Abstract
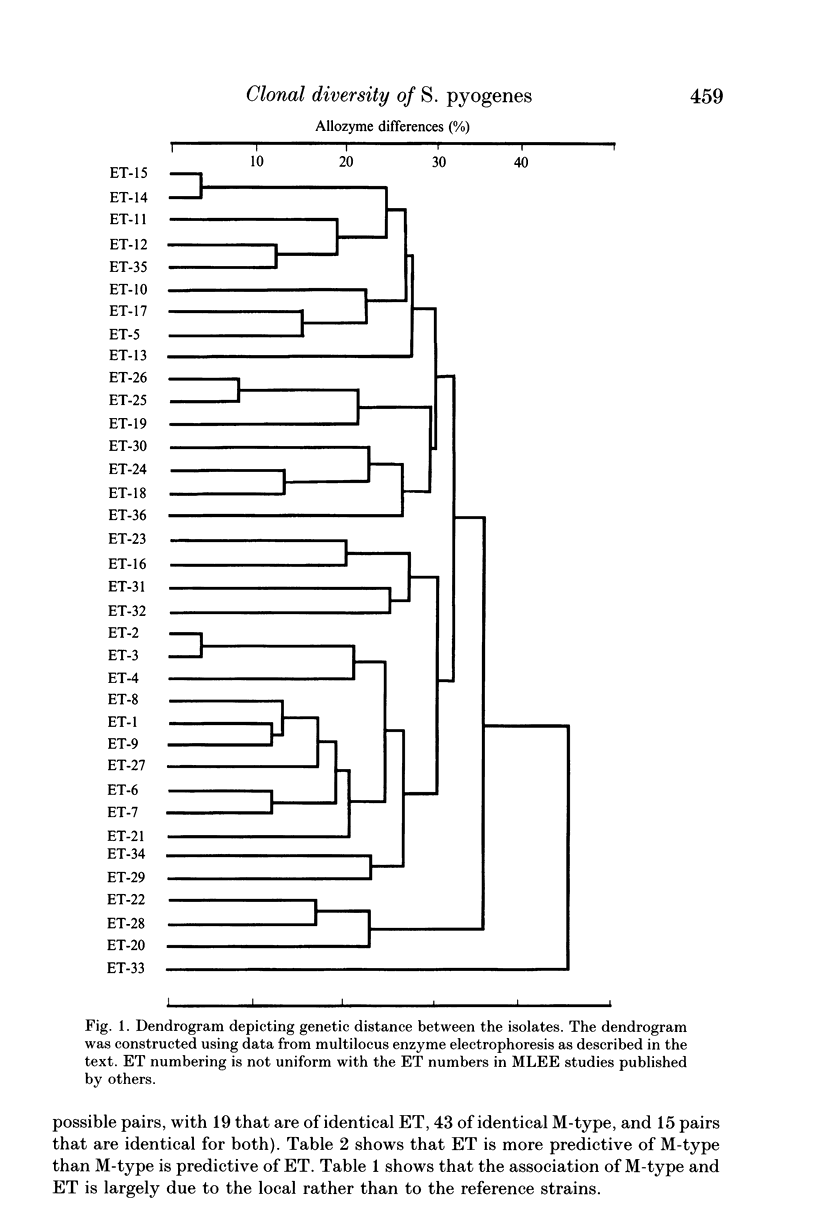
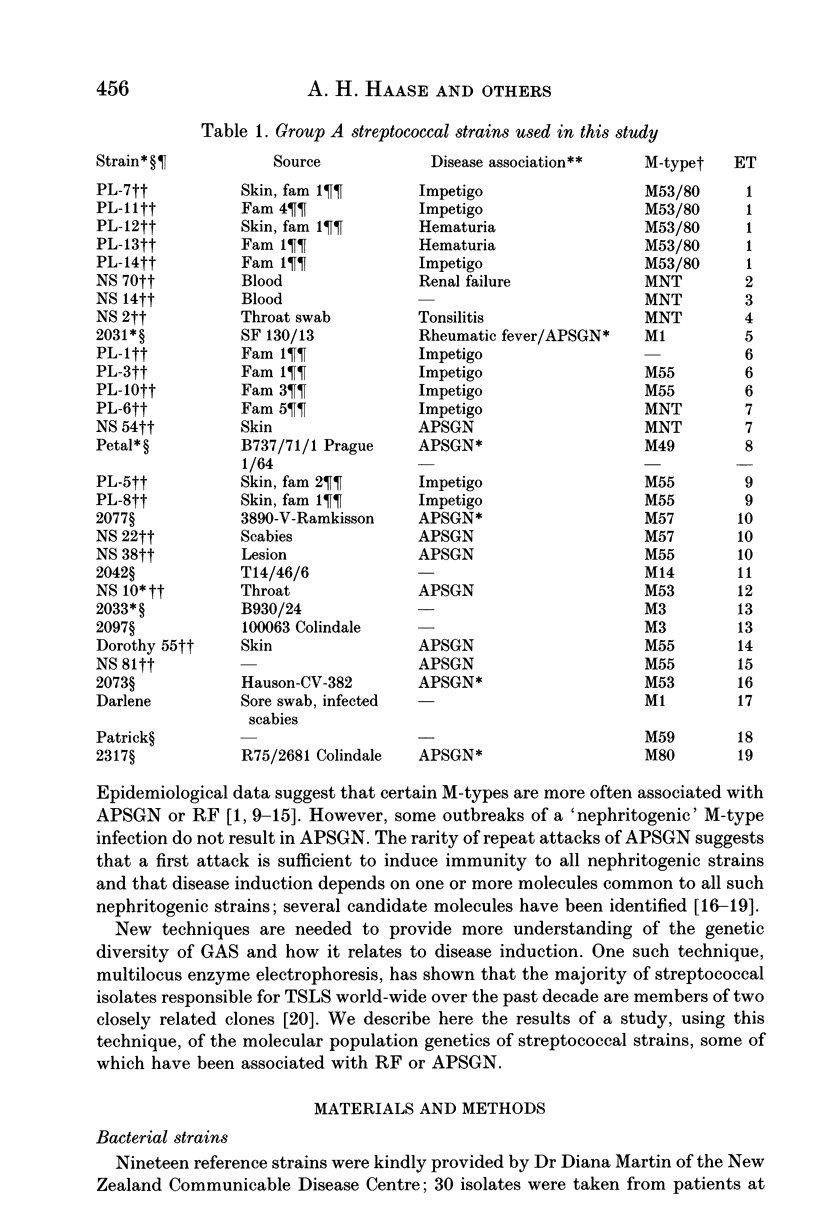
Twenty-two reference isolates and 30 local isolates of group A Streptococci were classified into 36 electrophoretic types (ET) on the basis of allozyme variation at 27 enzyme loci. Local isolates were characterized by a high frequency of M-non typable strains. M-type and ET were more closely associated in local isolates from an endemically-infected population; nevertheless, amongst the local isolates there were also strains of the same ET type with different M-types. A possible explanation is that genetic exchange between strains may introduce different M-types into strains of defined ET when these are exposed to strong selection in the presence of heavy loads of infection. In contrast to the reported clustering of strains associated with toxic shock-like syndrome into two closely related ET clones, we found no relationship of ET phenotype to acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis or rheumatic fever.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achtman M. Clonal properties of meningococci from epidemic meningitis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1991;85 (Suppl 1):24–31. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(91)90337-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berrios X., Quesney F., Morales A., Blazquez J., Lagomarsino E., Bisno A. L. Acute rheumatic fever and poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis in an open population: comparative studies of epidemiology and bacteriology. J Lab Clin Med. 1986 Dec;108(6):535–542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessen D., Jones K. F., Fischetti V. A. Evidence for two distinct classes of streptococcal M protein and their relationship to rheumatic fever. J Exp Med. 1989 Jan 1;169(1):269–283. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.1.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisno A. L. Group A streptococcal infections and acute rheumatic fever. N Engl J Med. 1991 Sep 12;325(11):783–793. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199109123251106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleary P. P., Kaplan E. L., Livdahl C., Skjold S. DNA fingerprints of Streptococcus pyogenes are M type specific. J Infect Dis. 1988 Dec;158(6):1317–1323. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.6.1317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cronin W., Deol H., Azadegan A., Lange K. Endostreptosin: isolation of the probable immunogen of acute post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis (PSGN). Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 May;76(2):198–203. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaworzewska E., Colman G. Changes in the pattern of infection caused by Streptococcus pyogenes. Epidemiol Infect. 1988 Apr;100(2):257–269. doi: 10.1017/s095026880006739x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston K. H., Zabriskie J. B. Purification and partial characterization of the nephritis strain-associated protein from Streptococcus pyogenes, group A. J Exp Med. 1986 Mar 1;163(3):697–712. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.3.697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latta K., Ehrich J. H., Brodehl J. Ist die Poststreptokokkenglomerulonephritis verschwunden? Monatsschr Kinderheilkd. 1992 Aug;140(8):490–492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennon D., Martin D., Wong E., Taylor L. R. Longitudinal study of poststreptococcal disease in Auckland; rheumatic fever, glomerulonephritis, epidemiology and M typing 1981-86. N Z Med J. 1988 Jun 8;101(847 Pt 2):396–398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majeed H. A., Khuffash F. A., Yousof A. M., Farwana S. S., Chugh T. D., Rotta J., Havlickpva H. The rheumatogenic and nephritogenic strains of the group A streptococcus: the Kuwait experience. N Z Med J. 1988 Jun 8;101(847 Pt 2):398–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin P. R., Høiby E. A. Streptococcal serogroup A epidemic in Norway 1987-1988. Scand J Infect Dis. 1990;22(4):421–429. doi: 10.3109/00365549009027073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musser J. M., Hauser A. R., Kim M. H., Schlievert P. M., Nelson K., Selander R. K. Streptococcus pyogenes causing toxic-shock-like syndrome and other invasive diseases: clonal diversity and pyrogenic exotoxin expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2668–2672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musser J. M., Kapur V., Kanjilal S., Shah U., Musher D. M., Barg N. L., Johnston K. H., Schlievert P. M., Henrichsen J., Gerlach D. Geographic and temporal distribution and molecular characterization of two highly pathogenic clones of Streptococcus pyogenes expressing allelic variants of pyrogenic exotoxin A (Scarlet fever toxin). J Infect Dis. 1993 Feb;167(2):337–346. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.2.337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poon-King R., Bannan J., Viteri A., Cu G., Zabriskie J. B. Identification of an extracellular plasmin binding protein from nephritogenic streptococci. J Exp Med. 1993 Aug 1;178(2):759–763. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.2.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter E. V., Svartman M., Burt E. G., Finklea J. F., Poon-King T., Earle D. P. Relationship of acute rheumatic fever to acute glomerulonephritis in Trinidad. J Infect Dis. 1972 Jun;125(6):619–625. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.6.619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz B., Facklam R. R., Breiman R. F. Changing epidemiology of group A streptococcal infection in the USA. Lancet. 1990 Nov 10;336(8724):1167–1171. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92777-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. J., Musser J. M., Cleary P. P. Evidence consistent with horizontal transfer of the gene (emm12) encoding serotype M12 protein between group A and group G pathogenic streptococci. Infect Immun. 1992 May;60(5):1890–1893. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.5.1890-1893.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Single L. A., Martin D. R. Clonal differences within M-types of the group A Streptococcus revealed by pulsed field gel electrophoresis. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Feb 1;70(1):85–89. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(92)90567-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strömberg A., Romanus V., Burman L. G. Outbreak of group A streptococcal bacteremia in Sweden: an epidemiologic and clinical study. J Infect Dis. 1991 Sep;164(3):595–598. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.3.595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler M. C., Roe M. H., Kaplan E. L., Schlievert P. M., Todd J. K. Outbreak of group A streptococcus septicemia in children. Clinical, epidemiologic, and microbiological correlates. JAMA. 1991 Jul 24;266(4):533–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshizawa N., Oshima S., Sagel I., Shimizu J., Treser G. Role of a streptococcal antigen in the pathogenesis of acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis. Characterization of the antigen and a proposed mechanism for the disease. J Immunol. 1992 May 15;148(10):3110–3116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


