Abstract
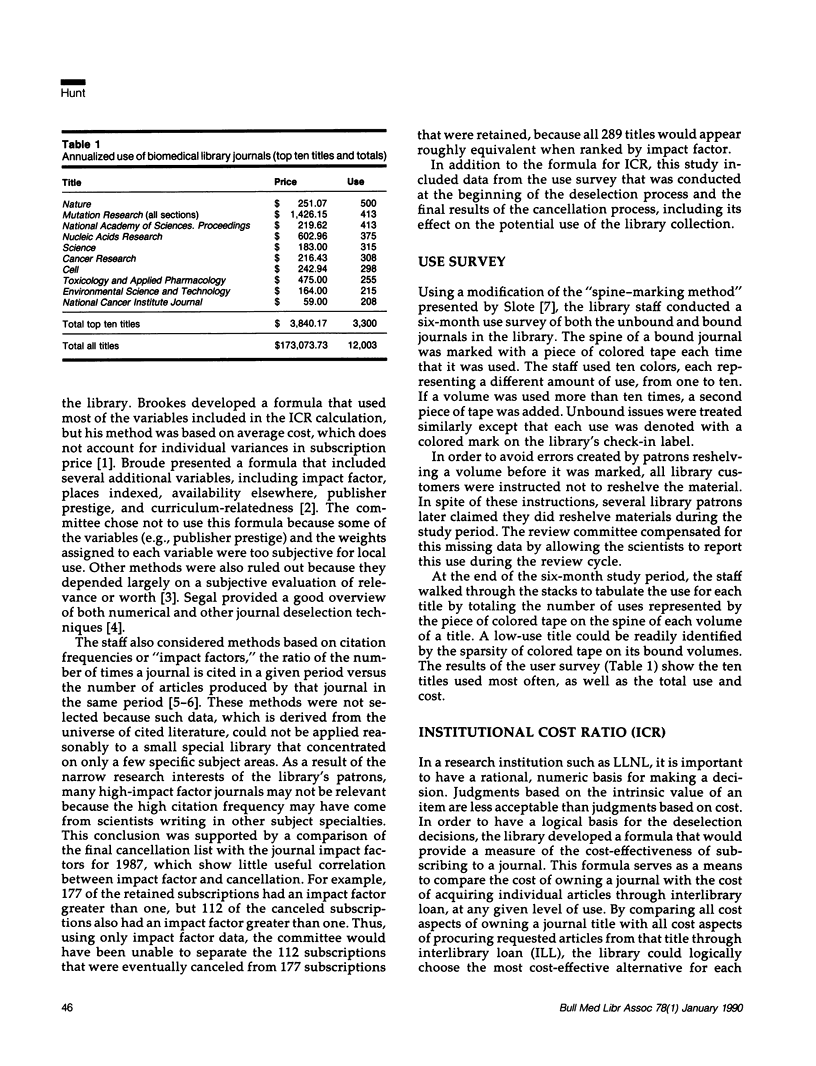
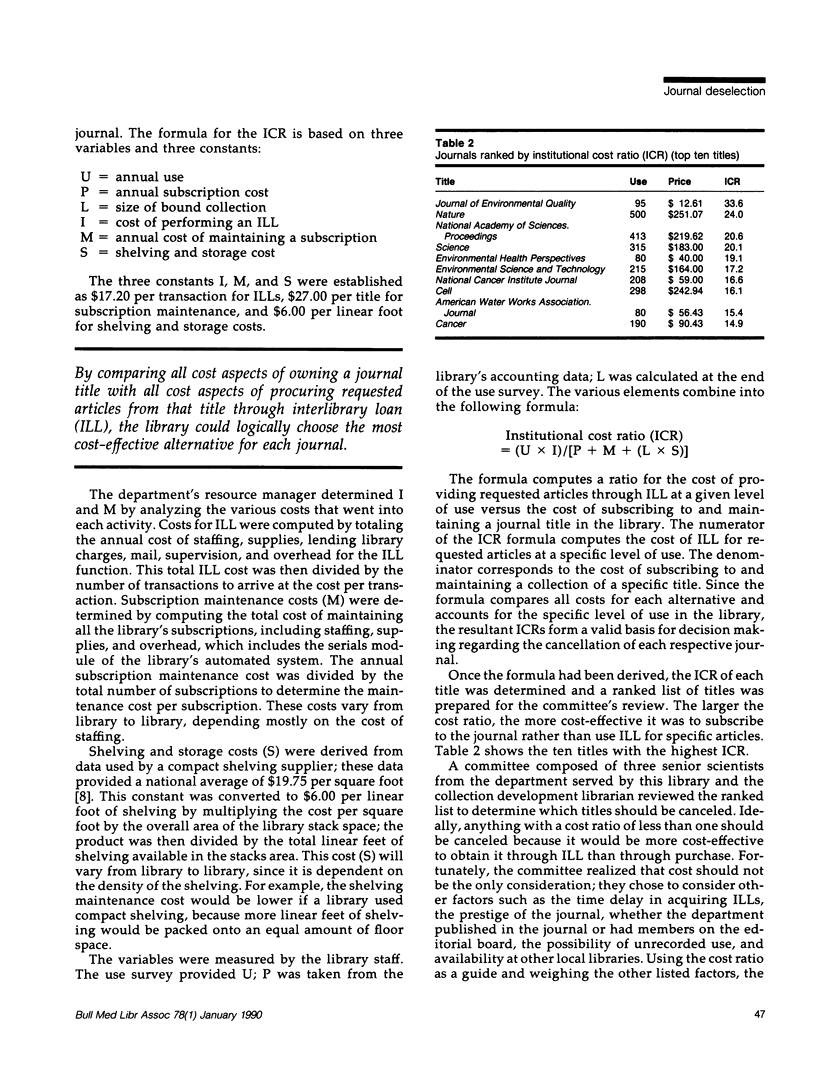
A unique mathematical formula was developed to use for journal deselection decisions. The formula factors in subscription cost, shelving and storage cost, interlibrary loan cost, staffing cost, and use level to determine the institutional cost ratio; this ratio serves as an indicator of the cost-effectiveness of each subscription title. Once the institutional cost ratio was calculated for each of 537 titles, a committee of library staff and senior library customers reviewed the ranked list to decide which subscriptions should be canceled. The committee also considered possible exceptions based on subjective criteria such as availability at local libraries, unrecorded use, and relative importance of the journal. The preliminary cancellation list was then reviewed by the library's research users. They were able to justify library subscriptions to a few additional titles. This method enabled the library to cut its subscription costs by 46%, while cutting only 8% of the total use. In addition, by mediating the mathematical approach with human intervention, the library made these severe cuts without unduly distressing its patrons.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Smith T. E. The Journal Citation Reports as a deselection tool. Bull Med Libr Assoc. 1985 Oct;73(4):387–389. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


