Abstract
Determining the relative value of novel antipsychotics such as clozapine requires measures of the utility of their different side-effect profiles. Many of these side effects (SE) are complex and difficult to describe adequately. Schizophrenic patients are also difficult to interview reliably. Even in normal subjects, utility assessment can be tedious, inconsistent, and difficult for subjects to understand. We addressed these challenges by developing a multimedia patient education and utility assessment tool. SE were described using short video sequences accompanied by digitized voice descriptions. Patients' preferences were assessed using visual analog scales, pairwise comparisons, and standard gambles. These assessment techniques were carefully explained and logically integrated. Instructions were presented both by digitized voice and in print, and, if necessary, were clarified by a moderator. Animated displays were used to graphically display probability. Reminder pictures, comprehension tests and validation questions were used throughout the survey. Thirty-three patients from VA and public clinic inpatient and outpatient settings took the survey. Five psychiatrists were surveyed as a reference group. Patients understood the SE and the survey (92% mean comprehension) and their answers were internally valid and consistent (74% internal consistency). The standard gamble disutilities for the SE were substantial, ranging from 12-20% decrease in their quality of life. Computer-based, multimedia techniques are useful in conducting utility assessment and evaluating its validity. They allow effective patient education and elicitation of useful values, even in subjects with cognitive impairments.
Full text
PDF
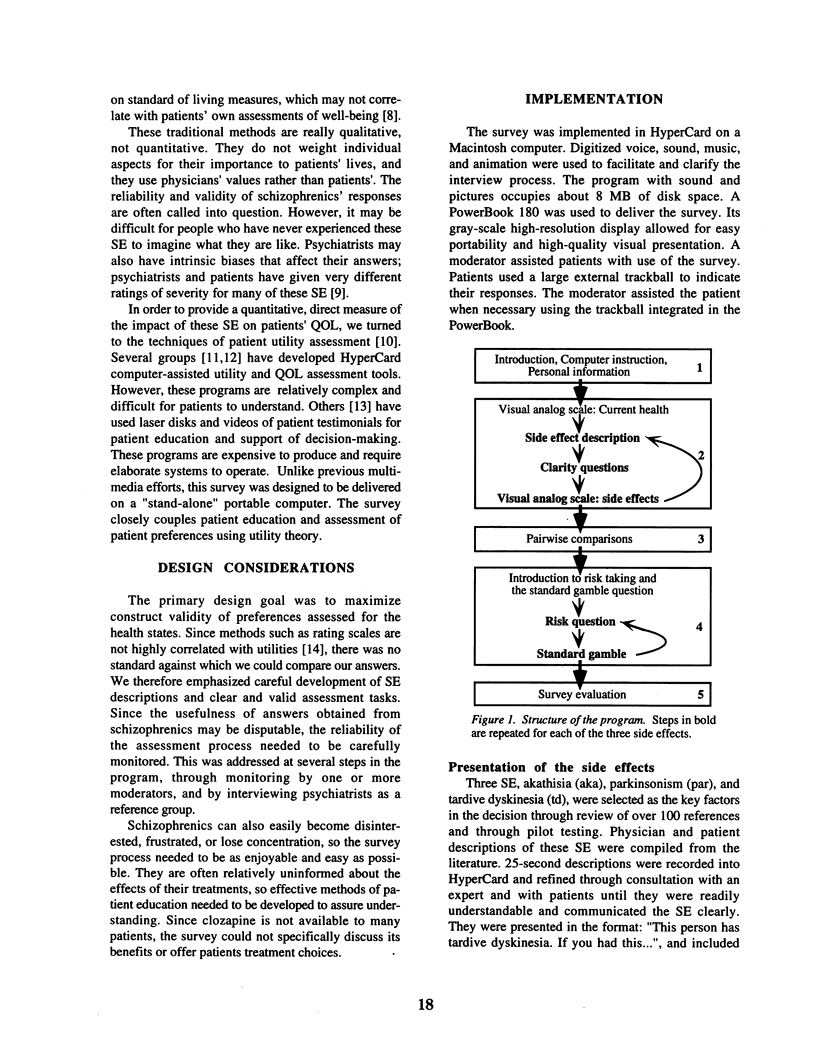
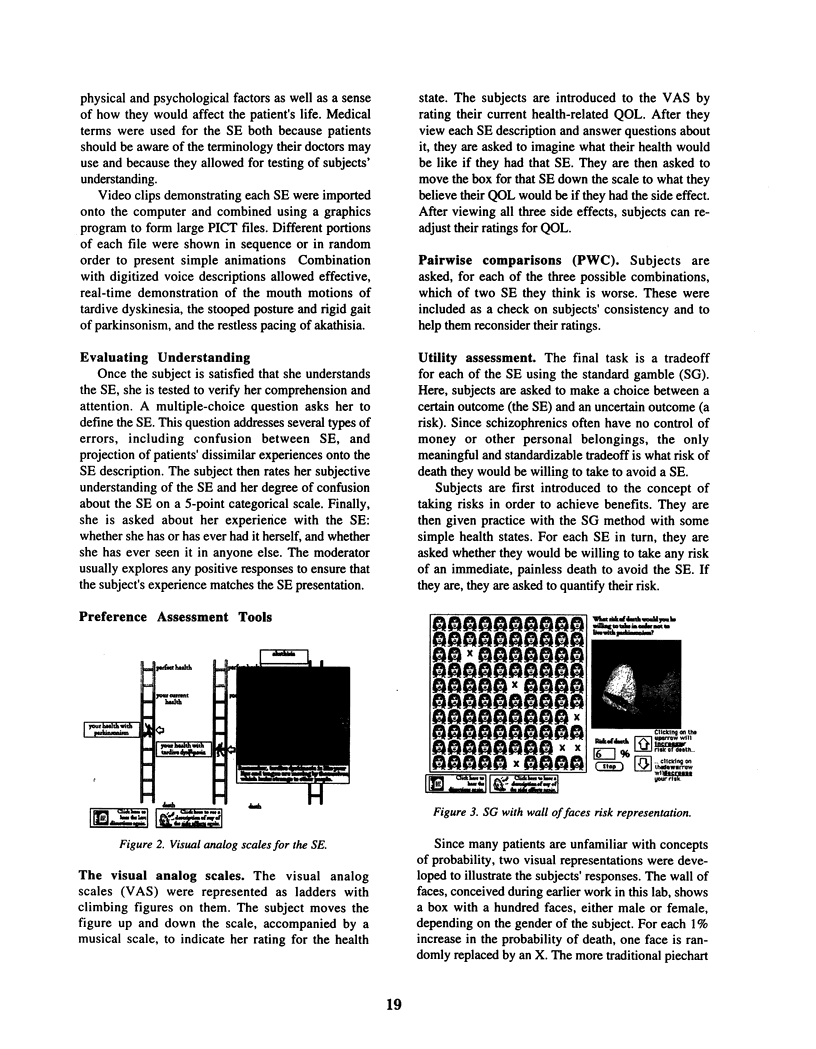


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes T. R. A rating scale for drug-induced akathisia. Br J Psychiatry. 1989 May;154:672–676. doi: 10.1192/bjp.154.5.672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finn S. E., Bailey J. M., Schultz R. T., Faber R. Subjective utility ratings of neuroleptics in treating schizophrenia. Psychol Med. 1990 Nov;20(4):843–848. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700036539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrichs D. W., Hanlon T. E., Carpenter W. T., Jr The Quality of Life Scale: an instrument for rating the schizophrenic deficit syndrome. Schizophr Bull. 1984;10(3):388–398. doi: 10.1093/schbul/10.3.388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornberger J. C., Redelmeier D. A., Petersen J. Variability among methods to assess patients' well-being and consequent effect on a cost-effectiveness analysis. J Clin Epidemiol. 1992 May;45(5):505–512. doi: 10.1016/0895-4356(92)90099-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaeger J., Bitter I., Czobor P., Volavka J. The measurement of subjective experience in schizophrenia: the Subjective Deficit Syndrome Scale. Compr Psychiatry. 1990 May-Jun;31(3):216–226. doi: 10.1016/0010-440x(90)90005-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer H. Y., Burnett S., Bastani B., Ramirez L. F. Effects of six months of clozapine treatment on the quality of life of chronic schizophrenic patients. Hosp Community Psychiatry. 1990 Aug;41(8):892–897. doi: 10.1176/ps.41.8.892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer H. Y. Dimensions of outcome with clozapine. Br J Psychiatry Suppl. 1992 May;(17):46–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson G. M., Angus J. W. A rating scale for extrapyramidal side effects. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl. 1970;212:11–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1970.tb02066.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skantze K., Malm U., Dencker S. J., May P. R., Corrigan P. Comparison of quality of life with standard of living in schizophrenic out-patients. Br J Psychiatry. 1992 Dec;161:797–801. doi: 10.1192/bjp.161.6.797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner W., Nease R., Littenberg B. U-titer: a utility assessment tool. Proc Annu Symp Comput Appl Med Care. 1991:701–705. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torrance G. W. Utility approach to measuring health-related quality of life. J Chronic Dis. 1987;40(6):593–603. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(87)90019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


