Abstract
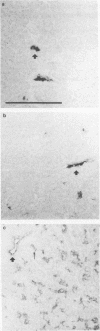
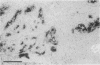
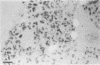
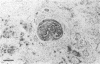
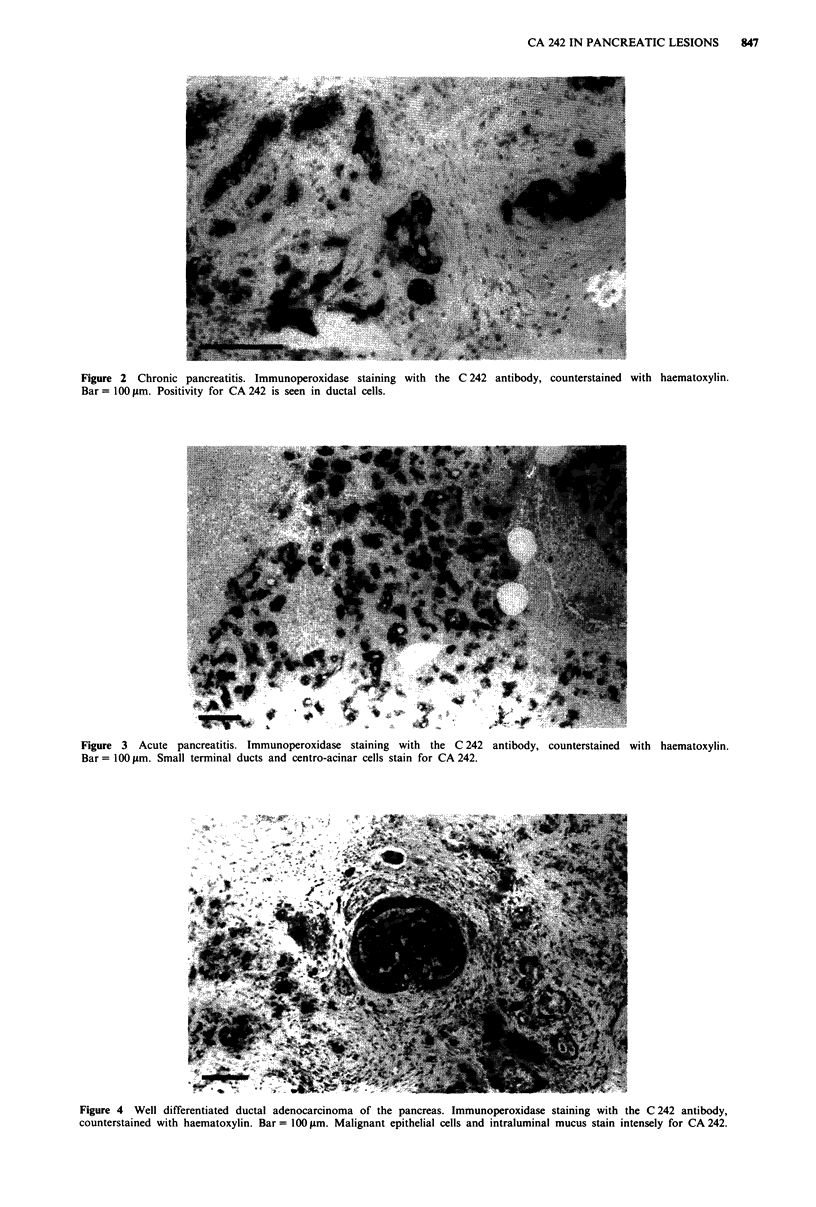
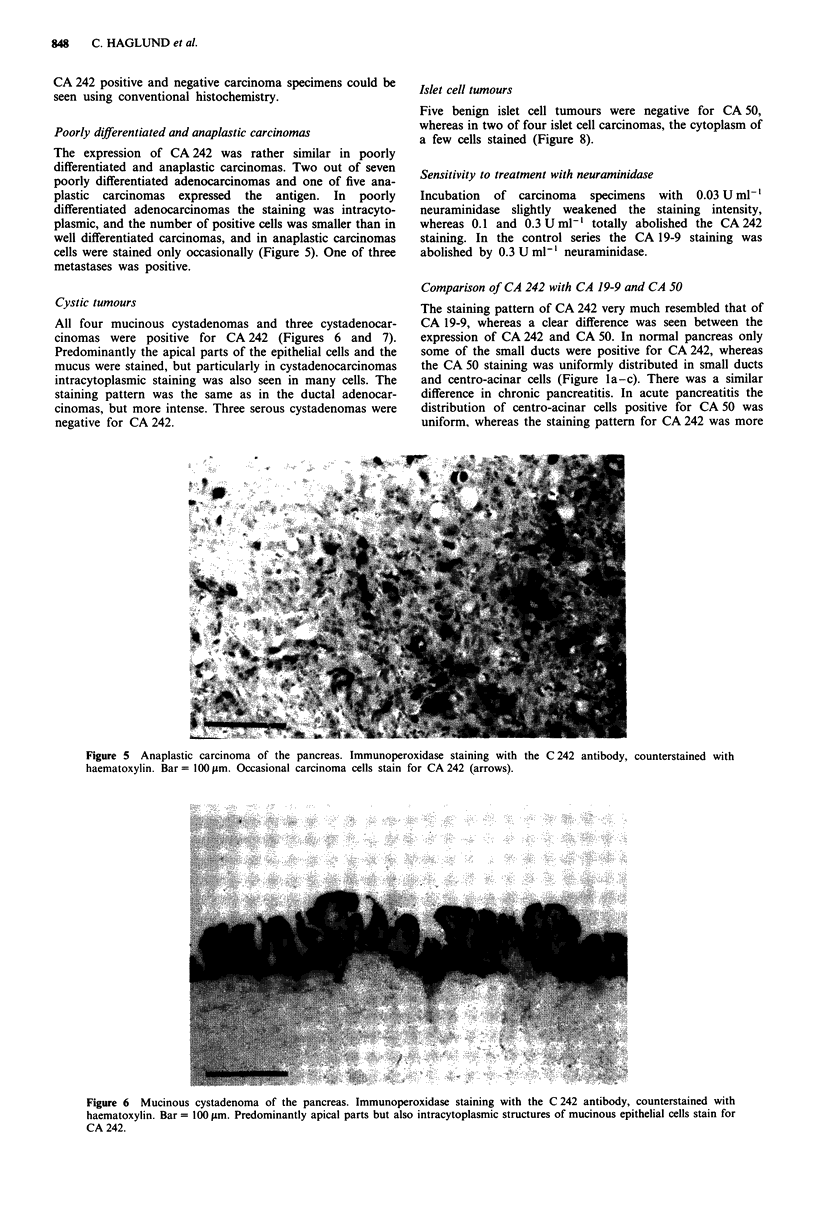
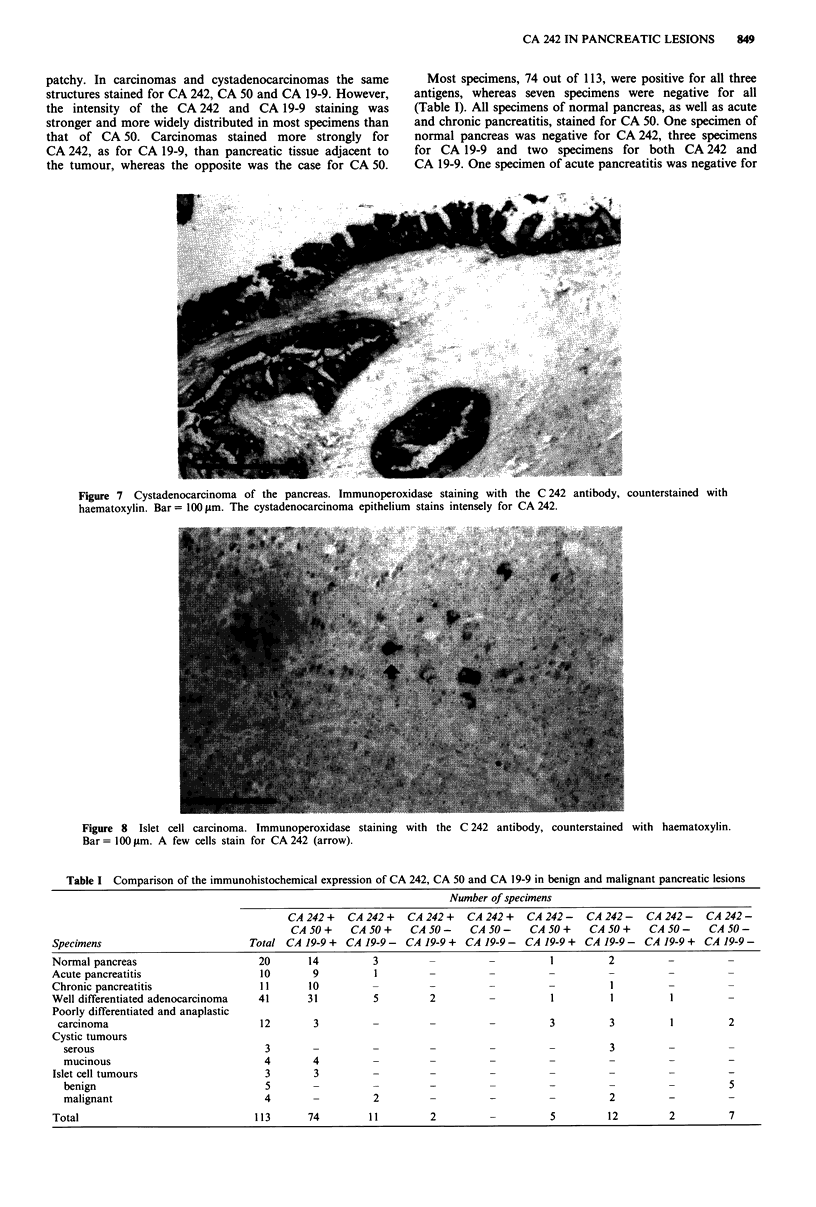
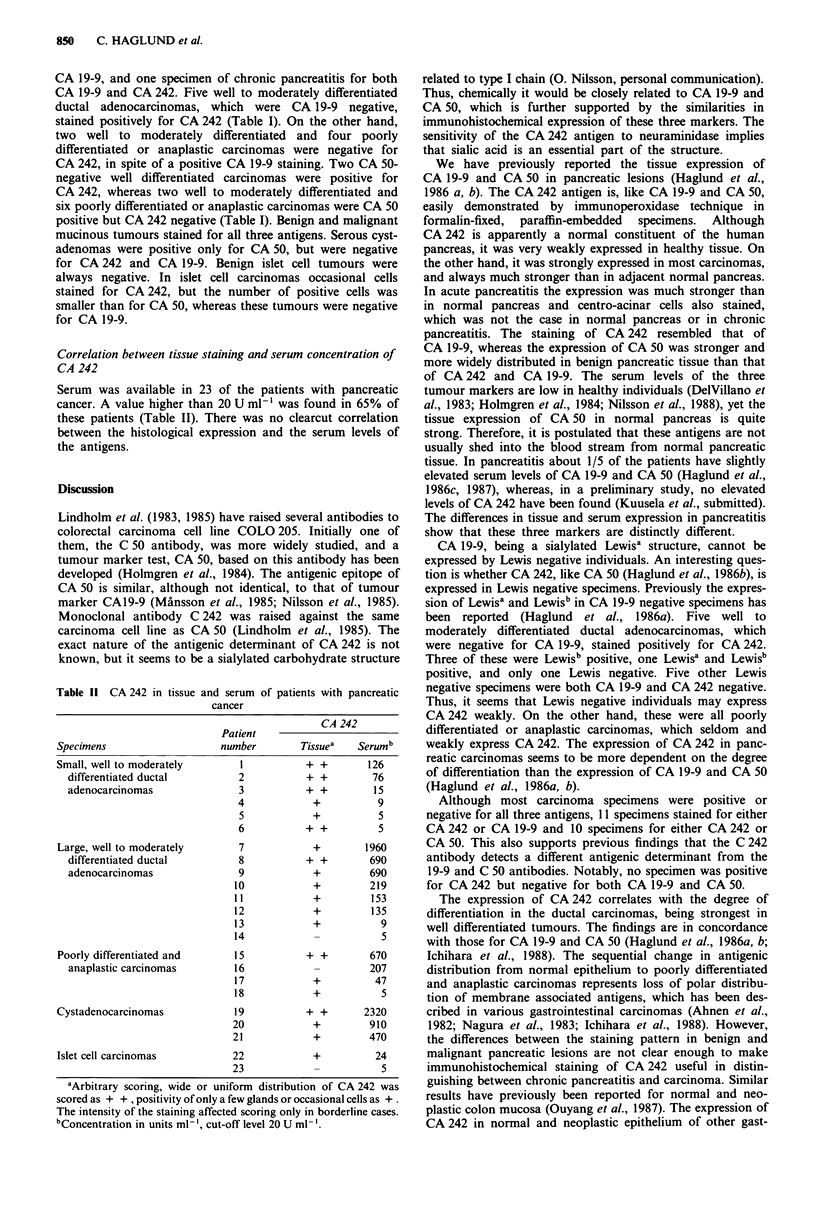
The expression of a novel tumour associated antigen CA 242, defined by the monoclonal antibody C 242, was studied by immunoperoxidase staining in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue sections from normal pancreata, pancreata with pancreatitis and benign and malignant pancreatic neoplasms. The antigenic determinant of the C 242 antibody is a sialylated carbohydrate structure, related but chemically different from tumour marker antigens CA 19-9 and CA 50. Thirty-eight of 41 (93%) well to moderately differentiated ductal adenocarcinomas of the pancreas and all cystadenocarcinomas were positive for CA 242. The staining was most intense in the apical border of the cells, and in the intraluminal mucus. Only two out of seven poorly differentiated adenocarcinomas stained, and the number of positive cells was smaller than in well differentiated carcinomas. Only occasional cells were stained in one out of five anaplastic carcinomas. Part of large ducts were positive in 91% (21/23) specimens of chronic pancreatitis. In acute pancreatitis small terminal ducts, centro-acinar cells and some large ducts stained for CA 242. In normal pancreas only a few small terminal ducts were CA 242 positive. Carcinomas always stained more strongly for CA 242 than normal pancreatic tissue adjacent to the carcinoma. The results of CA 242 are compared with those of tumour marker antigens CA 50 and CA 19-9. Serum CA 242 levels were determined in 23 of the patients with pancreatic cancer using a fluoroimmunoassay. Fifteen (65%) patients had an elevated value. There was no clear-cut correlation between the serum levels and the immunohistochemical expression of the CA 242 antigen. The expression of CA 242 in pancreatic tissue resembles that of CA 50 and is similar to CA 19-9. The antigen is expressed in serum of many patients with pancreatic cancer and, therefore, is a potential candidate for a serum tumour marker.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahnen D. J., Nakane P. K., Brown W. R. Ultrastructural localization of carcinoembryonic antigen in normal intestine and colon cancer: abnormal distribution of CEA on the surfaces of colon cancer cells. Cancer. 1982 May 15;49(10):2077–2090. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19820515)49:10<2077::aid-cncr2820491020>3.0.co;2-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Villano B. C., Brennan S., Brock P., Bucher C., Liu V., McClure M., Rake B., Space S., Westrick B., Schoemaker H. Radioimmunometric assay for a monoclonal antibody-defined tumor marker, CA 19-9. Clin Chem. 1983 Mar;29(3):549–552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haglund C., Kuusela P., Jalanko H., Roberts P. J. Serum CA 50 as a tumor marker in pancreatic cancer: a comparison with CA 19-9. Int J Cancer. 1987 Apr 15;39(4):477–481. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910390412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haglund C., Lindgren J., Roberts P. J., Nordling S. Gastrointestinal cancer-associated antigen CA 19-9 in histological specimens of pancreatic tumours and pancreatitis. Br J Cancer. 1986 Feb;53(2):189–195. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1986.34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haglund C., Lindgren J., Roberts P. J., Nordling S. Tissue expression of the tumor marker CA 50 in benign and malignant pancreatic lesions. A comparison with CA 19-9. Int J Cancer. 1986 Dec 15;38(6):841–846. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910380610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haglund C., Roberts P. J., Kuusela P., Scheinin T. M., Mäkelä O., Jalanko H. Evaluation of CA 19-9 as a serum tumour marker in pancreatic cancer. Br J Cancer. 1986 Feb;53(2):197–202. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1986.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Lindholm L., Persson B., Lagergård T., Nilsson O., Svennerholm L., Rudenstam C. M., Unsgaard B., Yngvason F., Pettersson S. Detection by monoclonal antibody of carbohydrate antigen CA 50 in serum of patients with carcinoma. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 May 19;288(6429):1479–1482. doi: 10.1136/bmj.288.6429.1479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichihara T., Nagura H., Nakao A., Sakamoto J., Watanabe T., Takagi H. Immunohistochemical localization of CA 19-9 and CEA in pancreatic carcinoma and associated diseases. Cancer. 1988 Jan 15;61(2):324–333. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19880115)61:2<324::aid-cncr2820610223>3.0.co;2-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalanko H., Kuusela P., Roberts P., Sipponen P., Haglund C. A., Mäkelä O. Comparison of a new tumour marker, CA 19-9, with alpha-fetoprotein and carcinoembryonic antigen in patients with upper gastrointestinal diseases. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Feb;37(2):218–222. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.2.218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koprowski H., Steplewski Z., Mitchell K., Herlyn M., Herlyn D., Fuhrer P. Colorectal carcinoma antigens detected by hybridoma antibodies. Somatic Cell Genet. 1979 Nov;5(6):957–971. doi: 10.1007/BF01542654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusela P., Haglund C., Roberts P. J., Jalanko H. Comparison of CA-50, a new tumour marker, with carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) in patients with gastrointestinal diseases. Br J Cancer. 1987 Jun;55(6):673–676. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1987.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindholm L., Holmgren J., Svennerholm L., Fredman P., Nilsson O., Persson B., Myrvold H., Lagergård T. Monoclonal antibodies against gastrointestinal tumour-associated antigens isolated as monosialogangliosides. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1983;71(2):178–181. doi: 10.1159/000233384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnani J. L., Nilsson B., Brockhaus M., Zopf D., Steplewski Z., Koprowski H., Ginsburg V. A monoclonal antibody-defined antigen associated with gastrointestinal cancer is a ganglioside containing sialylated lacto-N-fucopentaose II. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14365–14369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Månsson J. E., Fredman P., Nilsson O., Lindholm L., Holmgren J., Svennerholm L. Chemical structure of carcinoma ganglioside antigens defined by monoclonal antibody C-50 and some allied gangliosides of human pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Mar 27;834(1):110–117. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(85)90182-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagura H., Tsutsumi Y., Shioda Y., Watanabe K. Immunohistochemistry of gastric carcinomas and associated diseases: novel distribution of carcinoembryonic antigen and secretory component on the surface of gastric cancer cells. J Histochem Cytochem. 1983 Jan;31(1A):193–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson O., Månsson J. E., Lindholm L., Holmgren J., Svennerholm L. Sialosyllactotetraosylceramide, a novel ganglioside antigen detected in human carcinomas by a monoclonal antibody. FEBS Lett. 1985 Mar 25;182(2):398–402. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80341-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishida K., Miyagawa H., Yoshikawa T., Kondo M. Concentration and localization of carbohydrate antigen 19-9 in tissues of pancreatic cancer. Oncology. 1988;45(3):166–171. doi: 10.1159/000226556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang Q., Vilien M., Juhl B. R., Larsen L. G., Binder V. CEA and carbohydrate antigens in normal and neoplastic colon mucosa. An immunohistochemical study. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand A. 1987 Jul;95(4):177–183. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1987.tb00028_95a.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritts R. E., Jr, Del Villano B. C., Go V. L., Herberman R. B., Klug T. L., Zurawski V. R., Jr Initial clinical evaluation of an immunoradiometric assay for CA 19-9 using the NCI serum bank. Int J Cancer. 1984 Mar 15;33(3):339–345. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910330310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]