Abstract
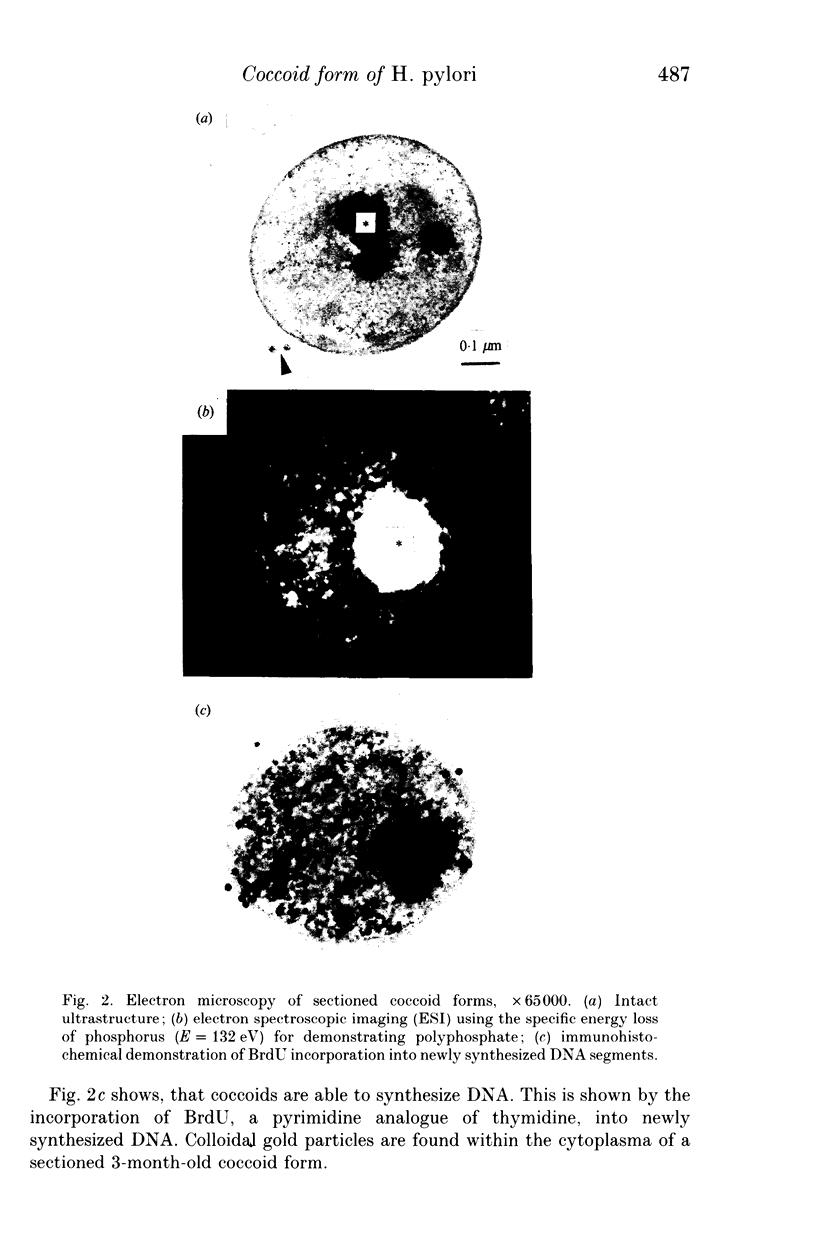
The fact that Helicobacter pylori can revert to a coccoid form has stimulated speculation about its role in transmission and as a possible cause of reinfection in duodenal ulcer disease. Bismuth subcitrate (32 micrograms/ml), bismuth subsalicylate (64 micrograms/ml), amoxicillin (0.05 micrograms/ml) and erythromycin (4 micrograms/ml) inhibited the growth of H. pylori and stimulated the formation of basically respiring but non-culturable coccoid structures. The presence of polyphosphates as energy and phosphorus source permits a certain level of endogenous metabolism to preserve RNA and DNA, as well as structural components like cell wall, cell membrane and cytoplasma for at least 3 months. However, the applied standard laboratory methods were insufficient for regrowth of H. pylori out of the coccoid form.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bode G., Malfertheiner P., Ströhle A., Mauch F., Nilius M., Ditschuneit H. Polymorphismus bei Helicobacter pylori--Schlüsselfunktion für Infektionsrezidive? Med Klin (Munich) 1992 Apr 15;87(4):179–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrd J. J., Xu H. S., Colwell R. R. Viable but nonculturable bacteria in drinking water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Mar;57(3):875–878. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.3.875-878.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costas M., Morgan D. D., Owen R. J., Morgan D. R. Differentiation of strains of Helicobacter pylori by numerical analysis of 1-D SDS-PAGE protein patterns: evidence for post-treatment recrudescence. Epidemiol Infect. 1991 Dec;107(3):607–617. doi: 10.1017/s095026880004930x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drumm B., Perez-Perez G. I., Blaser M. J., Sherman P. M. Intrafamilial clustering of Helicobacter pylori infection. N Engl J Med. 1990 Feb 8;322(6):359–363. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199002083220603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. G., Blanco M. C., Yan L., Shames B., Polidoro D., Dewhirst F. E., Paster B. J. Role of gastric pH in isolation of Helicobacter mustelae from the feces of ferrets. Gastroenterology. 1993 Jan;104(1):86–92. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90839-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. G., Paster B. J., Dewhirst F. E., Taylor N. S., Yan L. L., Macuch P. J., Chmura L. M. Helicobacter mustelae isolation from feces of ferrets: evidence to support fecal-oral transmission of a gastric Helicobacter. Infect Immun. 1992 Feb;60(2):606–611. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.2.606-611.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glupczynski Y., Burette A. Drug therapy for Helicobacter pylori infection: problems and pitfalls. Am J Gastroenterol. 1990 Dec;85(12):1545–1551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim Q. N., Maxwell R. H. Survival of Campylobacter pylori in artificially contaminated milk. J Clin Pathol. 1989 Jul;42(7):778–778. doi: 10.1136/jcp.42.7.778-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjelleberg S., Hermansson M., Mårdén P., Jones G. W. The transient phase between growth and nongrowth of heterotrophic bacteria, with emphasis on the marine environment. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:25–49. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.000325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein P. D., Graham D. Y., Gaillour A., Opekun A. R., Smith E. O. Water source as risk factor for Helicobacter pylori infection in Peruvian children. Gastrointestinal Physiology Working Group. Lancet. 1991 Jun 22;337(8756):1503–1506. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)93196-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koster T., Vandenbroucke J. P. Helicobacter pylori, musings from the epidemiologic armchair. Epidemiol Infect. 1992 Aug;109(1):81–85. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulaev I. S., Vagabov V. M. Polyphosphate metabolism in micro-organisms. Adv Microb Physiol. 1983;24:83–171. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60385-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A., Fox J. G., Otto G., Dick E. H., Krakowka S. Transmission of Helicobacter spp. A challenge to the dogma of faecal-oral spread. Epidemiol Infect. 1991 Aug;107(1):99–109. doi: 10.1017/s095026880004872x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NG L. K., Sherburne R., Taylor D. E., Stiles M. E. Morphological forms and viability of Campylobacter species studied by electron microscopy. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):338–343. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.338-343.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen R. J., Bell G. D., Desai M., Moreno M., Gant P. W., Jones P. H., Linton D. Biotype and molecular fingerprints of metronidazole-resistant strains of Helicobacter pylori from antral gastric mucosa. J Med Microbiol. 1993 Jan;38(1):6–12. doi: 10.1099/00222615-38-1-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Rosas N., Hazen T. C. In situ survival of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli in a tropical rain forest watershed. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Feb;55(2):495–499. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.2.495-499.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollins D. M., Colwell R. R. Viable but nonculturable stage of Campylobacter jejuni and its role in survival in the natural aquatic environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Sep;52(3):531–538. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.3.531-538.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roszak D. B., Grimes D. J., Colwell R. R. Viable but nonrecoverable stage of Salmonella enteritidis in aquatic systems. Can J Microbiol. 1984 Mar;30(3):334–338. doi: 10.1139/m84-049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saha S. K., Saha S., Sanyal S. C. Recovery of injured Campylobacter jejuni cells after animal passage. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Nov;57(11):3388–3389. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.11.3388-3389.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. E., Gibson G. R., Darboe M. K., Dale A., Weaver L. T. Isolation of Helicobacter pylori from human faeces. Lancet. 1992 Nov 14;340(8829):1194–1195. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)92894-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West A. P., Millar M. R., Tompkins D. S. Survival of Helicobacter pylori in water and saline. J Clin Pathol. 1990 Jul;43(7):609–609. doi: 10.1136/jcp.43.7.609-b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]