Full text
PDF


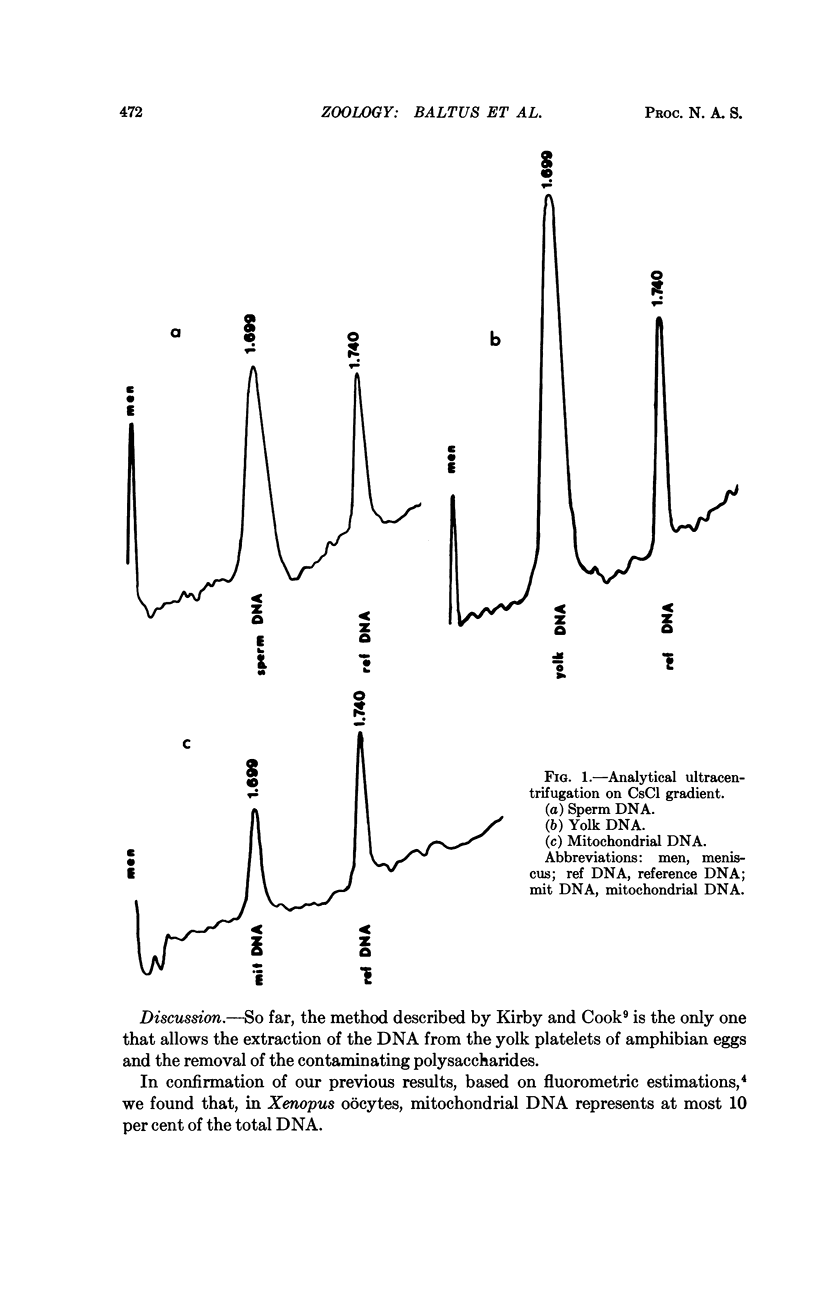
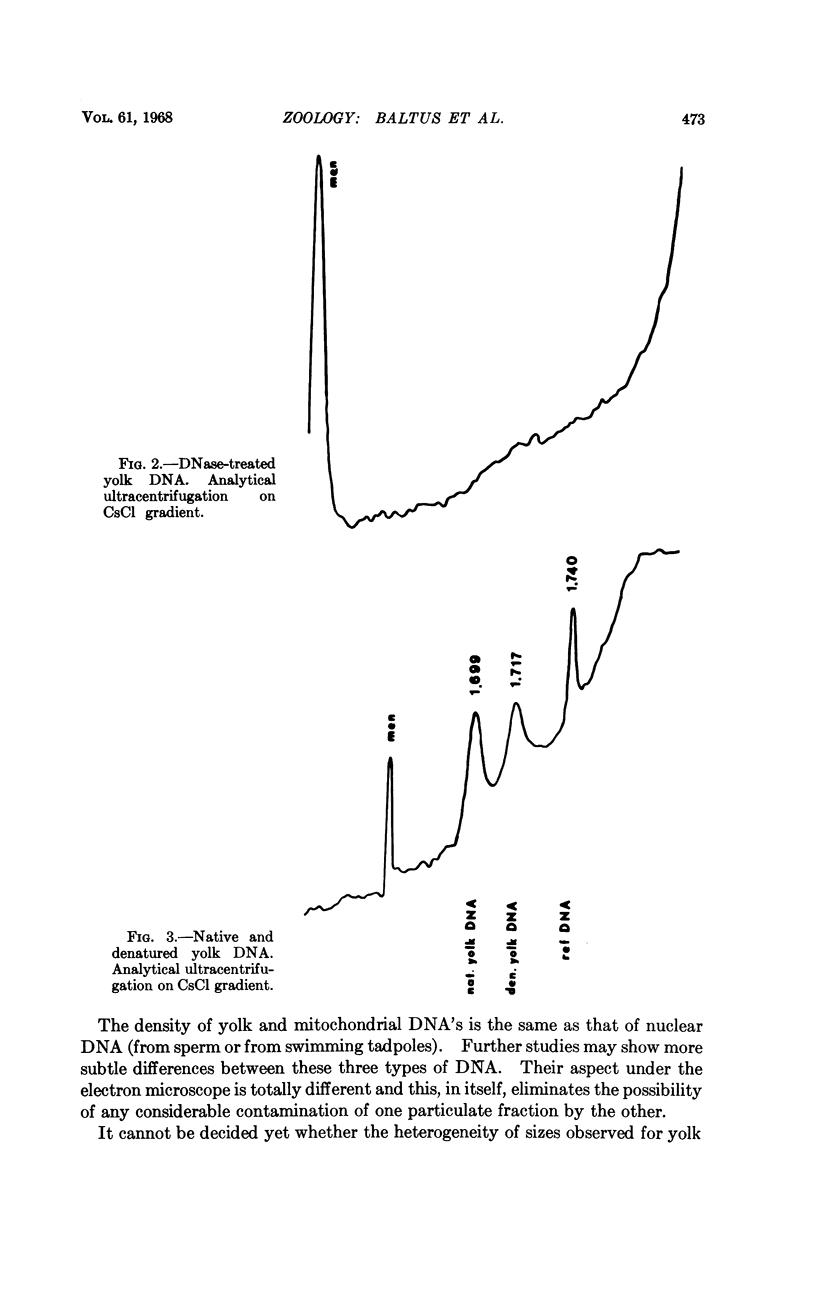
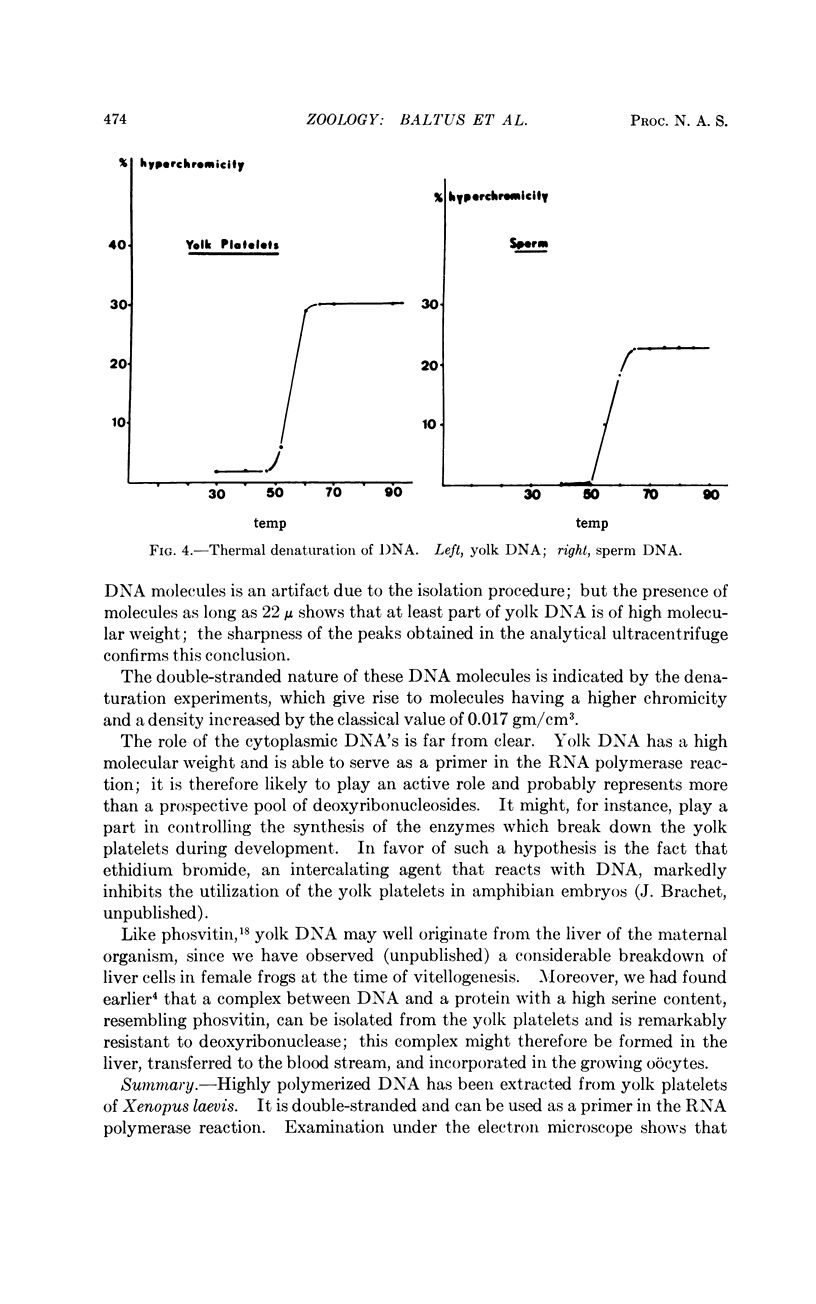
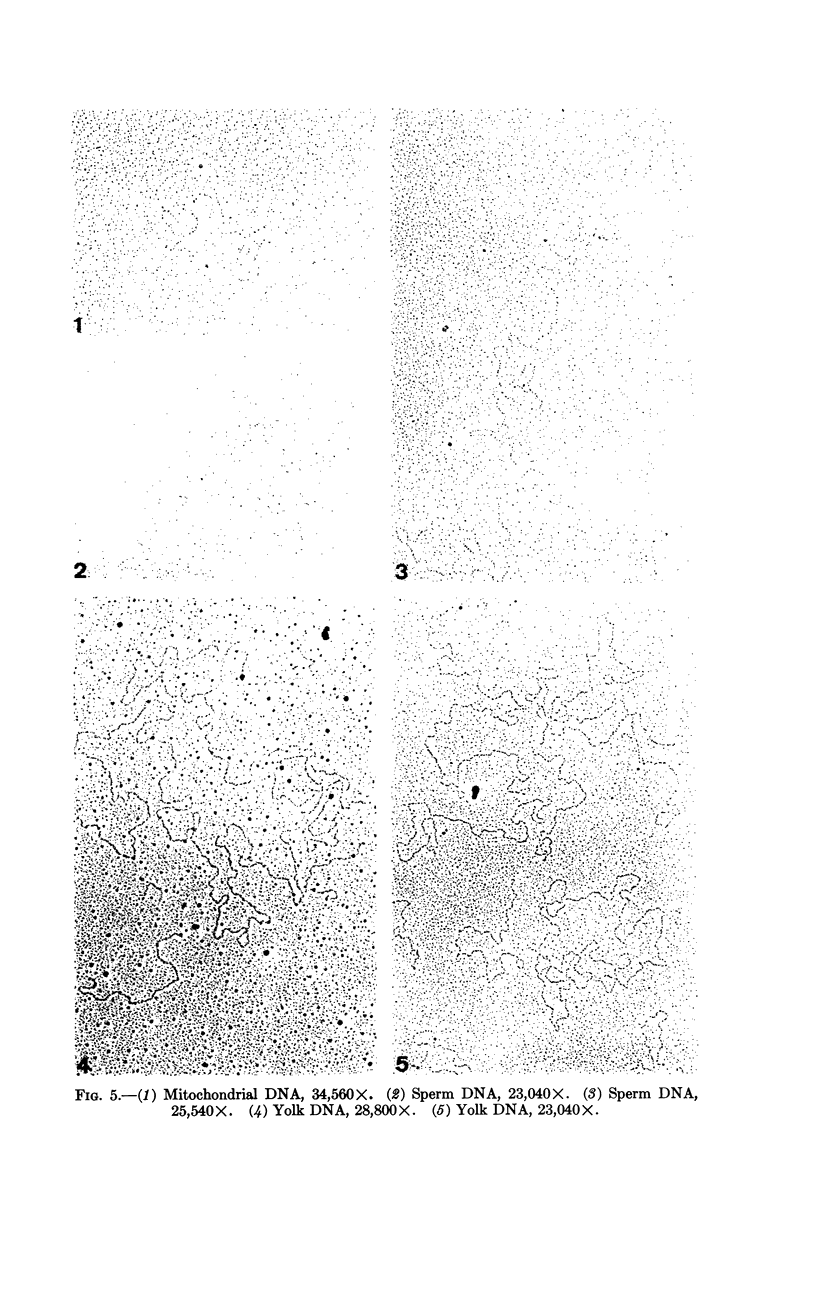

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BALTUS E., BRACHET J. [The determination of desoxyribonucleic acid in batrachian eggs]. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Aug 20;61:157–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRACHET J., FICQ A. BINDING SITES OF 14C-ACTINOMYCIN IN AMPHIBIAN OVOCYTES AND AN AUTORADIOGRAPHY TECHNIQUE FOR THE DETECTION OF CYTOPLASMIC DNA. Exp Cell Res. 1965 Apr;38:153–159. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(65)90437-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAMBERLIN M., BERG P. Deoxyribo ucleic acid-directed synthesis of ribonucleic acid by an enzyme from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jan 15;48:81–94. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawid I. B. Deoxyribonucleic acid in amphibian eggs. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jul;12(3):581–599. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80313-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawid I. B. Evidence for the mitochondrial origin of frog egg cytoplasmic DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jul;56(1):269–276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.1.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haggis A. J. Deoxyribonucleic acid in germinal vesicles of oocytes of Rana pipiens. Science. 1966 Nov 4;154(3749):670–671. doi: 10.1126/science.154.3749.670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanocq-Quertier J., Baltus E., Ficq A., Brachet J. Studies on the DNA of Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1968 Apr;19(2):273–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby K. S., Cook E. A. Isolation of deoxyribonucleic acid from mammalian tissues. Biochem J. 1967 Jul;104(1):254–257. doi: 10.1042/bj1040254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudack D., Wallace R. A. On the site of phosvitin synthesis in Xenopus laevis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jan 29;155(1):299–301. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90361-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHILDKRAUT C. L., MARMUR J., DOTY P. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its buoyant density in CsCl. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jun;4:430–443. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUEOKA N., MARMUR J., DOTY P., 2nd Dependence of the density of deoxyribonucleic acids on guanine-cytosine content. Nature. 1959 May 23;183(4673):1429–1431. doi: 10.1038/1831429a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALLACE R. A., KARASAKI S. Studies on amphibian yolk. 2. The isolation of yolk platelets from the eggs of Rana pipiens. J Cell Biol. 1963 Jul;18:153–166. doi: 10.1083/jcb.18.1.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolles R. S., Freeman G. Studies on the deproteinization of DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 May 30;138(3):506–512. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90547-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







