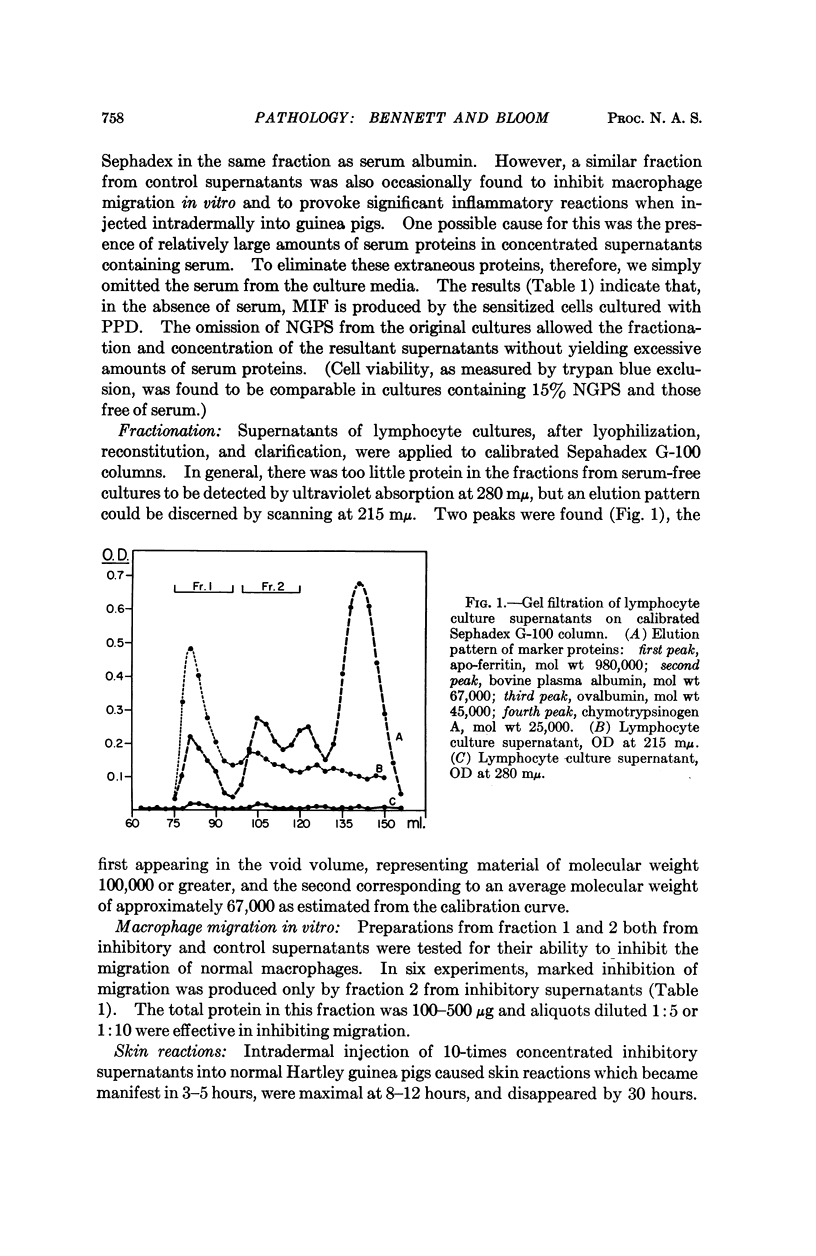
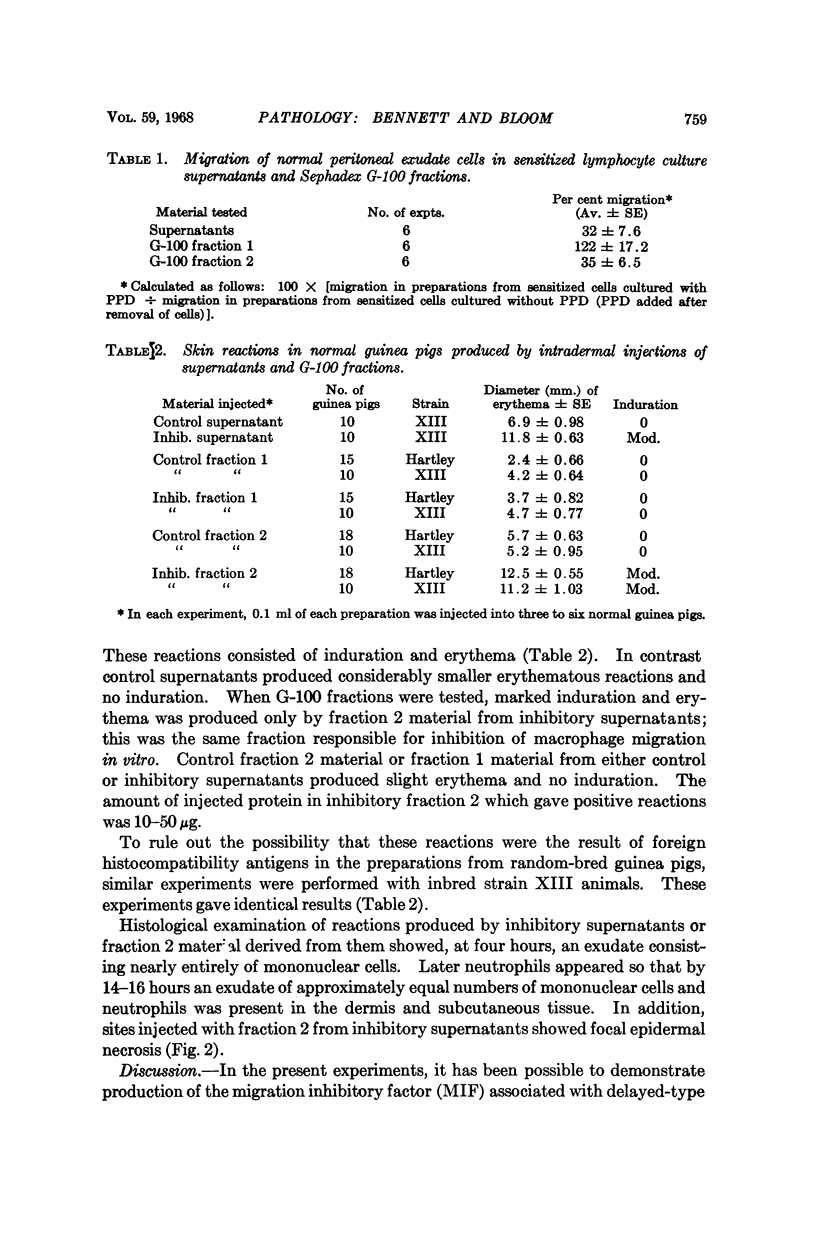
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett B., Bloom B. R. Studies on the migration inhibitory factor associated with delayed-type hypersensitivity: cytodynamics and specificity. Transplantation. 1967 Jul;5(4 Suppl):996–1000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom B. R., Bennett B. Mechanism of a reaction in vitro associated with delayed-type hypersensitivity. Science. 1966 Jul 1;153(3731):80–82. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3731.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom B. R., Bennett B. Migration inhibitory factor associated with delayed-type hypersensitivity. Fed Proc. 1968 Jan-Feb;27(1):13–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom B. R., Chase M. W. Transfer of delayed-type hypersensitivity. A critical review and experimental study in the guinea pig. Prog Allergy. 1967;10:151–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVID J. R., AL-ASKARI S., LAWRENCE H. S., THOMAS L. DELAYED HYPERSENSITIVITY IN VITRO. I. THE SPECIFICITY OF INHIBITION OF CELL MIGRATION BY ANTIGENS. J Immunol. 1964 Aug;93:264–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David J. R. Delayed hypersensitivity in vitro: its mediation by cell-free substances formed by lymphoid cell-antigen interaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jul;56(1):72–77. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.1.72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David J. R. Macrophage migration. Fed Proc. 1968 Jan-Feb;27(1):6–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David J. R. Suppression of delayed hypersensitivity in vitro by inhibition of protein synthesis. J Exp Med. 1965 Dec 1;122(6):1125–1134. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.6.1125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dienes L., Mallory T. B. Histological Studies of Hypersensitive Reactions. Am J Pathol. 1932 Nov;8(6):689–710.3. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEORGE M., VAUGHAN J. H. In vitro cell migration as a model for delayed hypersensitivity. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Nov;111:514–521. doi: 10.3181/00379727-111-27841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm G., Perlmann P. Cytotoxic potential of stimulated human lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1967 Apr 1;125(4):721–736. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.4.721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddle N. H., Waksman B. H. Cytotoxic effect of lymphocyte-antigen interaction in delayed hypersensitivity. Science. 1967 Sep 1;157(3792):1060–1062. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3792.1060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svejcar J., Johanovský J., Pekárek J. Studies on the mechanism of delayed type hypersensitivity in tissue culture. VII. An attempt to demonstrate the mediated action of antigen on cells from hypersensitive animals by means of simultaneous cultivation of two fragments in one chamber. Z Immunitatsforsch Allerg Klin Immunol. 1967 Feb;132(2):182–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]