Abstract
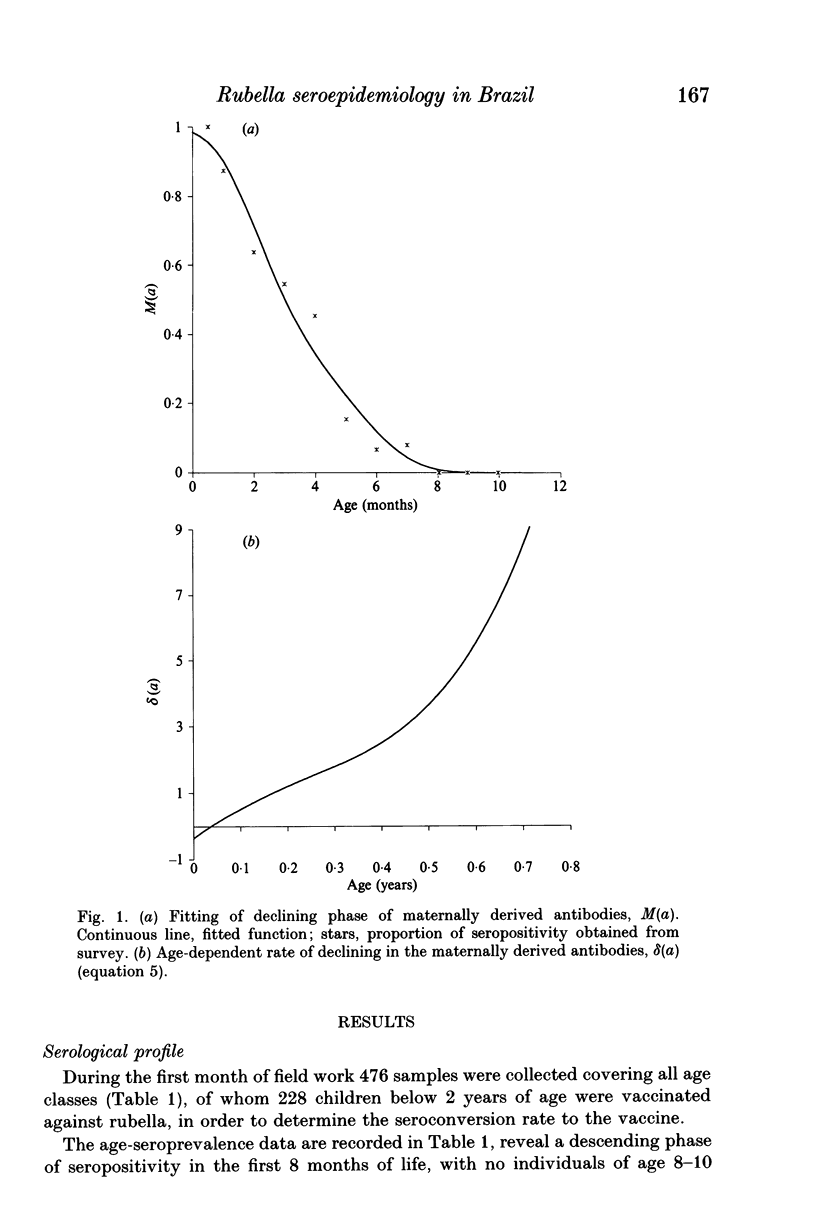
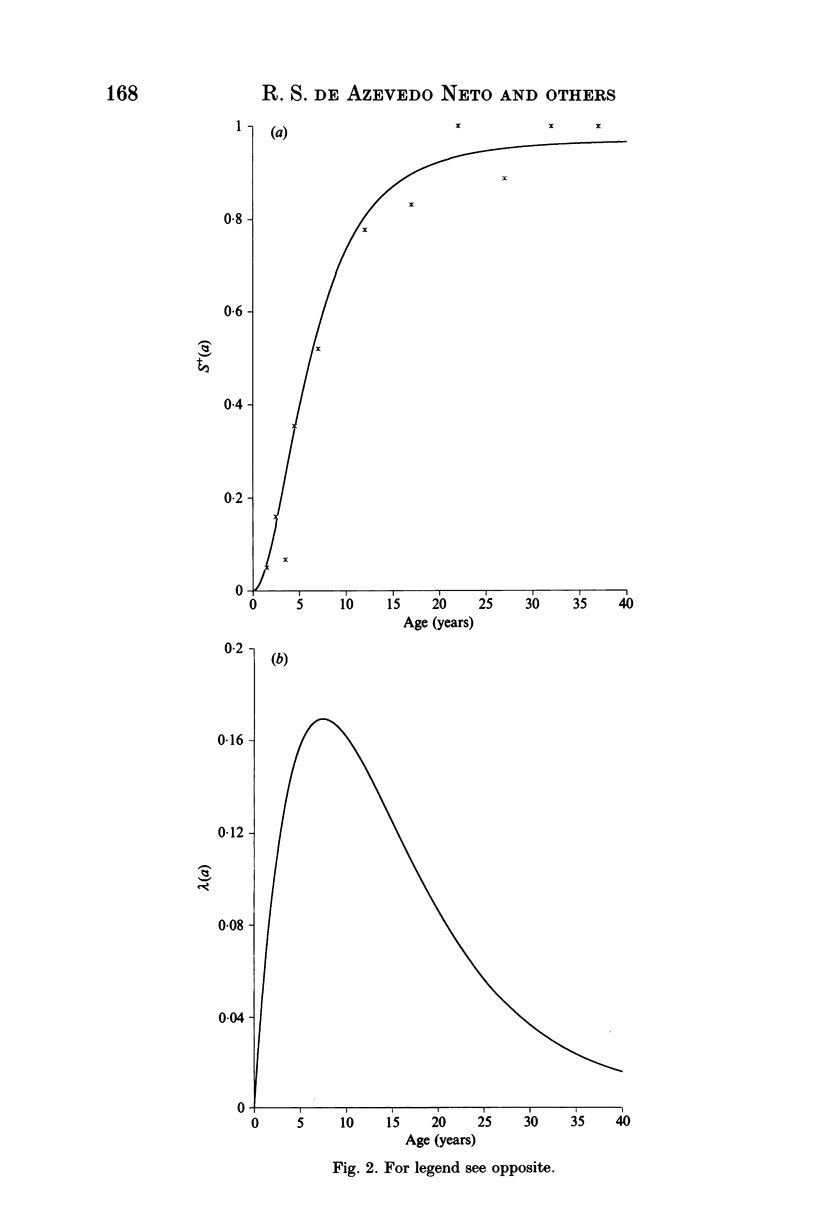
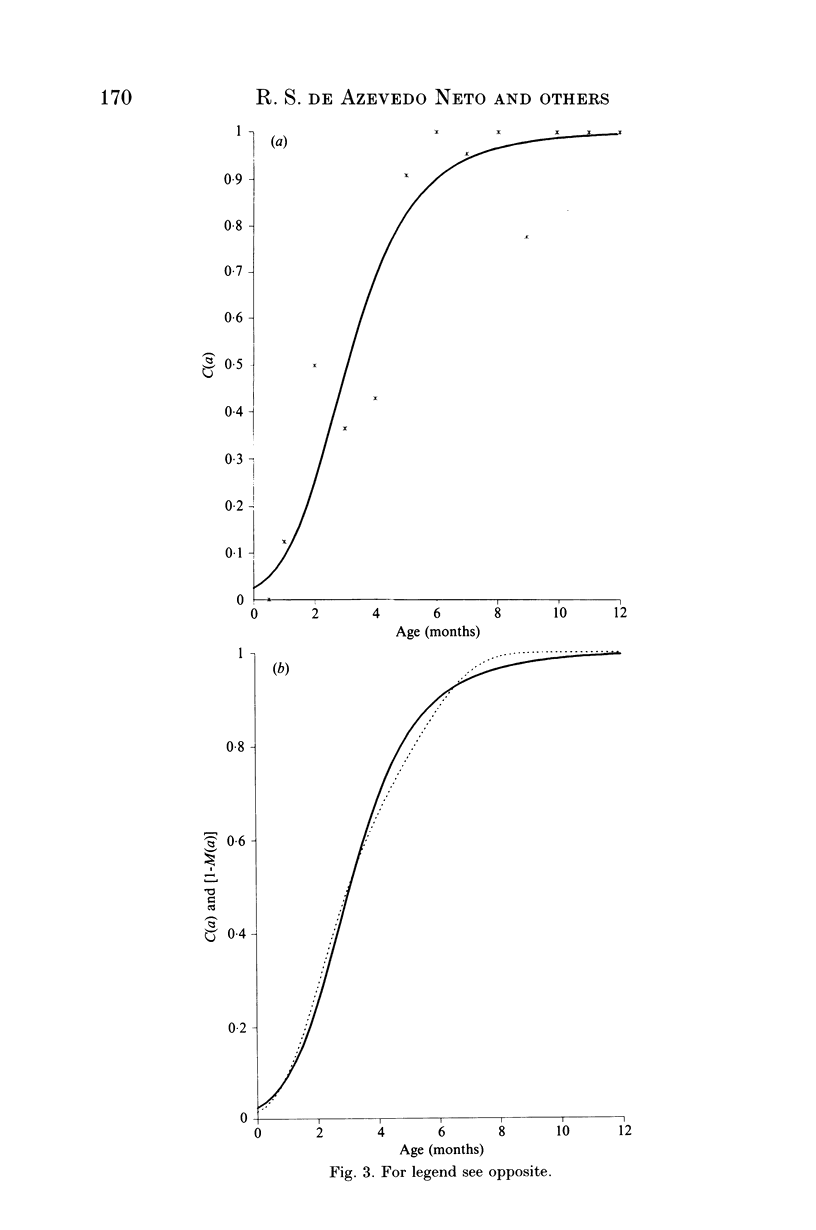
A rubella serological survey of 476 individuals selected by cluster sampling technique from Caieiras, a small town located in the outskirts of São Paulo city, southeastern Brazil, was carried out over the period November 1990-January 1991. The aim of the study was to characterize rubella epidemiology in a representative non-immunized community in south east Brazil. The survey comprised a seroprevalence study, stratified by age (0-40 years) and a seroconversion study of rubella vaccine in non-infected children below 2 years of age. Mathematical techniques were applied to resultant data sets to determine the age dependent rates of decay in the proportion of individuals with maternally derived antibodies, vaccine seroconversion, and infection of susceptibles, termed the force of infection, and to estimate the average age at first infection.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. M., May R. M. Vaccination against rubella and measles: quantitative investigations of different policies. J Hyg (Lond) 1983 Apr;90(2):259–325. doi: 10.1017/s002217240002893x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assaad F., Ljungars-Esteves K. Rubella--world impact. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Mar-Apr;7 (Suppl 1):S29–S36. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.supplement_1.s29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowdle W. R., Ferrera W., De Salles Gomes L. F., King D., Kourany M., Madalengoitia J., Pearson E., Swanston W. H., Tosi H. C., Vilches A. M. WHO collaborative study on the sero-epidemiology of rubella in Caribbean and Middle and South American populations in 1968. Bull World Health Organ. 1970;42(3):419–422. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enders-Ruckle G. Seroepidemiology of rubella and reinfection. Am J Dis Child. 1969 Jul;118(1):139–142. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1969.02100040141023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans A. S. Serological surveys. The role of the WHO Reference Serum Banks. WHO Chron. 1967 May;21(5):185–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrington C. P. Modelling forces of infection for measles, mumps and rubella. Stat Med. 1990 Aug;9(8):953–967. doi: 10.1002/sim.4780090811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenfell B. T., Anderson R. M. The estimation of age-related rates of infection from case notifications and serological data. J Hyg (Lond) 1985 Oct;95(2):419–436. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400062859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karchmer A. W., Herrmann K. L., Friedman J. P., Shope T. C., Page E. E., Jr, Dressler M. S., Armes W. H., Jr, Witte J. J. Comparative studies of rubella vaccines. Am J Dis Child. 1969 Aug;118(2):197–202. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1969.02100040199007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox E. G. Strategy for rubella vaccination. Int J Epidemiol. 1980 Mar;9(1):13–23. doi: 10.1093/ije/9.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massad E., Burattini M. N., de Azevedo Neto R. S., Yang H. M., Coutinho F. A., Zanetta D. M. A model-based design of a vaccination strategy against rubella in a non-immunized community of São Paulo State, Brazil. Epidemiol Infect. 1994 Jun;112(3):579–594. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800051281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nokes D. J., Anderson R. M., Anderson M. J. Rubella epidemiology in South East England. J Hyg (Lond) 1986 Apr;96(2):291–304. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400066067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAUL J. R. AIMS, PURPOSES AND METHODS OF WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION SERUM BANKS. Yale J Biol Med. 1963 Aug;36:2–4. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato H., Albrecht P., Reynolds D. W., Stagno S., Ennis F. A. Transfer of measles, mumps, and rubella antibodies from mother to infant. Its effect on measles, mumps, and rubella immunization. Am J Dis Child. 1979 Dec;133(12):1240–1243. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1979.02130120032005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatzmayr H. G. Aspects of rubella infection in Brazil. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Mar-Apr;7 (Suppl 1):S53–S55. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.supplement_1.s53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


