstein J. N. Pharmacokinetics of monoclonal immunoglobulin G1, F(ab')2, and Fab' in mice. Cancer Res. 1986 Aug;46(8):3969–3978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldenberg D. M., Gaffar S. A., Bennett S. J., Beach J. L. Experimental radioimmunotherapy of a xenografted human colonic tumor (GW-39) producing carcinoembryonic antigen. Cancer Res. 1981 Nov;41(11 Pt 1):4354–4360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond N. D., Moldofsky P. J., Beardsley M. R., Mulhern C. B., Jr External imaging techniques for quantitation of distribution of I-131 F(ab')2 fragments of monoclonal antibody in humans. Med Phys. 1984 Nov-Dec;11(6):778–783. doi: 10.1118/1.595580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwood P. J., Pedley R. B., Boden J., Rogers G. T. Significance of circulatory clearance of tumour-localising IgG and F(ab')2 for potential therapy studied in a CEA-producing xenograft model. Tumour Biol. 1987;8(1):19–25. doi: 10.1159/000217487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. H., Goldman A., Gordon I., Pritchard J., Gregory B. J., Kemshead J. T. Therapeutic application of a radiolabelled monoclonal antibody in nude mice xenografted with human neuroblastoma: tumoricidal effects and distribution studies. Int J Cancer. 1985 Jun 15;35(6):715–720. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910350604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledermann J. A., Begent R. H., Bagshawe K. D., Riggs S. J., Searle F., Glaser M. G., Green A. J., Dale R. G. Repeated antitumour antibody therapy in man with suppression of the host response by cyclosporin A. Br J Cancer. 1988 Nov;58(5):654–657. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1988.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. S., Bullard D. E., Zalutsky M. R., Coleman R. E., Wikstrand C. J., Friedman H. S., Colapinto E. V., Bigner D. D. Therapeutic efficacy of antiglioma mesenchymal extracellular matrix 131I-radiolabeled murine monoclonal antibody in a human glioma xenograft model. Cancer Res. 1988 Feb 1;48(3):559–566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leichner P. K., Klein J. L., Fishman E. K., Siegelman S. S., Ettinger D. S., Order S. E. Comparative tumor dose from 131I-labeled polyclonal anti-ferritin, anti-AFP, and anti-CEA in primary liver cancers. Cancer Drug Deliv. 1984 Fall;1(4):321–328. doi: 10.1089/cdd.1984.1.321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leichner P. K., Klein J. L., Garrison J. B., Jenkins R. E., Nickoloff E. L., Ettinger D. S., Order S. E. Dosimetry of 131I-labeled anti-ferritin in hepatoma: a model for radioimmunoglobulin dosimetry. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1981 Mar;7(3):323–333. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(81)90105-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenhard R. E., Jr, Order S. E., Spunberg J. J., Asbell S. O., Leibel S. A. Isotopic immunoglobulin: a new systemic therapy for advanced Hodgkin's disease. J Clin Oncol. 1985 Oct;3(10):1296–1300. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1985.3.10.1296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mach J. P., Carrel S., Forni M., Ritschard J., Donath A., Alberto P. Tumor localization of radiolabeled antibodies against carcinoembryonic antigen in patients with carcinoma: a critical evaluation. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jul 3;303(1):5–10. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198007033030102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Order S. E., Stillwagon G. B., Klein J. L., Leichner P. K., Siegelman S. S., Fishman E. K., Ettinger D. S., Haulk T., Kopher K., Finney K. Iodine 131 antiferritin, a new treatment modality in hepatoma: a Radiation Therapy Oncology Group study. J Clin Oncol. 1985 Dec;3(12):1573–1582. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1985.3.12.1573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raso V. Antibody mediated delivery of toxic molecules to antigen bearing target cells. Immunol Rev. 1982;62:93–117. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00391.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen S. T., Zimmer A. M., Goldman-Leikin R., Gordon L. I., Kazikiewicz J. M., Kaplan E. H., Variakojis D., Marder R. J., Dykewicz M. S., Piergies A. Radioimmunodetection and radioimmunotherapy of cutaneous T cell lymphomas using an 131I-labeled monoclonal antibody: an Illinois Cancer Council Study. J Clin Oncol. 1987 Apr;5(4):562–573. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1987.5.4.562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharkey R. M., Pykett M. J., Siegel J. A., Alger E. A., Primus F. J., Goldenberg D. M. Radioimmunotherapy of the GW-39 human colonic tumor xenograft with 131I-labeled murine monoclonal antibody to carcinoembryonic antigen. Cancer Res. 1987 Nov 1;47(21):5672–5677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas S. R., Maxon H. R., Kereiakes J. G. In vivo quantitation of lesion radioactivity using external counting methods. Med Phys. 1976 Jul-Aug;03(04):253–255. doi: 10.1118/1.594287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakabayashi S., Okamoto S., Taniguchi M. Anti-tumor effects of radiolabeled syngeneic monoclonal anti-melanoma antibodies. Gan. 1984 Aug;75(8):707–713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalcberg J. R., Thompson C. H., Lichtenstein M., McKenzie I. F. Tumor immunotherapy in the mouse with the use of 131I-labeled monoclonal antibodies. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1984 Mar;72(3):697–704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]