Abstract
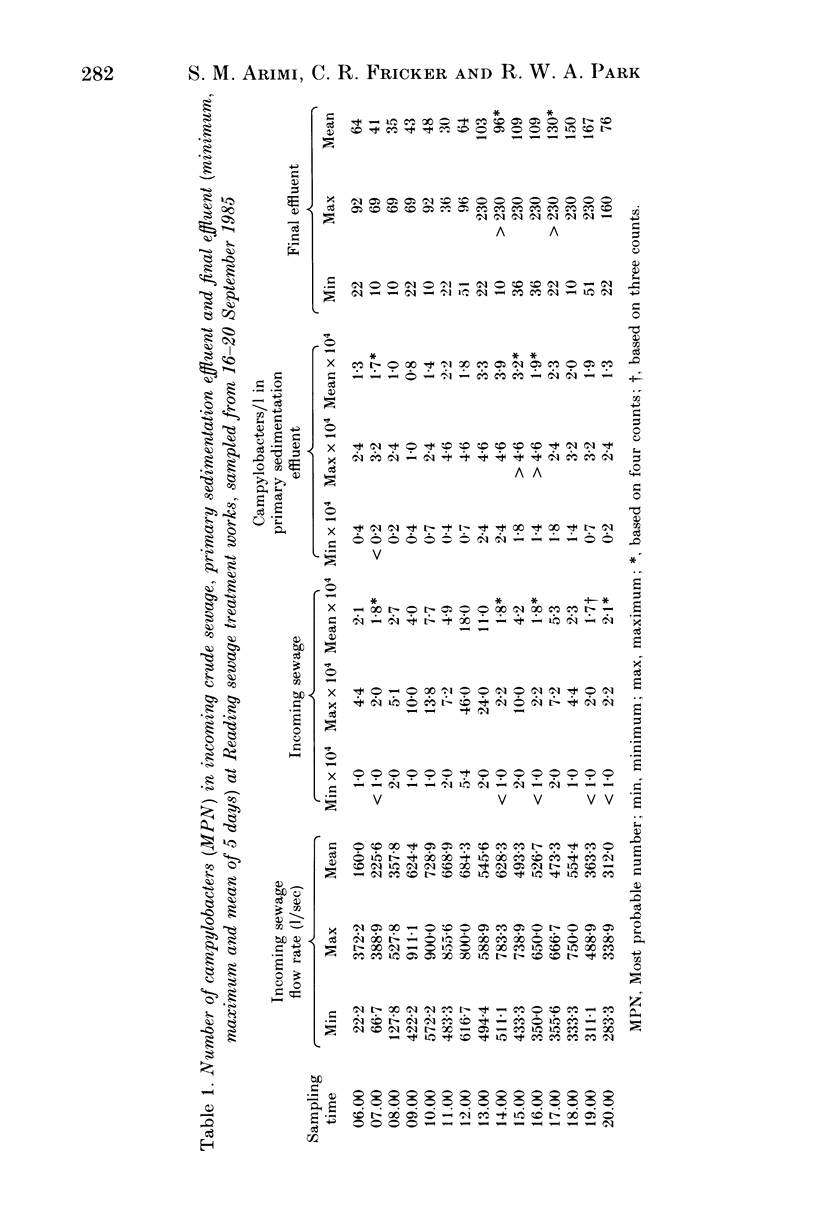
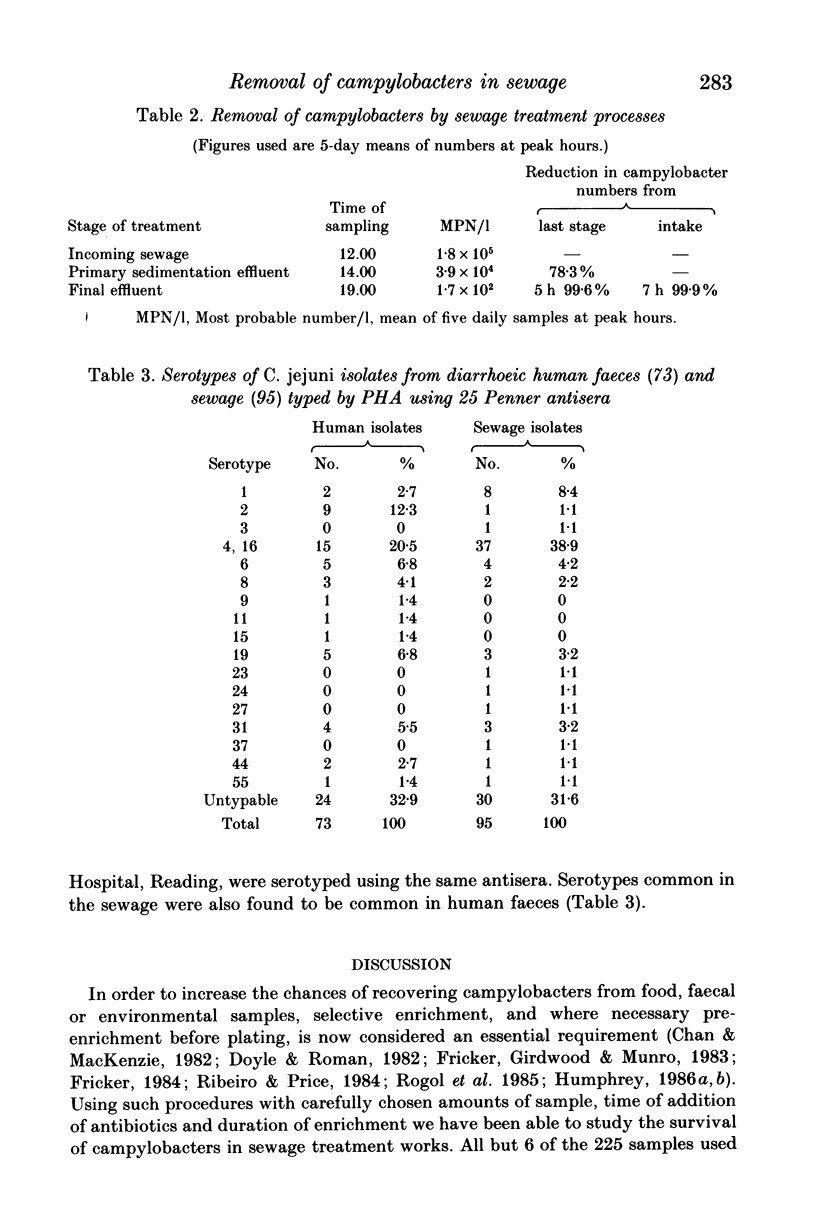
Removal of thermophilic campylobacters from sewage at three different stages of treatment at a trickling filter sewage works has been assessed. Samples of incoming sewage, primary sedimentation effluent and final effluent were taken daily from 06.00 h to 20.00 h for 5 consecutive days and the numbers of campylobacters determined by using a most probable number method. Each sample was cultured using 2 h pre-enrichment followed by enrichment in Preston broth for 48 h and detection by plating. Over 78% of the incoming campylobacters were removed after primary sedimentation and less than 0.1% remained in the final effluent. Campylobacter jejuni biotype I and biotype II constituted 81.5% and 15.9% respectively of the 232 isolates tested. Serotypes common in sewage were common in human faeces. It appears that the trickling filter sewage works removes most of the campylobacters entering the sewage works, but large numbers, estimated to be approximately 10(10), are released into the environment daily from a local sewage works.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barwick SW, Price PB, Stevenson JD. Radioactive decay of 232U by 24Ne emission. Phys Rev C Nucl Phys. 1985 May;31(5):1984–1986. doi: 10.1103/physrevc.31.1984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Glass R. I., Huq M. I., Stoll B., Kibriya G. M., Alim A. R. Isolation of Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni from Bangladeshi children. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Dec;12(6):744–747. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.6.744-747.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton F. J., Hinchliffe P. M., Coates D., Robertson L. A most probable number method for estimating small numbers of campylobacters in water. J Hyg (Lond) 1982 Oct;89(2):185–190. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400070716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brouwer R., Mertens M. J., Siem T. H., Katchaki J. An explosive outbreak of Campylobacter enteritis in soldiers. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1979;45(3):517–519. doi: 10.1007/BF00443293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butzler J. P., Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis. Clin Gastroenterol. 1979 Sep;8(3):737–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan F. T., Mackenzie A. M. Enrichment medium and control system for isolation of Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni from stools. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jan;15(1):12–15. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.1.12-15.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle M. P., Roman D. J. Recovery of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli from inoculated foods by selective enrichment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jun;43(6):1343–1353. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.6.1343-1353.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fricker C. R. A note on the effect of different storage procedures on the ability of Preston medium to recover campylobacters. J Appl Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;58(1):57–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1985.tb01429.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fricker C. R., Alemohammad M. M., Park R. W. A study of factors affecting the sensitivity of the passive haemagglutination method for serotyping Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli and recommendations for a more rapid procedure. Can J Microbiol. 1987 Jan;33(1):33–39. doi: 10.1139/m87-006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fricker C. R., Girdwood R. W., Munro D. A comparison of procedures for the isolation of campylobacters from seagull faeces. J Hyg (Lond) 1983 Dec;91(3):445–450. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400060484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fricker C. R., Metcalfe N. Campylobacters in wading birds (Charadrii): incidence, biotypes and isolation techniques. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg B. 1984 Oct;179(5):469–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George H. A., Hoffman P. S., Smibert R. M., Krieg N. R. Improved media for growth and aerotolerance of Campylobacter fetus. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Jul;8(1):36–41. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.1.36-41.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey S. M., Greenwood J. R. Probable Campylobacter fetus subsp. fetus gastroenteritis. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Nov;18(5):1278–1279. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.5.1278-1279.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey T. J., Cruickshank J. G. Antibiotic and deoxycholate resistance in Campylobacter jejuni following freezing or heating. J Appl Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;59(1):65–71. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1985.tb01777.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson D. N., Bolton F. J., Hinchliffe P. M., Dawkins H. C., Horsley S. D., Jessop E. G., Robertshaw P. A., Counter D. E. Evidence of udder excretion of Campylobacter jejuni as the cause of milk-borne campylobacter outbreak. J Hyg (Lond) 1985 Apr;94(2):205–215. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400061416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kampelmacher E. H., Noorle Jansen LM vnn Salmonella--its presence in and removal from a wastewater system. Dis Colon Rectum. 1970 Nov-Dec;13(6):2069–2073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein B. S., Vergeront J. M., Blaser M. J., Edmonds P., Brenner D. J., Janssen D., Davis J. P. Campylobacter infection associated with raw milk. An outbreak of gastroenteritis due to Campylobacter jejuni and thermotolerant Campylobacter fetus subsp fetus. JAMA. 1986 Jan 17;255(3):361–364. doi: 10.1001/jama.255.3.361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luechtefeld N. W., Cambre R. C., Wang W. L. Isolation of Campylobacter fetus subsp jejuni from zoo animals. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1981 Dec 1;179(11):1119–1122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mentzing L. O. Waterborne outbreaks of campylobacter enteritis in central Sweden. Lancet. 1981 Aug 15;2(8242):352–354. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90658-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer S. R., Gully P. R., White J. M., Pearson A. D., Suckling W. G., Jones D. M., Rawes J. C., Penner J. L. Water-borne outbreak of campylobacter gastroenteritis. Lancet. 1983 Feb 5;1(8319):287–290. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91698-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner J. L., Hennessy J. N. Passive hemagglutination technique for serotyping Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni on the basis of soluble heat-stable antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Dec;12(6):732–737. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.6.732-737.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro C. D., Price T. H. The use of Preston enrichment broth for the isolation of 'thermophilic' campylobacters from water. J Hyg (Lond) 1984 Feb;92(1):45–51. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400064019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson N. J., Koornhof H. J., Bokkenheuser V. D. Long-term infections with Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 May;13(5):846–849. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.5.846-849.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley L. W., Finch M. J. Results of the first year of national surveillance of Campylobacter infections in the United States. J Infect Dis. 1985 May;151(5):956–959. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.5.956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson D. A., Edgar W. J., Gibson G. L., Matchett A. A., Robertson L. Campylobacter enteritis associated with consumption of unpasteurised milk. Br Med J. 1979 May 5;1(6172):1171–1173. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6172.1171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson D. A. Infective dose of Campylobacter jejuni in milk. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 May 16;282(6276):1584–1584. doi: 10.1136/bmj.282.6276.1584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogol M., Shpak B., Rothman D., Sechter I. Enrichment medium for isolation of Campylobacter jejuni-Campylobacter coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jul;50(1):125–126. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.1.125-126.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollins D. M., Colwell R. R. Viable but nonculturable stage of Campylobacter jejuni and its role in survival in the natural aquatic environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Sep;52(3):531–538. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.3.531-538.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosef O., Gondrosen B., Kapperud G., Underdal B. Isolation and characterization of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli from domestic and wild mammals in Norway. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Oct;46(4):855–859. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.4.855-859.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simor A. E., Wilcox L. Enteritis associated with Campylobacter laridis. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jan;25(1):10–12. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.1.10-12.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis - the first five years. J Hyg (Lond) 1982 Oct;89(2):175–184. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400070704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele T. W., McDermott S. Campylobacter enteritis in South Australia. Med J Aust. 1978 Oct 21;2(9):404–406. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1978.tb76814.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Totten P. A., Fennell C. L., Tenover F. C., Wezenberg J. M., Perine P. L., Stamm W. E., Holmes K. K. Campylobacter cinaedi (sp. nov.) and Campylobacter fennelliae (sp. nov.): two new Campylobacter species associated with enteric disease in homosexual men. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jan;151(1):131–139. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.1.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterman S. C., Park R. W., Bramley A. J. A search for the source of Campylobacter jejuni in milk. J Hyg (Lond) 1984 Oct;93(2):333–337. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400064871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaziz M. I., Lloyd B. J. The removal of salmonellas in conventional sewage treatment processes. J Appl Bacteriol. 1979 Feb;46(1):131–142. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1979.tb02590.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


