Abstract
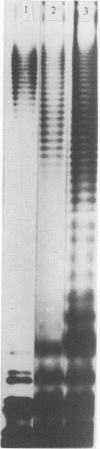
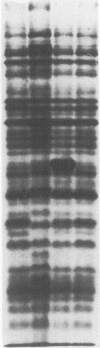
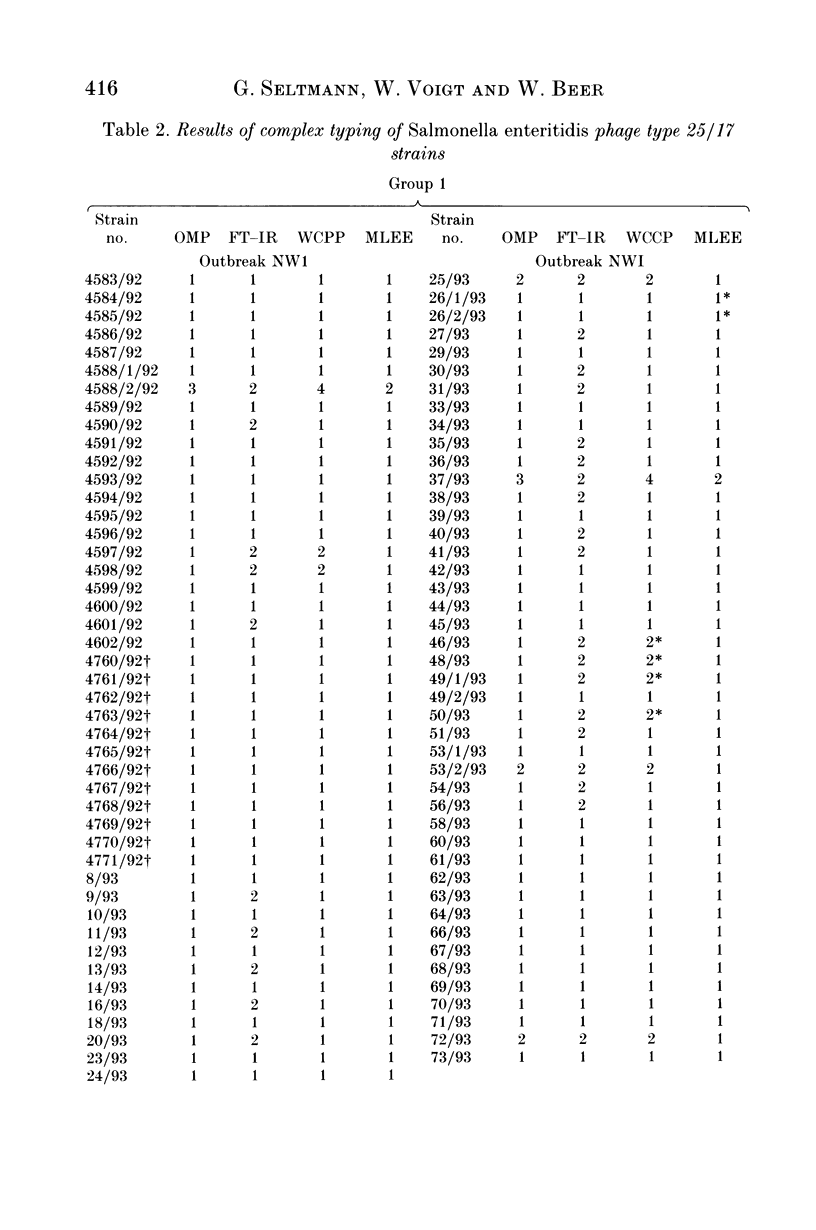
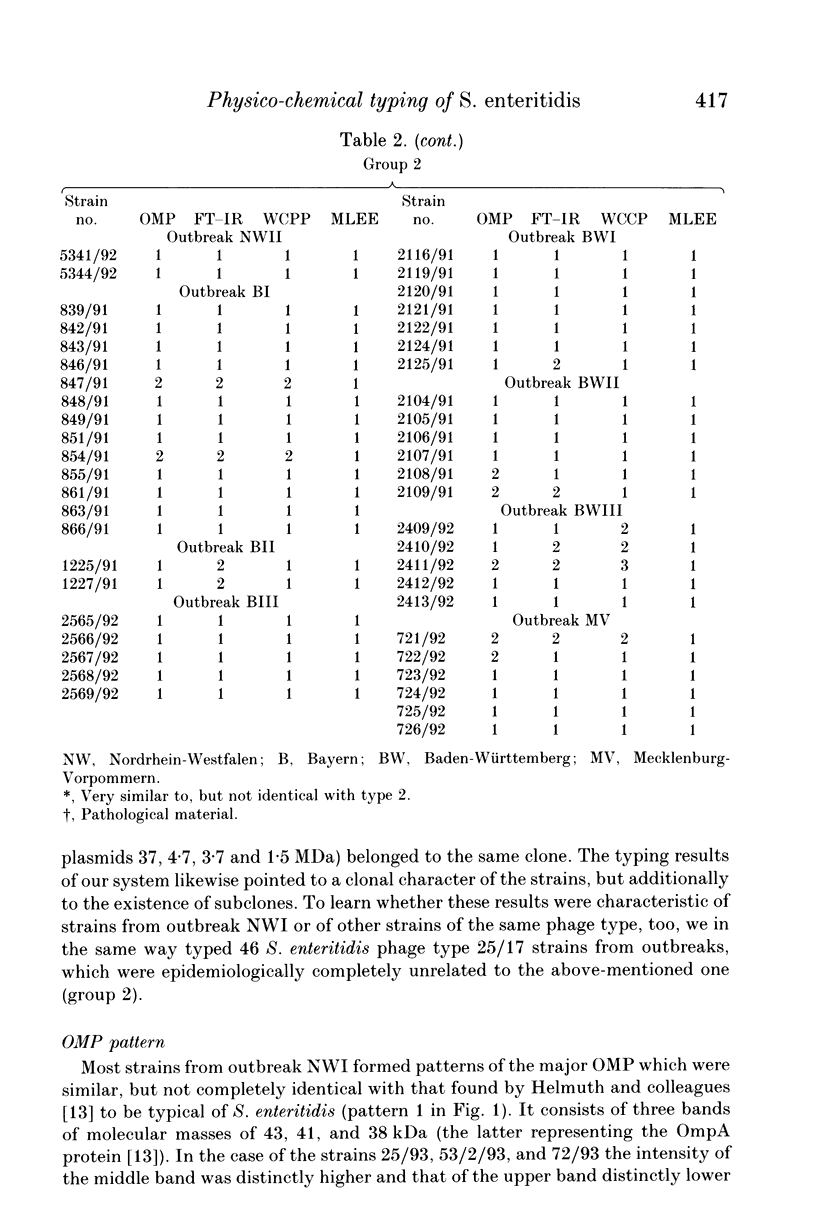
Eighty-nine Salmonella enteritidis phage type 25/17 strains isolated from a localized outbreak in the German state Nordrhein-Westfalen (outbreak NWI) could not be further differentiated by biochemotyping and plasmid pattern analysis. They were submitted to a complex typing system consisting of modern physico-chemical analytical procedures. In lipopolysaccharide pattern analysis the strains proved to be homogeneous. In multilocus enzyme electrophoresis, outer membrane and whole cell protein pattern (WCPP) analysis, and Fourier-transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy (increasing extent of differentiation in the given order) strains deviating from each basal pattern were found. The extent of correspondence in these deviations was satisfactory. Forty-six strains of the same sero- and phage type, however, obtained from different outbreaks, were additionally typed. The results obtained with them indicate that the data of the first group were not restricted to strains from outbreak NWI, but of general validity. It was found that both WCPP and FT-IR represent valuable methods for the sub-grouping of bacteria.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achtman M., Mercer A., Kusecek B., Pohl A., Heuzenroeder M., Aaronson W., Sutton A., Silver R. P. Six widespread bacterial clones among Escherichia coli K1 isolates. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):315–335. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.315-335.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bastin D. A., Stevenson G., Brown P. K., Haase A., Reeves P. R. Repeat unit polysaccharides of bacteria: a model for polymerization resembling that of ribosomes and fatty acid synthetase, with a novel mechanism for determining chain length. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Mar;7(5):725–734. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01163.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costas M., Holmes B., Sloss L. L. Numerical analysis of electrophoretic protein patterns of Providencia rustigianii strains from human diarrhoea and other sources. J Appl Bacteriol. 1987 Oct;63(4):319–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1987.tb02709.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helm D., Labischinski H., Schallehn G., Naumann D. Classification and identification of bacteria by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Jan;137(1):69–79. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-1-69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmuth R., Stephan R., Bunge C., Hoog B., Steinbeck A., Bulling E. Epidemiology of virulence-associated plasmids and outer membrane protein patterns within seven common Salmonella serotypes. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):175–182. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.175-182.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn H., Rabsch W., Liesegang A. Gegenwärtige epidemiologische Situation bei der Salmonellose des Menschen in Deutschland. Immun Infekt. 1994 Feb;22(1):4–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Meijers J., Peters R., van der Hoek P., van Alphen L. Electrophoretic resolution of the "major outer membrane protein" of Escherichia coli K12 into four bands. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- László V. G., Csórián E. S., Pászti J. Phage types and epidemiological significance of Salmonella enteritidis strains in Hungary between 1976 and 1983. Acta Microbiol Hung. 1985;32(4):321–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller K. D., Husmann H., Nalik H. P. A new and rapid method for the assay of bacterial fatty acids using high resolution capillary gas chromatography and trimethylsulfonium hydroxide. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1990 Nov;274(2):174–182. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8840(11)80100-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nørrung B., Gerner-Smidt P. Comparison of multilocus enzyme electrophoresis (MEE), ribotyping, restriction enzyme analysis (REA) and phage typing for typing of Listeria monocytogenes. Epidemiol Infect. 1993 Aug;111(1):71–79. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800056697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen J. E., Brown D. J., Baggesen D. L., Bisgaard M. Biochemical and molecular characterization of Salmonella enterica serovar berta, and comparison of methods for typing. Epidemiol Infect. 1992 Apr;108(2):243–260. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800049724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov F., Orskov I. From the national institutes of health. Summary of a workshop on the clone concept in the epidemiology, taxonomy, and evolution of the enterobacteriaceae and other bacteria. J Infect Dis. 1983 Aug;148(2):346–357. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.2.346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabilloud T. A comparison between low background silver diammine and silver nitrate protein stains. Electrophoresis. 1992 Jul;13(7):429–439. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150130190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., Caugant D. A., Ochman H., Musser J. M., Gilmour M. N., Whittam T. S. Methods of multilocus enzyme electrophoresis for bacterial population genetics and systematics. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 May;51(5):873–884. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.5.873-884.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubbs A. D., Hickman-Brenner F. W., Cameron D. N., Farmer J. J., 3rd Differentiation of Salmonella enteritidis phage type 8 strains: evaluation of three additional phage typing systems, plasmid profiles, antibiotic susceptibility patterns, and biotyping. J Clin Microbiol. 1994 Jan;32(1):199–201. doi: 10.1128/jcm.32.1.199-201.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugawara E., Nikaido H. Pore-forming activity of OmpA protein of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2507–2511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usera M. A., Popovic T., Bopp C. A., Strockbine N. A. Molecular subtyping of Salmonella enteritidis phage type 8 strains from the United States. J Clin Microbiol. 1994 Jan;32(1):194–198. doi: 10.1128/jcm.32.1.194-198.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward L. R., de Sa J. D., Rowe B. A phage-typing scheme for Salmonella enteritidis. Epidemiol Infect. 1987 Oct;99(2):291–294. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800067765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]