Abstract
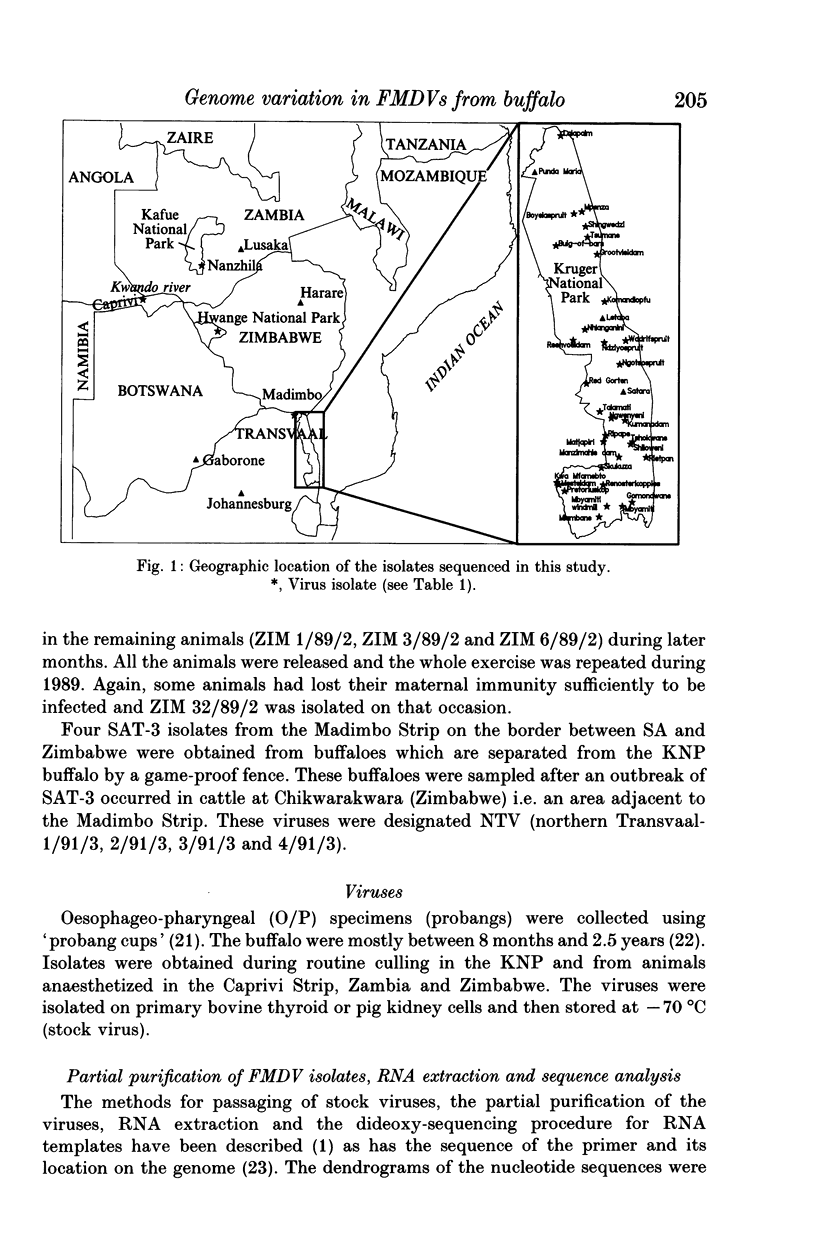
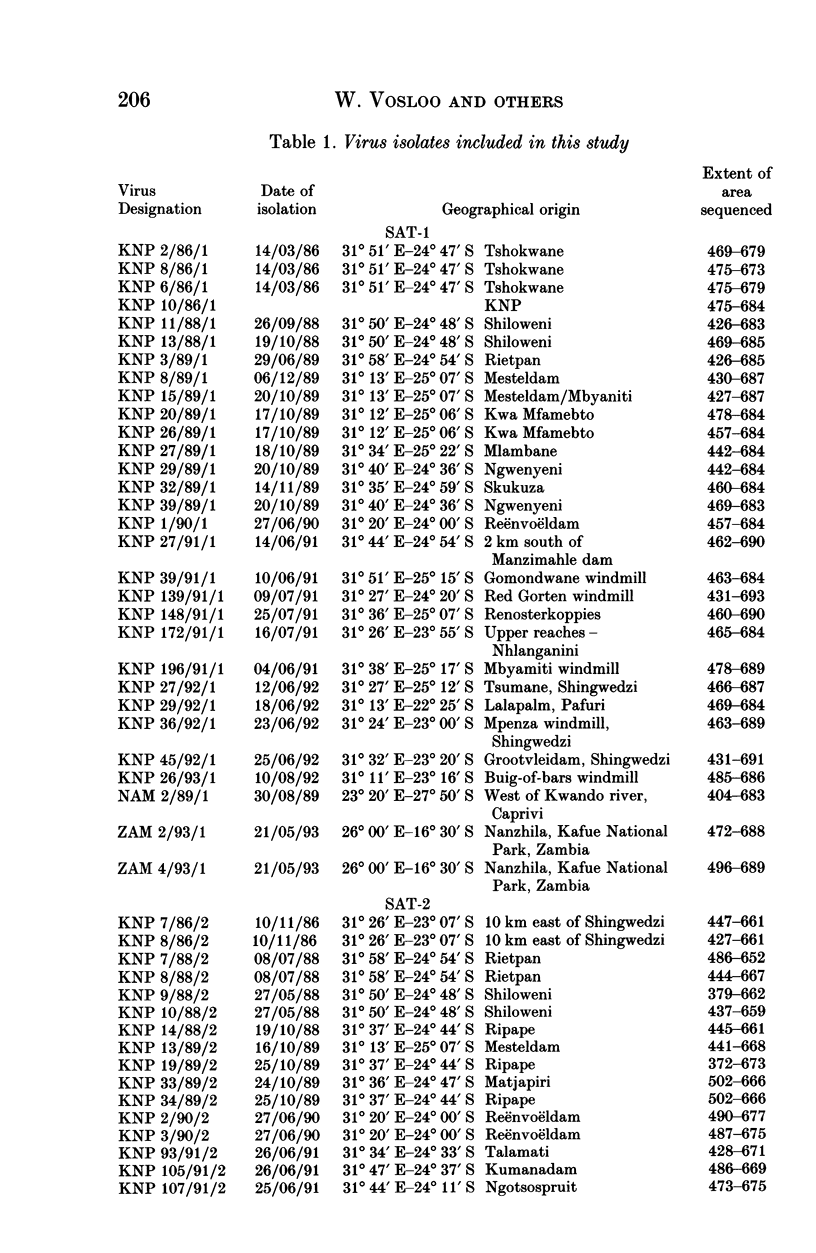
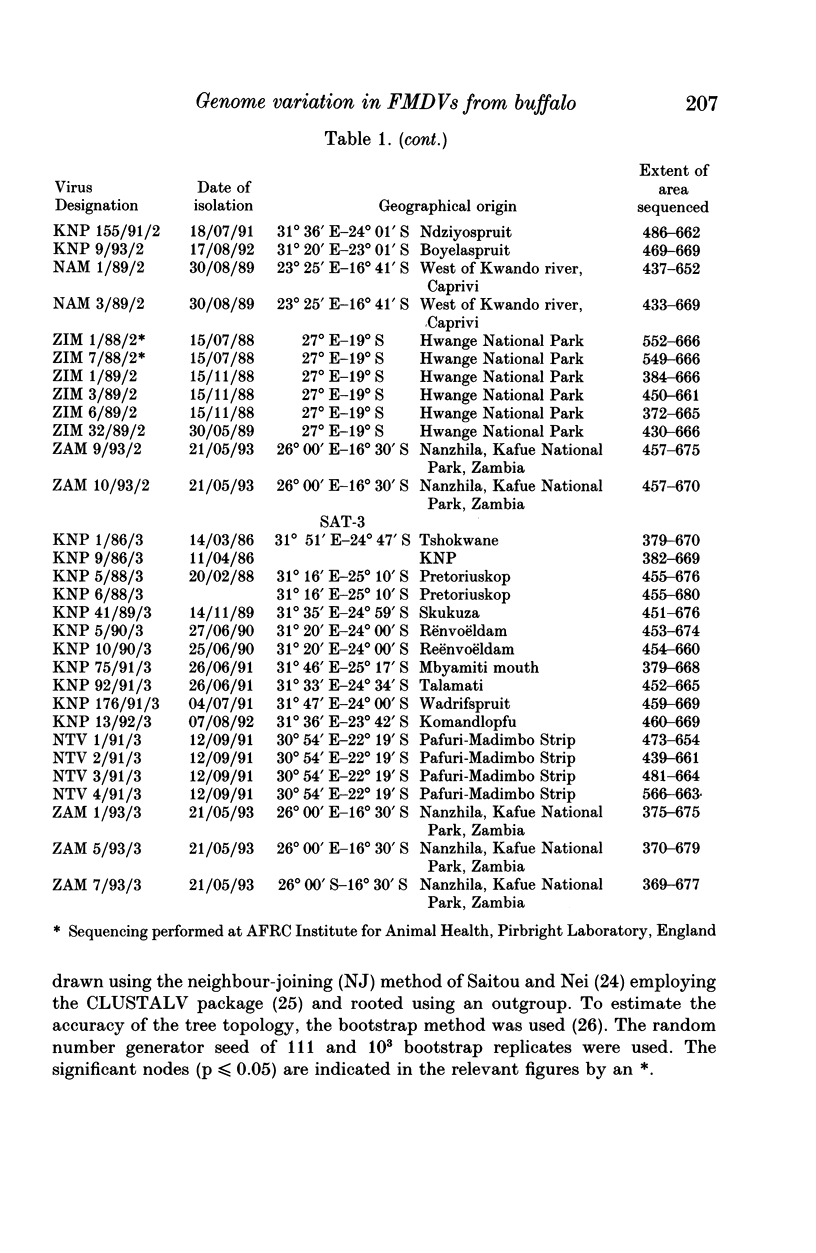
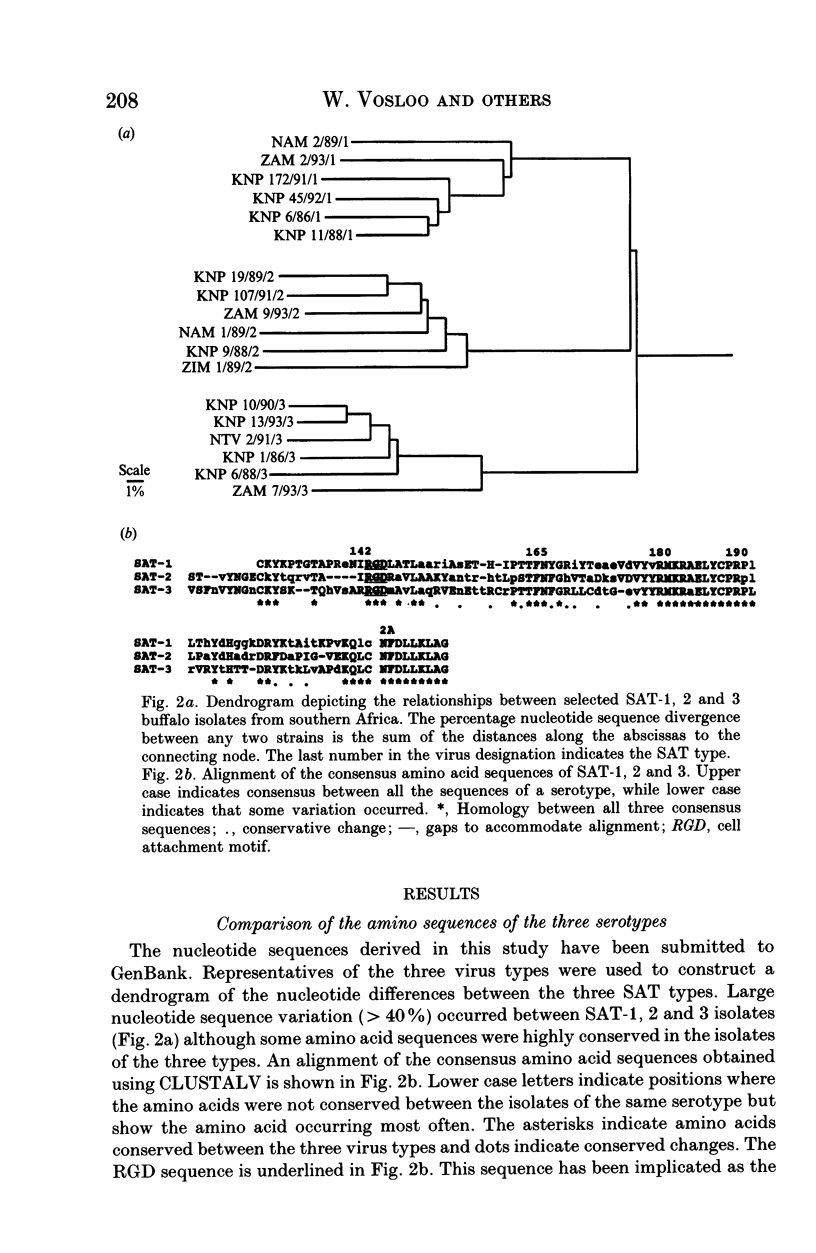
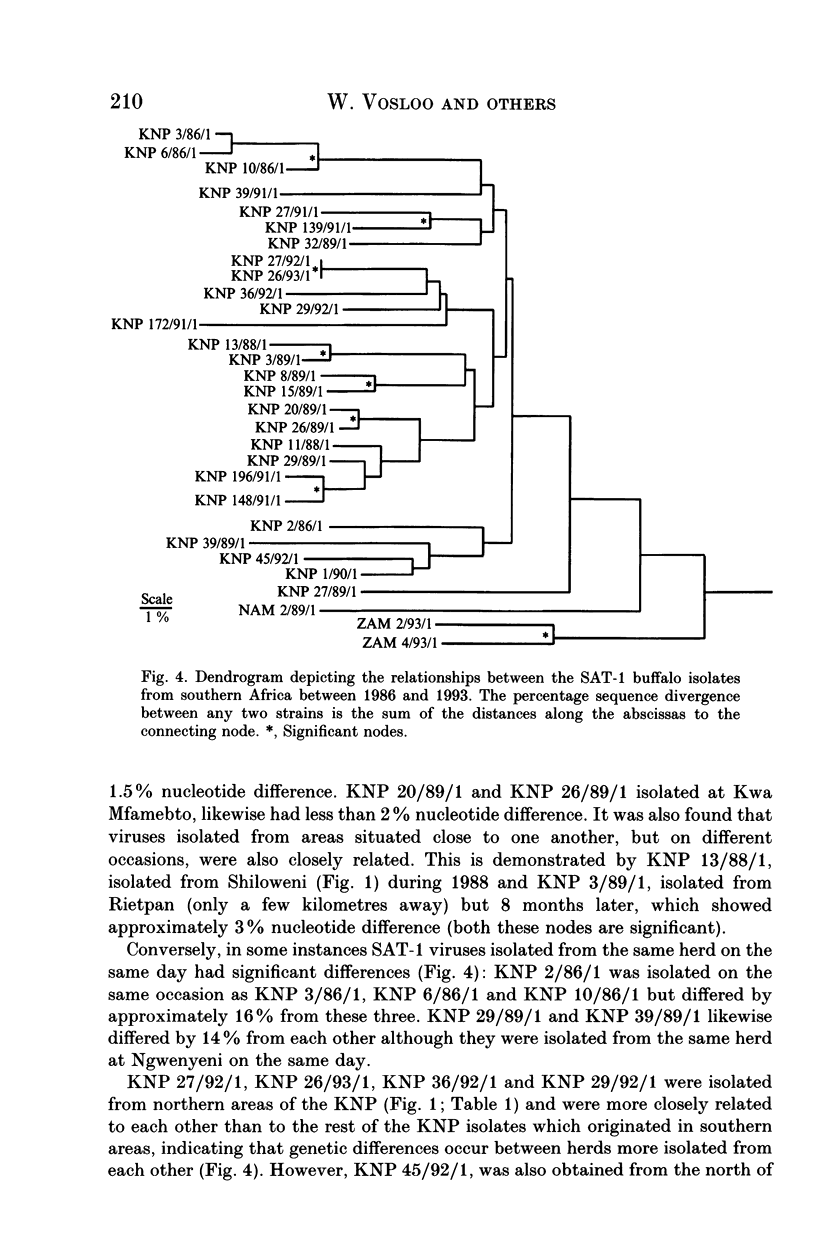
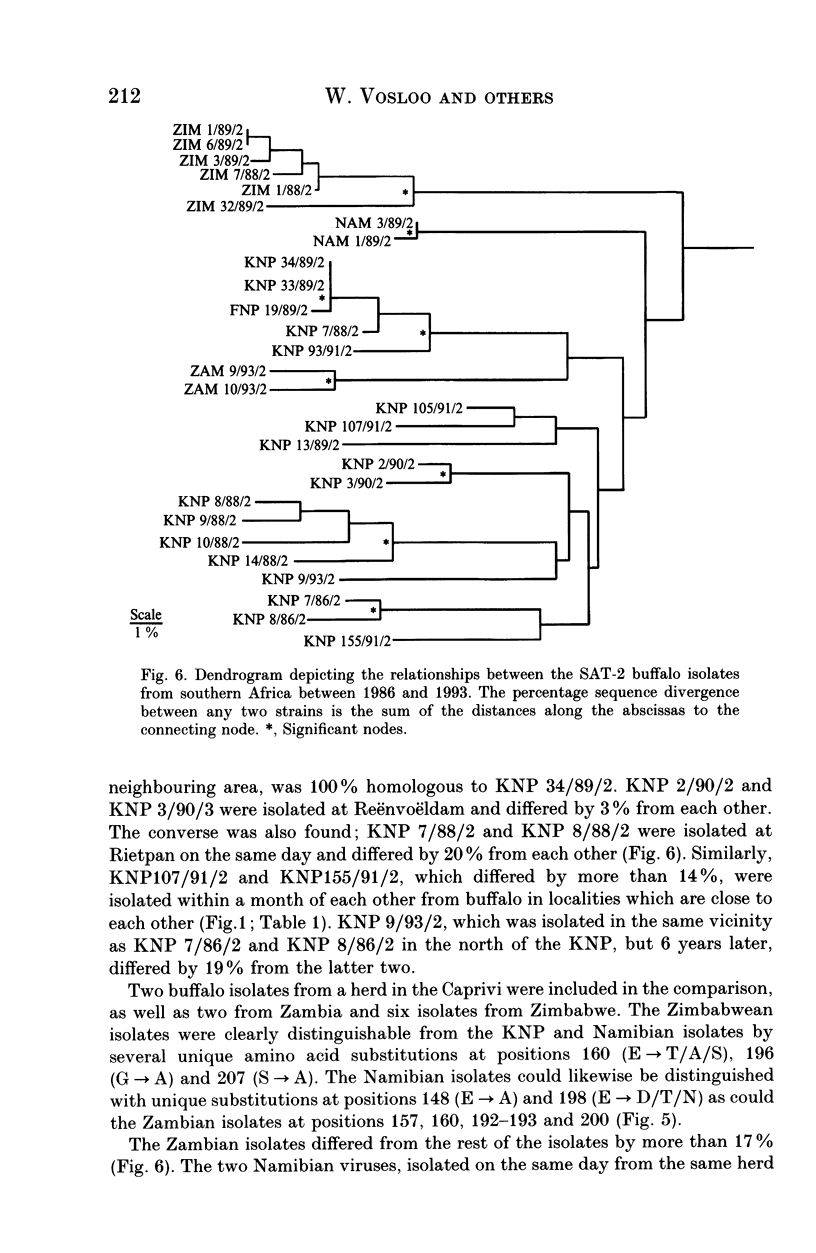
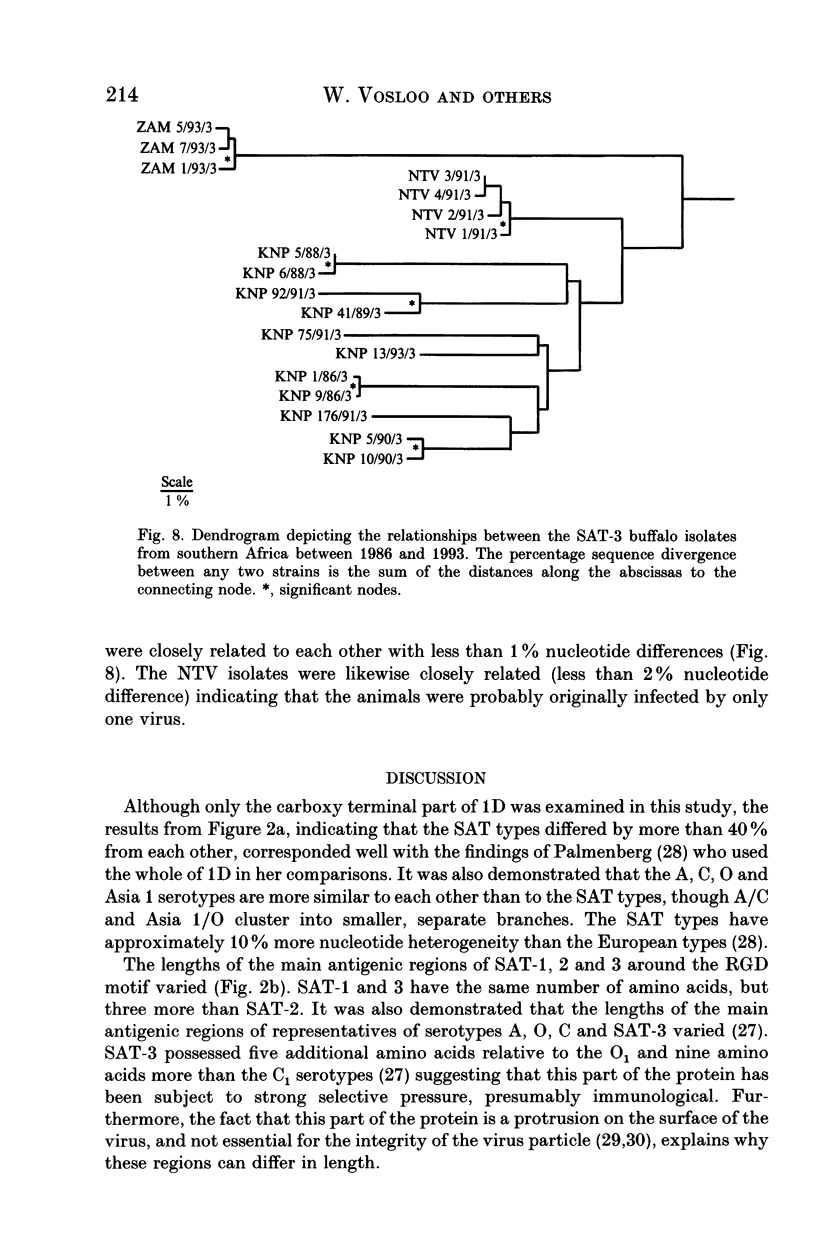
Dideoxy nucleotide sequencing of a portion of the 1D gene of SAT-type foot-and-mouth disease viruses (FMDV) was used to derive phylogenetic relationships between viruses recovered from the oesophageo-pharyngeal secretions of buffalo in the Kruger National Park as well as several other wildlife areas in southern Africa. The three serotypes differed from one another by more than 40% while intratypic variation did not exceed 29%. Within each type, isolates from particular countries were more closely related to one another than to isolates from other countries lending credence to previous observations that FMDV evolve independently in different regions of the subcontinent.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acharya R., Fry E., Stuart D., Fox G., Rowlands D., Brown F. The structure of foot-and-mouth disease virus: implications for its physical and biological properties. Vet Microbiol. 1990 Jun;23(1-4):21–34. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(90)90134-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Acharya R., Fry E., Stuart D., Fox G., Rowlands D., Brown F. The three-dimensional structure of foot-and-mouth disease virus at 2.9 A resolution. Nature. 1989 Feb 23;337(6209):709–716. doi: 10.1038/337709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck E., Strohmaier K. Subtyping of European foot-and-mouth disease virus strains by nucleotide sequence determination. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1621–1629. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1621-1629.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengis R. G., Thomson G. R., Hedger R. S., De Vos V., Pini A. Foot-and-mouth disease and the African buffalo (Syncerus caffer). 1. Carriers as a source of infection for cattle. Onderstepoort J Vet Res. 1986 Jun;53(2):69–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bittle J. L., Houghten R. A., Alexander H., Shinnick T. M., Sutcliffe J. G., Lerner R. A., Rowlands D. J., Brown F. Protection against foot-and-mouth disease by immunization with a chemically synthesized peptide predicted from the viral nucleotide sequence. Nature. 1982 Jul 1;298(5869):30–33. doi: 10.1038/298030a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. L., Campbell R. O., Clarke B. E. The nucleotide sequence of the structural-protein-coding region of foot-and-mouth disease virus serotype SAT3. Gene. 1989 Feb 20;75(2):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90268-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung A., DeLamarter J., Weiss S., Küpper H. Comparison of the major antigenic determinants of different serotypes of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):451–459. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.451-459.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke B. E., Sangar D. V. Processing and assembly of foot-and-mouth disease virus proteins using subgenomic RNA. J Gen Virol. 1988 Sep;69(Pt 9):2313–2325. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-9-2313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condy J. B., Hedger R. S., Hamblin C., Barnett I. T. The duration of the foot-and-mouth disease virus carrier state in African buffalo (i) in the individual animal and (ii) in a free-living herd. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 1985;8(3-4):259–265. doi: 10.1016/0147-9571(85)90004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condy J. B., Hedger R. S. The survival of foot-and-mouth disease virus in African buffalo with non-transference of infection to domestic cattle. Res Vet Sci. 1974 Mar;16(2):182–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G., Parry N. R., Barnett P. V., McGinn B., Rowlands D. J., Brown F. The cell attachment site on foot-and-mouth disease virus includes the amino acid sequence RGD (arginine-glycine-aspartic acid). J Gen Virol. 1989 Mar;70(Pt 3):625–637. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-3-625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedger R. S., Condy J. B. Transmission of foot-and-mouth disease from African buffalo virus carriers to bovines. Vet Rec. 1985 Aug 31;117(9):205–205. doi: 10.1136/vr.117.9.205-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. G., Bleasby A. J., Fuchs R. CLUSTAL V: improved software for multiple sequence alignment. Comput Appl Biosci. 1992 Apr;8(2):189–191. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/8.2.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinnunen L., Pöyry T., Hovi T. Generation of virus genetic lineages during an outbreak of poliomyelitis. J Gen Virol. 1991 Oct;72(Pt 10):2483–2489. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-10-2483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laporte J., Grosclaude J., Wantyghem J., Bernard S., Rouzé P. Neutralisation en culture cellulaire du pouvoir infectieuz du virus de la fièvre aphteuse par des sérums provenant de porcs immunisés à l'aide d'une protéine virale purifiée. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1973 Jun 18;276(25):3399–3401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebermann H., Dölling R., Schmidt D., Thalmann G. RGD-containing peptides of VP1 of foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV) prevent virus infection in vitro. Acta Virol. 1991 Jan;35(1):90–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez M. A., Dopazo J., Hernández J., Mateu M. G., Sobrino F., Domingo E., Knowles N. J. Evolution of the capsid protein genes of foot-and-mouth disease virus: antigenic variation without accumulation of amino acid substitutions over six decades. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3557–3565. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3557-3565.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaff E., Mussgay M., Böhm H. O., Schulz G. E., Schaller H. Antibodies against a preselected peptide recognize and neutralize foot and mouth disease virus. EMBO J. 1982;1(7):869–874. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01262.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rico-Hesse R., Pallansch M. A., Nottay B. K., Kew O. M. Geographic distribution of wild poliovirus type 1 genotypes. Virology. 1987 Oct;160(2):311–322. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90001-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson B. H., Jansen R. W., Khanna B., Totsuka A., Nainan O. V., Siegl G., Widell A., Margolis H. S., Isomura S., Ito K. Genetic relatedness of hepatitis A virus strains recovered from different geographical regions. J Gen Virol. 1992 Jun;73(Pt 6):1365–1377. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-6-1365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan M. D., Belsham G. J., King A. M. Specificity of enzyme-substrate interactions in foot-and-mouth disease virus polyprotein processing. Virology. 1989 Nov;173(1):35–45. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90219-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitou N., Nei M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol. 1987 Jul;4(4):406–425. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel A. R., Knowles N. J., Kitching R. P. Serological and biochemical analysis of some recent type A foot-and-mouth disease virus isolates from the Middle East. Epidemiol Infect. 1988 Dec;101(3):577–590. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800029447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobrino F., Martinez M. A., Carrillo C., Beck E. Antigenic variation of foot-and-mouth disease virus of serotype C during propagation in the field is mainly restricted to only one structural protein (VP1). Virus Res. 1989 Dec;14(4):273–280. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(89)90021-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strohmaier K., Franze R., Adam K. H. Location and characterization of the antigenic portion of the FMDV immunizing protein. J Gen Virol. 1982 Apr;59(Pt 2):295–306. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-59-2-295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutmoller P., Gaggero A. Foot-and mouth diseases carriers. Vet Rec. 1965 Aug 14;77(33):968–969. doi: 10.1136/vr.77.33.968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson G. R., Vosloo W., Esterhuysen J. J., Bengis R. G. Maintenance of foot and mouth disease viruses in buffalo (Syncerus caffer Sparrman, 1779) in southern Africa. Rev Sci Tech. 1992 Dec;11(4):1097–1107. doi: 10.20506/rst.11.4.646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vosloo W., Knowles N. J., Thomson G. R. Genetic relationships between southern African SAT-2 isolates of foot-and-mouth-disease virus. Epidemiol Infect. 1992 Dec;109(3):547–558. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800050536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


