Abstract
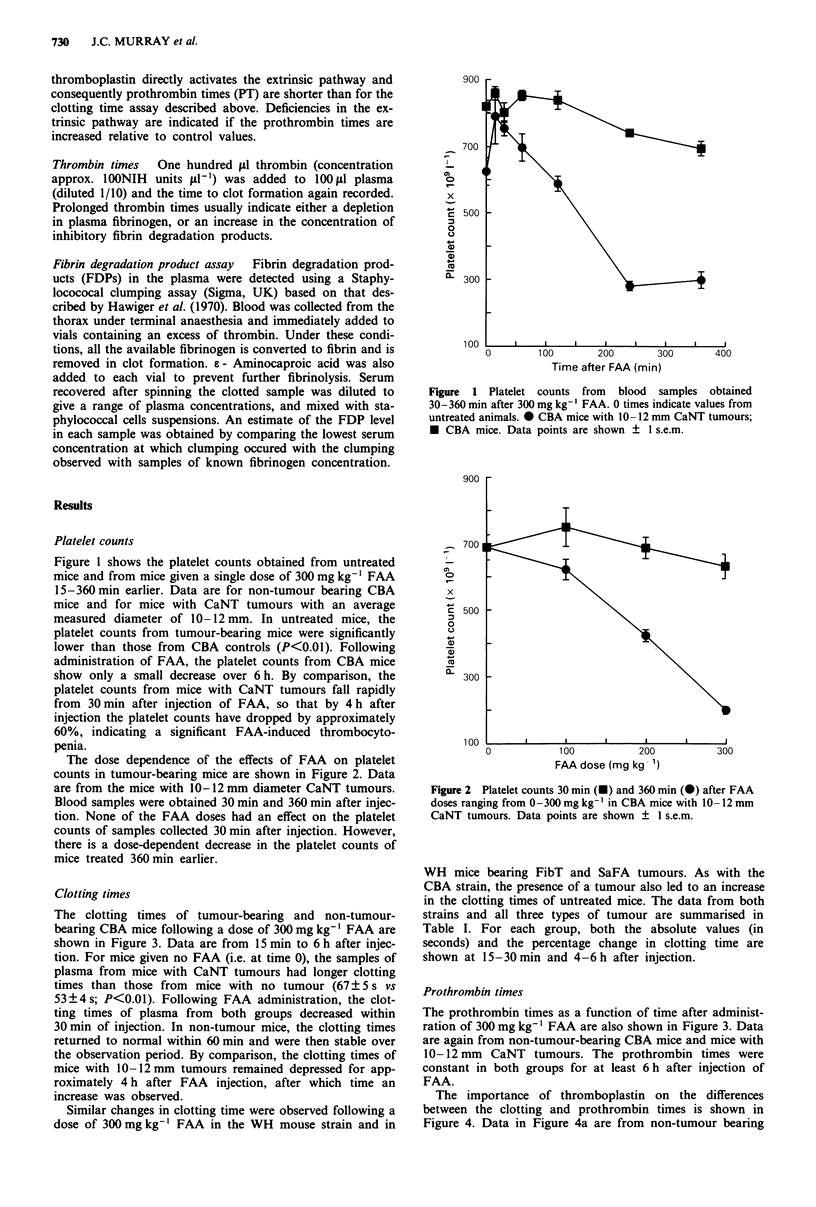
The effects of flavone acetic acid (FAA) on the coagulation properties of plasma from tumour-bearing and non-tumour-bearing mice have been investigated. The study was carried out primarily on CBA mice and the CaNT tumour, although substantiating data are included for two other tumours grown in the WH strain. FAA was injected at a range of single doses up to a maximum of 300 mg kg-1, and clotting properties of the plasma were measured in vitro at various times after FAA administration. Platelet numbers and the concentration of fibrin degradation products (FDP) in the plasma were also determined. Following a dose of 300 mg kg-1, the clotting times were significantly reduced at 15-30 min in both tumour-bearing and non-tumour-bearing mice of both strains. Detailed studies on coagulation in the CBA strain (+/- CaNT tumour) indicate that in tumour-bearing animals the initial decrease in clotting time is followed 4-6 h later by an increase in clotting time, thrombin time and FDP levels. Platelet counts of tumour-bearing mice also decreased significantly over this period. Similar experiments in non-tumour-bearing mice did not show these late effects. All the data from the coagulation tests on mice with CaNT tumours are consistent with the hypothesis that intravascular coagulation occurs following treatment with FAA, and that vascular occlusion in tumours, as a results of FAA-induced coagulopathy, may contribute to tumour regression.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bibby M. C., Double J. A., Loadman P. M., Duke C. V. Reduction of tumor blood flow by flavone acetic acid: a possible component of therapy. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1989 Feb 1;81(3):216–220. doi: 10.1093/jnci/81.3.216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibby M. C., Double J. A., Phillips R. M., Loadman P. M. Factors involved in the anti-cancer activity of the investigational agents LM985 (flavone acetic acid ester) and LM975 (flavone acetic acid). Br J Cancer. 1987 Feb;55(2):159–163. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1987.32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capolongo L. S., Balconi G., Ubezio P., Giavazzi R., Taraboletti G., Regonesi A., Yoder O. C., D'Incalci M. Antiproliferative properties of flavone acetic acid (NSC 347512) (LM 975), a new anticancer agent. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1987 Oct;23(10):1529–1535. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(87)90096-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Double J. A., Bibby M. C., Loadman P. M. Pharmacokinetics and anti-tumour activity of LM985 in mice bearing transplantable adenocarcinomas of the colon. Br J Cancer. 1986 Oct;54(4):595–600. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1986.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay G. J., Smith G. P., Fray L. M., Baguley B. C. Effect of flavone acetic acid on Lewis lung carcinoma: evidence for an indirect effect. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1988 Apr 20;80(4):241–245. doi: 10.1093/jnci/80.4.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawiger J., Niewiarowski S., Gurewich V., Thomas D. P. Measurement of fibrinogen and fibrin degradation products in serum by staphylococcal clumping test. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Jan;75(1):93–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawroth P., Handley D., Matsueda G., De Waal R., Gerlach H., Blohm D., Stern D. Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin-induced intravascular fibrin formation in meth A fibrosarcomas. J Exp Med. 1988 Aug 1;168(2):637–647. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.2.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old L. J. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF). Science. 1985 Nov 8;230(4726):630–632. doi: 10.1126/science.2413547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parr I., Wheeler E., Alexander P. Similarities of the anti-tumour actions of endotoxin, lipid A and double-stranded RNA. Br J Cancer. 1973 May;27(5):370–389. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1973.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin J., Ames M. M., Schutt A. J., Nichols W. L., Bowie E. J., Kovach J. S. Flavone-8-acetic acid inhibits ristocetin-induced platelet agglutination and prolongs bleeding time. Lancet. 1987 Nov 7;2(8567):1081–1082. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91501-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroyens W. A., Dodion P. F., Sanders C., Loos M., Dethier N. E., Delforge A. R., Stryckmans P. A., Kenis Y. In vitro chemosensitivity testing of flavone acetic acid (LM975; NSC 347512) and its diethylaminoethyl ester derivative (LM985; NSC 293015). Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1987 Aug;23(8):1135–1139. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(87)90146-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. P., Calveley S. B., Smith M. J., Baguley B. C. Flavone acetic acid (NSC 347512) induces haemorrhagic necrosis of mouse colon 26 and 38 tumours. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1987 Aug;23(8):1209–1211. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(87)90157-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A., Hill S. A., Begg A. C., Denekamp J. Validation of the fluorescent dye Hoechst 33342 as a vascular space marker in tumours. Br J Cancer. 1988 Mar;57(3):247–253. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1988.54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


