Abstract
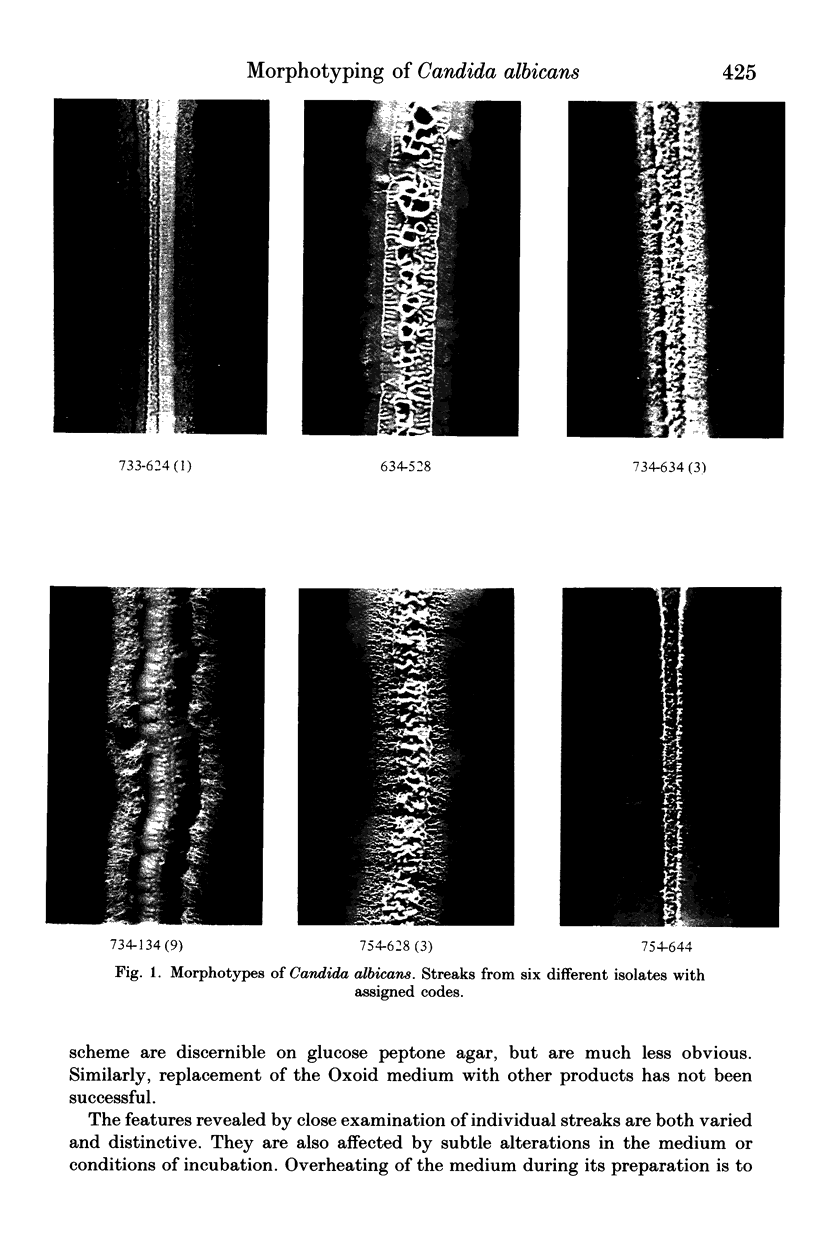
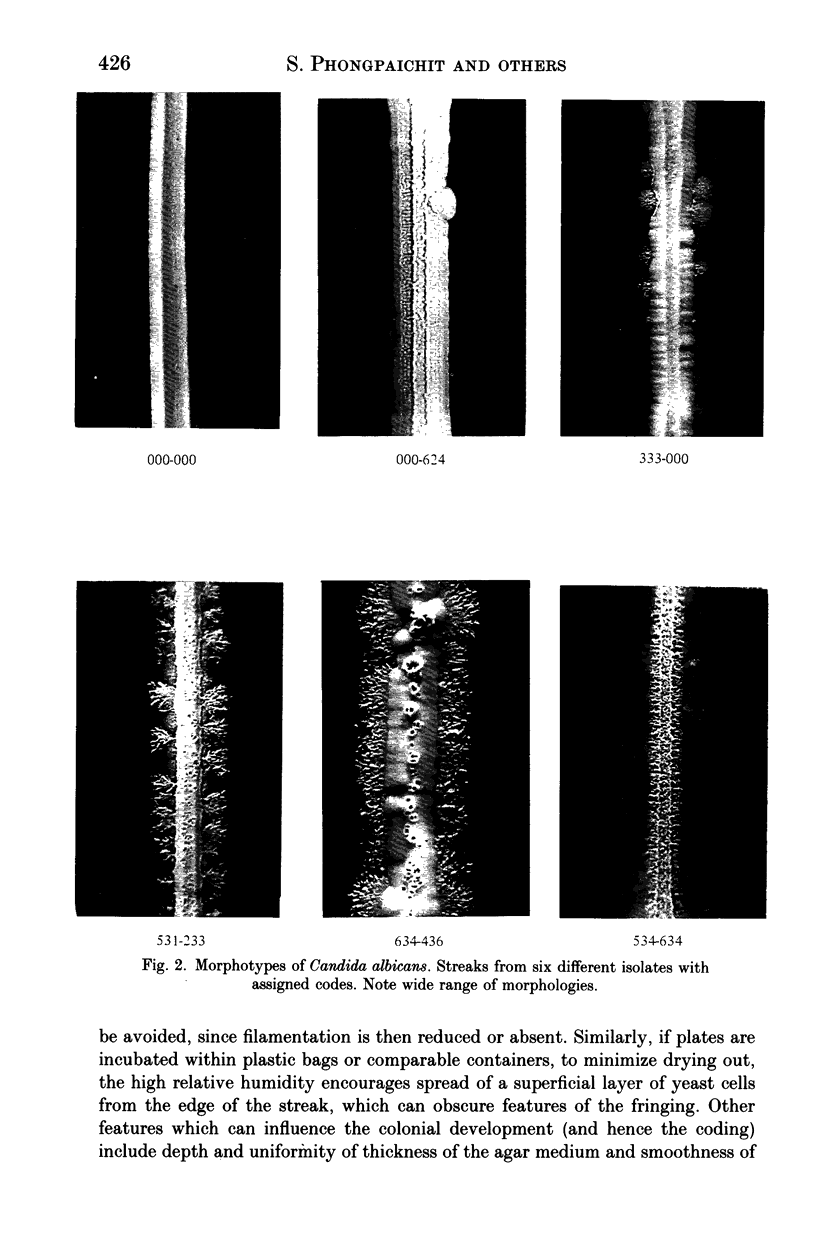
Strains of Candida albicans can be differentiated by the morphological features of streak colonies developed on malt agar. A morphotyping system is proposed, where numerical codes are assigned primarily on the basis of the nature and extent of marginal fringing and the surface topography of the streak colony. The system allows ready differentiation to be made of morphotypes, requires no specialized equipment or expertise and provides a simple and reproducible means for epidemiological studies of candida and candidosis.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- HASENCLEVER H. F., MITCHELL W. O. Antigenic studies of Candida. I. Observation of two antigenic groups in Candida albicans. J Bacteriol. 1961 Oct;82:570–573. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.4.570-573.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Burnie J., Matthews R. Fingerprinting Candida albicans. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Nov 6;93(2):177–182. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90186-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCreight M. C., Warnock D. W. Enhanced differentiation of isolates of Candida albicans using a modified resistogram method. Mykosen. 1982 Nov;25(11):589–598. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0507.1982.tb01926.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor M. I., Sobel J. D. Epidemiology of recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis: identification and strain differentiation of Candida albicans. J Infect Dis. 1986 Aug;154(2):358–363. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.2.358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odds F. C., Abbott A. B. A simple system for the presumptive identification of Candida albicans and differentiation of strains within the species. Sabouraudia. 1980 Dec;18(4):301–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odds F. C., Abbott A. B., Stiller R. L., Scholer H. J., Polak A., Stevens D. A. Analysis of Candida albicans phenotypes from different geographical and anatomical sources. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Oct;18(4):849–857. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.4.849-857.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polonelli L., Archibusacci C., Sestito M., Morace G. Killer system: a simple method for differentiating Candida albicans strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 May;17(5):774–780. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.5.774-780.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Román M. C., Linares Sicilia M. J. Preliminary investigation of Candida albicans biovars. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;18(2):430–431. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.2.430-431.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STALLYBRASS F. C. THE INCIDENCE OF THE SEROLOGICAL GROUPS OF CANDIDA ALBICANS IN SOUTHERN ENGLAND. J Hyg (Lond) 1964 Sep;62:395–399. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400040110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slutsky B., Buffo J., Soll D. R. High-frequency switching of colony morphology in Candida albicans. Science. 1985 Nov 8;230(4726):666–669. doi: 10.1126/science.3901258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warnock D. W., Speller C. D., Milne J. D., Hilton A. L., Kershaw P. I. Epidemiological investigation of patients with vulvovaginal candidosis. Application of a resistogram method for strain differentiation of Candida albicans. Br J Vener Dis. 1979 Oct;55(5):357–361. doi: 10.1136/sti.55.5.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]