Abstract
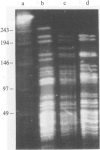
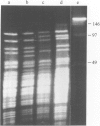
The results of typing of 121 strains in the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex by PFGE are presented. Every isolate from patients in Scotland over a 3-month period for M. tuberculosis and for 1 year for M. bovis were included along with several laboratory strains including those of BCG. The PFGE results suggest that the population structure of all the strains in this complex is distinctly simple with limited genetic diversity and also suggest that M. bovis is not a distinct species.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arbeit R. D., Slutsky A., Barber T. W., Maslow J. N., Niemczyk S., Falkinham J. O., 3rd, O'Connor G. T., von Reyn C. F. Genetic diversity among strains of Mycobacterium avium causing monoclonal and polyclonal bacteremia in patients with AIDS. J Infect Dis. 1993 Jun;167(6):1384–1390. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.6.1384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baess I. Deoxyribonucleic acid relatedness among species of slowly-growing mycobacteria. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1979 Aug;87(4):221–226. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1979.tb02430.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrow P. A. Aspects of the epidemiology of bovine tuberculosis in badgers and cattle. II. The development and use of a typing system for Mycobacterium bovis. J Hyg (Lond) 1981 Jun;86(3):247–257. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400068996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrow P. A. Physiological characteristics of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis-M. bovis group of organisms with particular reference to heterogeneity within M. bovis. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Feb;132(2):427–430. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-2-427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chevrel-Dellagi D., Abderrahman A., Haltiti R., Koubaji H., Gicquel B., Dellagi K. Large-scale DNA fingerprinting of Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains as a tool for epidemiological studies of tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Sep;31(9):2446–2450. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.9.2446-2450.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffin J. W., Condon C., Compston C. A., Potter K. N., Lamontagne L. R., Shafiq J., Kunimoto D. Y. Use of restriction fragment length polymorphisms resolved by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis for subspecies identification of mycobacteria in the Mycobacterium avium complex and for isolation of DNA probes. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jul;30(7):1829–1836. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.7.1829-1836.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins C. H., Yates M. D., Grange J. M. Subdivision of Mycobacterium tuberculosis into five variants for epidemiological purposes: methods and nomenclature. J Hyg (Lond) 1982 Oct;89(2):235–242. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400070765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins D. M., De Lisle G. W. BCG identification by DNA restriction fragment patterns. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Jun;133(6):1431–1434. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-6-1431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins D. M., De Lisle G. W. DNA restriction endonuclease analysis of Mycobacterium bovis and other members of the tuberculosis complex. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Apr;21(4):562–564. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.4.562-564.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins D. M., De Lisle G. W. DNA restriction endonuclease analysis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium bovis BCG. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Apr;130(4):1019–1021. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-4-1019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins D. M., De Lisle G. W., Gabric D. M. Geographic distribution of restriction types of Mycobacterium bovis isolates from brush-tailed possums (Trichosurus vulpecula) in New Zealand. J Hyg (Lond) 1986 Jun;96(3):431–438. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400066201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins D. M., Erasmuson S. K., Stephens D. M., Yates G. F., De Lisle G. W. DNA fingerprinting of Mycobacterium bovis strains by restriction fragment analysis and hybridization with insertion elements IS1081 and IS6110. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 May;31(5):1143–1147. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.5.1143-1147.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cousins D. V., Francis B. R., Gow B. L., Collins D. M., McGlashan C. H., Gregory A., Mackenzie R. M. Tuberculosis in captive seals: bacteriological studies on an isolate belonging to the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. Res Vet Sci. 1990 Mar;48(2):196–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cousins D. V., Williams S. N., Reuter R., Forshaw D., Chadwick B., Coughran D., Collins P., Gales N. Tuberculosis in wild seals and characterisation of the seal bacillus. Aust Vet J. 1993 Mar;70(3):92–97. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1993.tb03284.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fevre A., Fougerat J., Bruneau S., Guinet R. Characterization of Mycobacterium species by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Appl Theor Electrophor. 1991;2(1):13–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floyd M. M., Silcox V. A., Jones W. D., Jr, Butler W. R., Kilburn J. O. Separation of Mycobacterium bovis BCG from Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium bovis by using high-performance liquid chromatography of mycolic acids. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 May;30(5):1327–1330. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.5.1327-1330.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fomukong N. G., Dale J. W., Osborn T. W., Grange J. M. Use of gene probes based on the insertion sequence IS986 to differentiate between BCG vaccine strains. J Appl Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;72(2):126–133. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1992.tb01813.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fomukong N. G., Dale J. W. Transpositional activity of IS986 in Mycobacterium smegmatis. Gene. 1993 Aug 16;130(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90351-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frothingham R., Hills H. G., Wilson K. H. Extensive DNA sequence conservation throughout the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. J Clin Microbiol. 1994 Jul;32(7):1639–1643. doi: 10.1128/jcm.32.7.1639-1643.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grange J. M., Aber V. R., Allen B. W., Mitchison D. A., Goren M. B. The correlation of bacteriophage types of Mycobacterium tuberculosis with guinea-pig virulence and in vitro-indicators of virulence. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 Sep;108(1):1–7. doi: 10.1099/00221287-108-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hector J. S., Pang Y., Mazurek G. H., Zhang Y., Brown B. A., Wallace R. J., Jr Large restriction fragment patterns of genomic Mycobacterium fortuitum DNA as strain-specific markers and their use in epidemiologic investigation of four nosocomial outbreaks. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 May;30(5):1250–1255. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.5.1250-1255.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffner S. E., Svenson S. B., Norberg R., Dias F., Ghebremichael S., Källenius G. Biochemical heterogeneity of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex isolates in Guinea-Bissau. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Aug;31(8):2215–2217. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.8.2215-2217.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristjansson M., Green P., Manning H. L., Slutsky A. M., Brecher S. M., von Reyn C. F., Arbeit R. D., Maslow J. N. Molecular confirmation of bacillus Calmette-Guérin as the cause of pulmonary infection following urinary tract instillation. Clin Infect Dis. 1993 Aug;17(2):228–230. doi: 10.1093/clinids/17.2.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labidi A., Thoen C. O. Genetic relatedness among Mycobacterium tuberculosis and M. bovis. Acta Leprol. 1989;7 (Suppl 1):217–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lévy-Frébault V. V., Portaels F. Proposed minimal standards for the genus Mycobacterium and for description of new slowly growing Mycobacterium species. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;42(2):315–323. doi: 10.1099/00207713-42-2-315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lévy-Frébault V. V., Thorel M. F., Varnerot A., Gicquel B. DNA polymorphism in Mycobacterium paratuberculosis, "wood pigeon mycobacteria," and related mycobacteria analyzed by field inversion gel electrophoresis. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2823–2826. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2823-2826.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazurek G. H., Hartman S., Zhang Y., Brown B. A., Hector J. S., Murphy D., Wallace R. J., Jr Large DNA restriction fragment polymorphism in the Mycobacterium avium-M. intracellulare complex: a potential epidemiologic tool. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Feb;31(2):390–394. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.2.390-394.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millership S. E., Want S. V. Whole-cell protein electrophoresis for typing Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Nov;30(11):2784–2787. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.11.2784-2787.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman M. C., Sicilia M. J. Preliminary investigation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis biovars. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Nov;20(5):1015–1016. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.5.1015-1016.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Römling U., Grothues D., Heuer T., Tümmler B. Physical genome analysis of bacteria. Electrophoresis. 1992 Sep-Oct;13(9-10):626–631. doi: 10.1002/elps.11501301128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thierry D., Cave M. D., Eisenach K. D., Crawford J. T., Bates J. H., Gicquel B., Guesdon J. L. IS6110, an IS-like element of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jan 11;18(1):188–188. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.1.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson P. J., Cousins D. V., Gow B. L., Collins D. M., Williamson B. H., Dagnia H. T. Seals, seal trainers, and mycobacterial infection. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 Jan;147(1):164–167. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/147.1.164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamura M., Mizuno S., Toyama H. Taxonomic studies on the Mycobacterium tuberculosis series. Microbiol Immunol. 1985;29(4):285–299. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1985.tb00827.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varnerot A., Clément F., Gheorghiu M., Vincent-Lévy-Frébault V. Pulsed field gel electrophoresis of representatives of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium bovis BCG strains. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Nov 1;77(1-3):155–160. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(92)90148-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. J., Jr, Zhang Y., Brown B. A., Fraser V., Mazurek G. H., Maloney S. DNA large restriction fragment patterns of sporadic and epidemic nosocomial strains of Mycobacterium chelonae and Mycobacterium abscessus. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Oct;31(10):2697–2701. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.10.2697-2701.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieten G., Haverkamp J., Meuzelaar H. L., Engel H. W., Berwald L. G. Pyrolysis mass spectrometry: a new method to differentiate between the mycobacteria of the 'tuberculosis complex' and other mycobacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Jan;122(1):109–118. doi: 10.1099/00221287-122-1-109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates M. D., Collins C. H., Grange J. M. "Classical" and "Asian" variants of Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolated in South East England 1977-1980. Tubercle. 1982 Mar;63(1):55–61. doi: 10.1016/s0041-3879(82)80009-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Mazurek G. H., Cave M. D., Eisenach K. D., Pang Y., Murphy D. T., Wallace R. J., Jr DNA polymorphisms in strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis analyzed by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis: a tool for epidemiology. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jun;30(6):1551–1556. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.6.1551-1556.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Embden J. D., Cave M. D., Crawford J. T., Dale J. W., Eisenach K. D., Gicquel B., Hermans P., Martin C., McAdam R., Shinnick T. M. Strain identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by DNA fingerprinting: recommendations for a standardized methodology. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Feb;31(2):406–409. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.2.406-409.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Soolingen D., de Haas P. E., Hermans P. W., Groenen P. M., van Embden J. D. Comparison of various repetitive DNA elements as genetic markers for strain differentiation and epidemiology of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Aug;31(8):1987–1995. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.8.1987-1995.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Reyn C. F., Maslow J. N., Barber T. W., Falkinham J. O., 3rd, Arbeit R. D. Persistent colonisation of potable water as a source of Mycobacterium avium infection in AIDS. Lancet. 1994 May 7;343(8906):1137–1141. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)90239-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]