Abstract
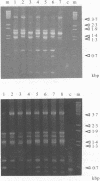
Ribosomal RNA gene patterns, randomly amplified polymorphic genomic DNA (RAPD) profiles and plasmid profiles were used to discriminate between 28 strains of Campylobacter jejuni serogroups O1 and O2 (Penner). Most isolates were biotype I (Lior). The strains were representative isolates from a UK school outbreak of enteritis (7 cases) and from 21 sporadic human cases of enteritis in 4 countries. The molecular techniques discriminated to various degrees between strains in each of the serogroups. The outbreak strains were homogeneous in most molecular features but a variety of types was detected amongst the isolates from the sporadic cases. Five groups of two or more strains with identical ribopatterns were identified and within each, strains from different patients were homogenous with respect to serogroup. RAPD profile typing based on numerical analysis generally matched ribotyping. Plasmid profiling overall gave least discrimination but was useful in separating some strains similar in other features. We concluded that optimal discrimination of C. jejuni could best be achieved using a combination of phenotypic and genotypic properties. Hae III ribotyping was the single most discriminatory and reproducible technique investigated. Several strains of C. jejuni from sporadic infections had similar molecular profiles which have potential for general typing purposes.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bruce D., Hookey J. V., Waitkins S. A. Numerical classification of campylobacters by DNA-restriction endonuclease analysis. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1988 Nov;269(3):284–297. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(88)80172-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butzler J. P., Oosterom J. Campylobacter: pathogenicity and significance in foods. Int J Food Microbiol. 1991 Jan;12(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0168-1605(91)90043-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costas M. Numerical analysis of sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoretic protein patterns for the classification, identification and typing of medically important bacteria. Electrophoresis. 1990 May;11(5):382–391. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150110507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cover T. L., Blaser M. J. The pathobiology of Campylobacter infections in humans. Annu Rev Med. 1989;40:269–285. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.40.020189.001413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fayos A., Owen R. J., Desai M., Hernandez J. Ribosomal RNA gene restriction fragment diversity amongst Lior biotypes and Penner serotypes of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Aug 1;74(1):87–93. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(92)90741-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser A. D., Brooks B. W., Garcia M. M., Lior H. Molecular discrimination of Campylobacter coli serogroup 20 biotype I (Lior) strains. Vet Microbiol. 1992 Feb;30(2-3):267–280. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(92)90120-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fricker C. R., Park R. W. A two-year study of the distribution of 'thermophilic' campylobacters in human, environmental and food samples from the Reading area with particular reference to toxin production and heat-stable serotype. J Appl Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;66(6):477–490. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1989.tb04568.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geilhausen B., Mauff G., Vlaes L., Goossens H., Butzler J. P. Restriction fragment length polymorphism for the identification of Campylobacter jejuni-isolates. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1990 Dec;274(3):366–371. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8840(11)80694-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grajewski B. A., Kusek J. W., Gelfand H. M. Development of a bacteriophage typing system for Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jul;22(1):13–18. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.1.13-18.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths P. L., Park R. W. Campylobacters associated with human diarrhoeal disease. J Appl Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;69(3):281–301. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1990.tb01519.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez J., Owen R. J., Costas M., Lastovica A. DNA-DNA hybridization and analysis of restriction endonuclease and rRNA gene patterns of atypical (catalase-weak/negative) Campylobacter jejuni from paediatric blood and faecal cultures. J Appl Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;70(1):71–80. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1991.tb03789.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok S., Higuchi R. Avoiding false positives with PCR. Nature. 1989 May 18;339(6221):237–238. doi: 10.1038/339237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lastovica A. J., Le Roux E., Congi R. V., Penner J. L. Distribution of sero-biotypes of Campylobacter jejuni and C. coli isolated from paediatric patients. J Med Microbiol. 1986 Feb;21(1):1–5. doi: 10.1099/00222615-21-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lior H. New, extended biotyping scheme for Campylobacter jejuni, Campylobacter coli, and "Campylobacter laridis". J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Oct;20(4):636–640. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.4.636-640.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lior H., Woodward D. L., Edgar J. A., Laroche L. J., Gill P. Serotyping of Campylobacter jejuni by slide agglutination based on heat-labile antigenic factors. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 May;15(5):761–768. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.5.761-768.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazurier S., van de Giessen A., Heuvelman K., Wernars K. RAPD analysis of Campylobacter isolates: DNA fingerprinting without the need to purify DNA. Lett Appl Microbiol. 1992 Jun;14(6):260–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-765x.1992.tb00700.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen R. J. Chromosomal DNA fingerprinting--a new method of species and strain identification applicable to microbial pathogens. J Med Microbiol. 1989 Oct;30(2):89–99. doi: 10.1099/00222615-30-2-89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen R. J., Costas M., Dawson C. Application of different chromosomal DNA restriction digest fingerprints to specific and subspecific identification of Campylobacter isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Oct;27(10):2338–2343. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.10.2338-2343.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen R. J., Hernandez J., Bolton F. DNA restriction digest and ribosomal RNA gene patterns of Campylobacter jejuni: a comparison with bio-, sero-, and bacteriophage-types of United Kingdom outbreak strains. Epidemiol Infect. 1990 Oct;105(2):265–275. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800047877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton C. M., Wachsmuth I. K., Evins G. M., Kiehlbauch J. A., Plikaytis B. D., Troup N., Tompkins L., Lior H. Evaluation of 10 methods to distinguish epidemic-associated Campylobacter strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Apr;29(4):680–688. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.4.680-688.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner J. L., Hennessy J. N. Passive hemagglutination technique for serotyping Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni on the basis of soluble heat-stable antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Dec;12(6):732–737. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.6.732-737.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner J. L. The genus Campylobacter: a decade of progress. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1988 Apr;1(2):157–172. doi: 10.1128/cmr.1.2.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salama S. M., Bolton F. J., Hutchinson D. N. Application of a new phagetyping scheme to campylobacters isolated during outbreaks. Epidemiol Infect. 1990 Jun;104(3):405–411. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800047427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skirrow M. B. A demographic survey of campylobacter, salmonella and shigella infections in England. A Public Health Laboratory Service Survey. Epidemiol Infect. 1987 Dec;99(3):647–657. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800066504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenover F. C., Williams S., Gordon K. P., Harris N., Nolan C., Plorde J. J. Utility of plasmid fingerprinting for epidemiological studies of Campylobacter jejuni infections. J Infect Dis. 1984 Feb;149(2):279–279. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.2.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan W., Chang N., Taylor D. E. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli genomic DNA and its epidemiologic application. J Infect Dis. 1991 May;163(5):1068–1072. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.5.1068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]