Abstract
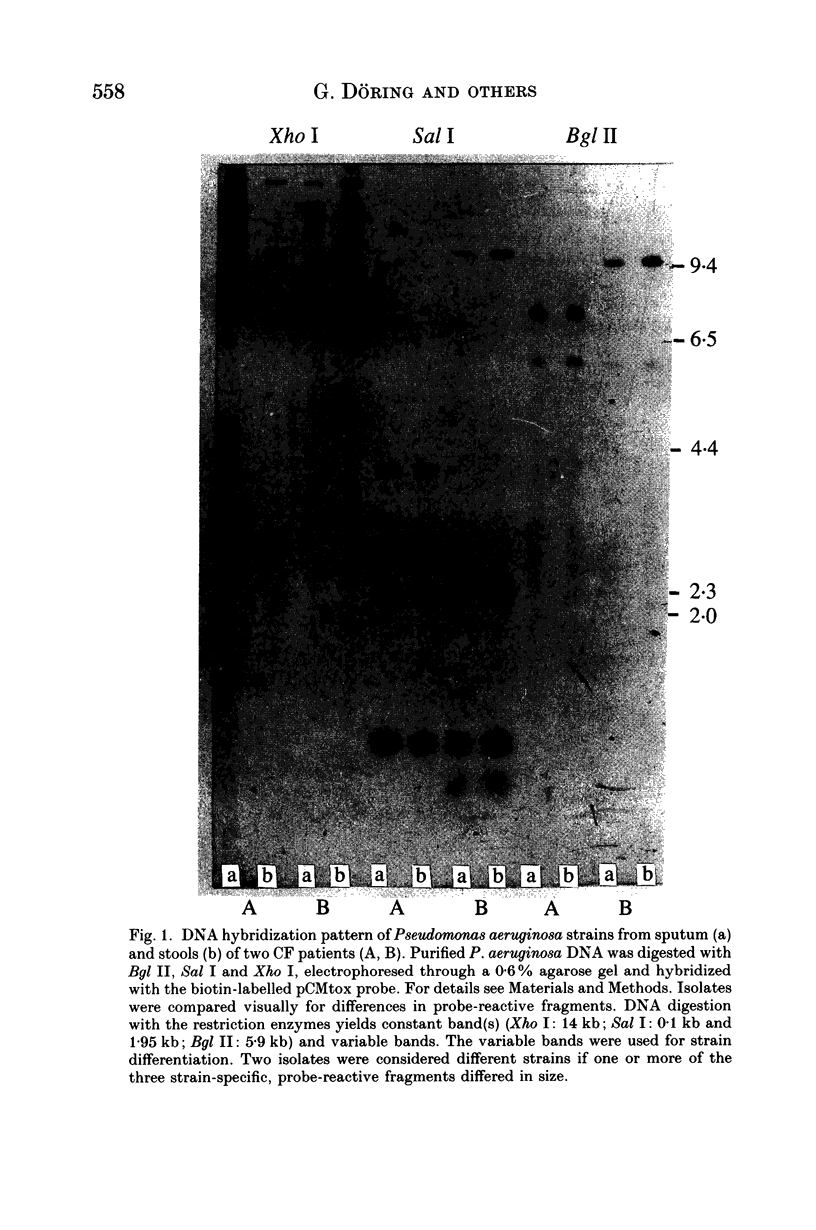
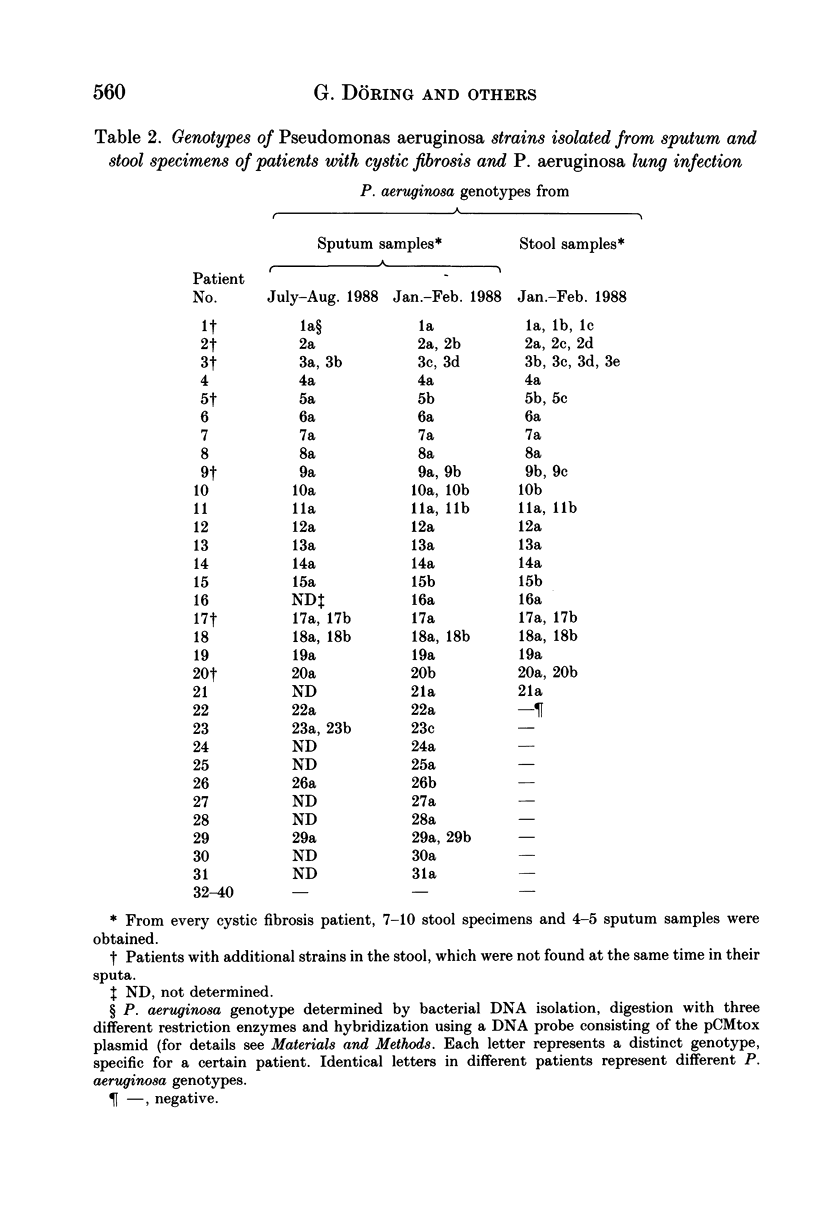
Three hundred and fifty-eight stool and 131 sputum specimens from 40 cystic fibrosis (CF) patients and 100 toilet sinks were investigated for occurrence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa; 67% (21/31) of the patients with chronic P. aeruginosa lung infections carried the organism repeatedly in the stool but the organism was found only once in the stools of nine uninfected patients. P. aeruginosa stool carriage was correlated to high P. aeruginosa numbers in patients' sputa. Typing of P. aeruginosa with a DNA probe showed identity of sputum and stool strains. Seven patients repeatedly carried additional stool strains, not found in the sputum, suggesting intestinal colonization. No differences were seen in the clinical state of patients with P. aeruginosa-negative stool samples and patients with positive stool samples. Toilets in households of P. aeruginosa-infected CF patients were significantly more often contaminated with P. aeruginosa (42%) than toilets in households of non-infected CF patients (20%; P less than 0.03). The study shows that P. aeruginosa-infected CF patients may harbour the organisms also in the intestinal tract, and may spread the bacteria into toilets.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agnarsson U., Glass S., Govan J. R. Fecal isolation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from patients with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jan;27(1):96–98. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.1.96-98.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce M. C., Poncz L., Klinger J. D., Stern R. C., Tomashefski J. F., Jr, Dearborn D. G. Biochemical and pathologic evidence for proteolytic destruction of lung connective tissue in cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Sep;132(3):529–535. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.3.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck A. C., Cooke E. M. The fate of ingested Pseudomonas aeruginosa in normal persons. J Med Microbiol. 1969 Nov 4;2(4):521–525. doi: 10.1099/00222615-2-4-521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DARLOW H. M., BALE W. R. Infective hazards of water-closets. Lancet. 1959 Jun 6;1(7084):1196–1200. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(59)91201-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerba C. P., Wallis C., Melnick J. L. Microbiological hazards of household toilets: droplet production and the fate of residual organisms. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Aug;30(2):229–237. doi: 10.1128/am.30.2.229-237.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentges D. J., Stein A. J., Casey S. W., Que J. U. Protective role of intestinal flora against infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in mice: influence of antibiotics on colonization resistance. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):118–122. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.118-122.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly N. M., Falkiner F. R., Keane C. T. Acetamide broth for isolation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from patients with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jan;17(1):159–159. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.1.159-.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessner D. M., Lepper M. H. Epidemiologic studies on gram-negative bacilli in the hospital and community. Am J Epidemiol. 1967 Jan;85(1):45–60. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINDE K., KITTLICK M. [On the demonstration of Bact. Pyocyaneum in human material for examination]. Arch Hyg Bakteriol. 1962 May;146:126–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lányi B., Gregács M., Adám M. M. Incidence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa serogroups in water and human faeces. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1966;13(4):319–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogle J. W., Janda J. M., Woods D. E., Vasil M. L. Characterization and use of a DNA probe as an epidemiological marker for Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jan;155(1):119–126. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.1.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington J. S., Schimpff S. C. Occasional notes. Please don't eat the salads. N Engl J Med. 1981 Feb 12;304(7):433–435. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198102123040730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy C. C., Delage G., Fontaine A., Robitaille L., Chartrand L., Weber A., Morin C. L. The fecal microflora and bile acids in children with cystic fibrosis. Am J Clin Nutr. 1979 Dec;32(12):2404–2409. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/32.12.2404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speert D. P., Campbell M. E. Hospital epidemiology of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from patients with cystic fibrosis. J Hosp Infect. 1987 Jan;9(1):11–21. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(87)90089-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tancrède C. H., Andremont A. O. Bacterial translocation and gram-negative bacteremia in patients with hematological malignancies. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jul;152(1):99–103. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.1.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGT D. Uber den gegenwärtigen Stand der Akzeleration in Bayern. Arch Kinderheilkd. 1959;159(2):141–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vander Wauven C., Piérard A., Kley-Raymann M., Haas D. Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutants affected in anaerobic growth on arginine: evidence for a four-gene cluster encoding the arginine deiminase pathway. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):928–934. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.928-934.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasil M. L., Chamberlain C., Grant C. C. Molecular studies of Pseudomonas exotoxin A gene. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):538–548. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.538-548.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolz C., Kiosz G., Ogle J. W., Vasil M. L., Schaad U., Botzenhart K., Döring G. Pseudomonas aeruginosa cross-colonization and persistence in patients with cystic fibrosis. Use of a DNA probe. Epidemiol Infect. 1989 Apr;102(2):205–214. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800029873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood R. E., Boat T. F., Doershuk C. F. Cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Jun;113(6):833–878. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.113.6.833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]