Abstract
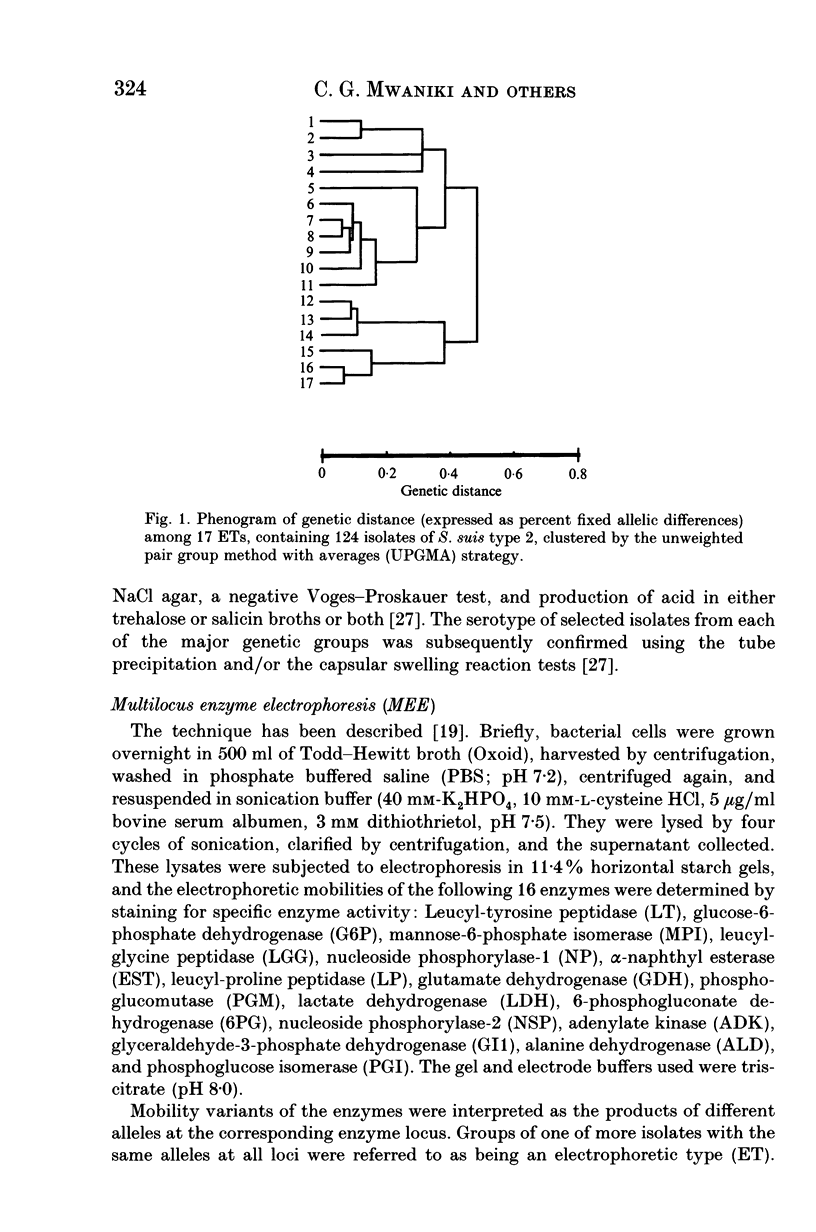
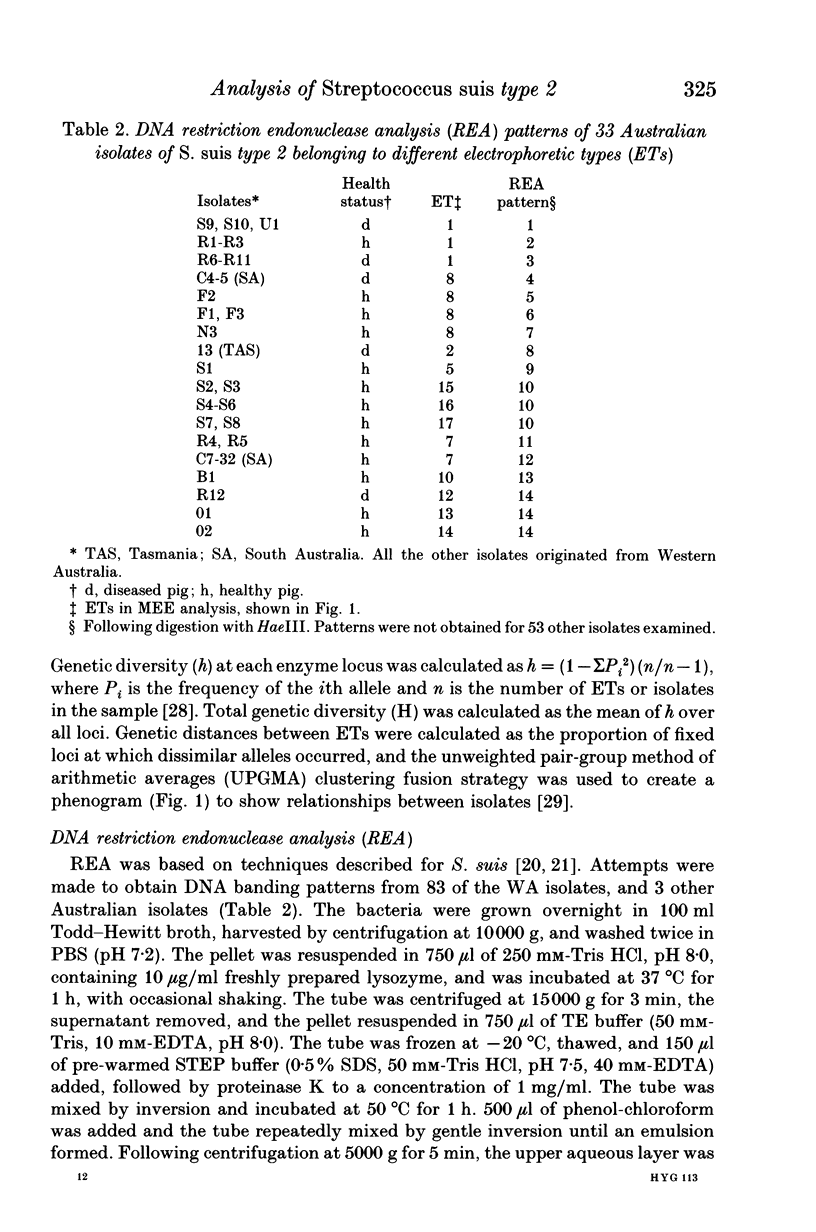
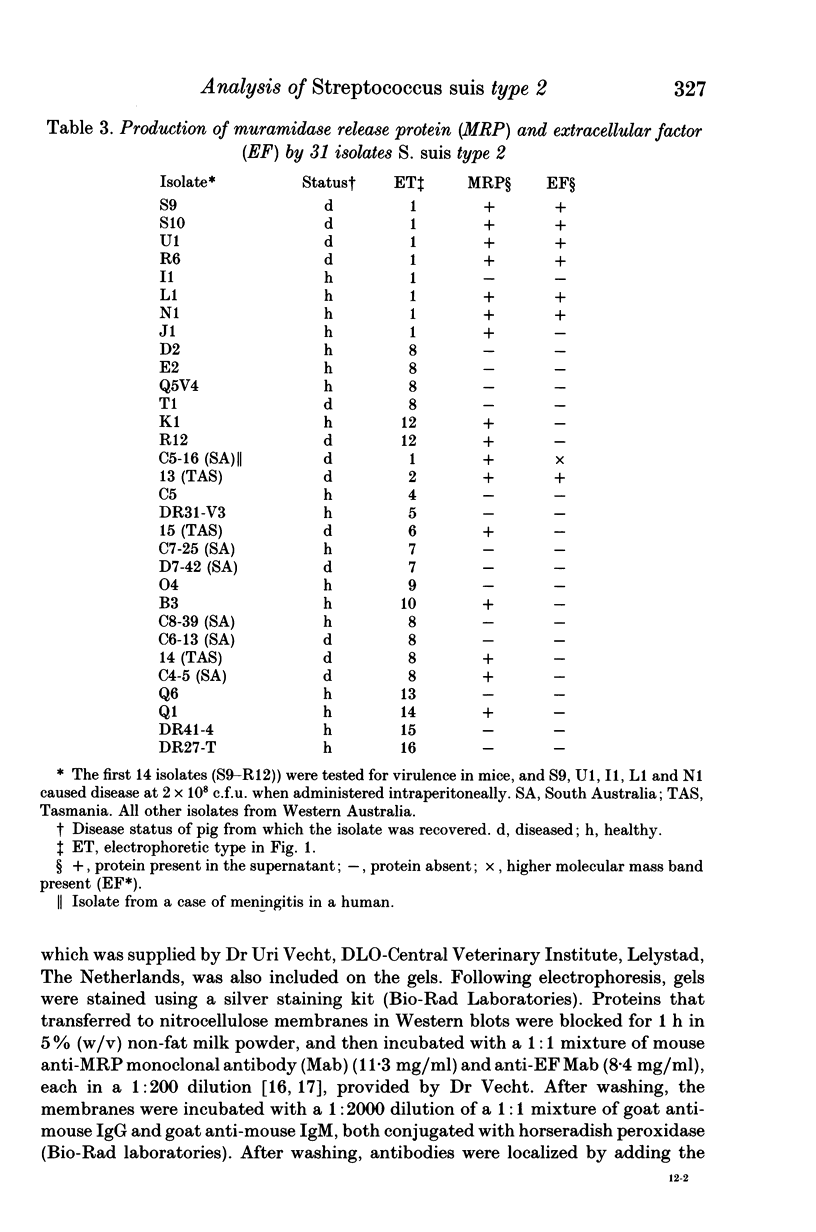
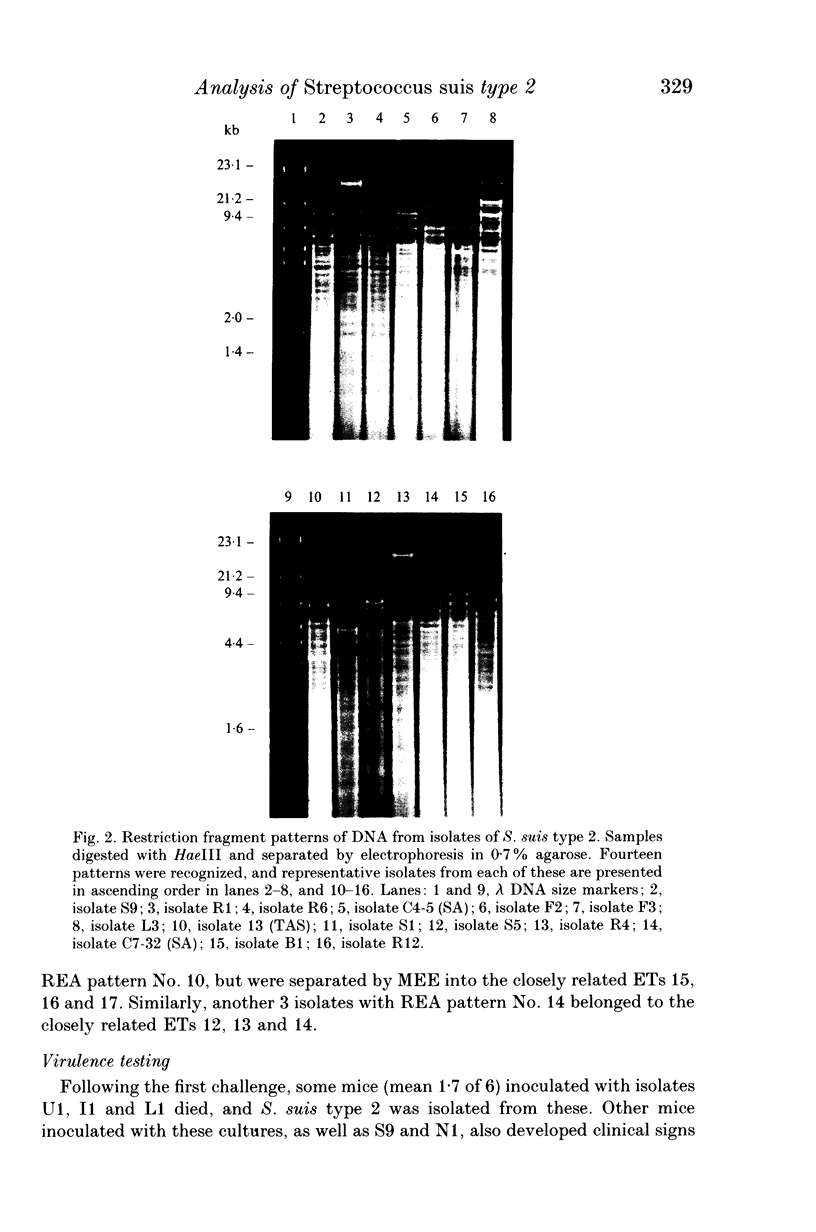
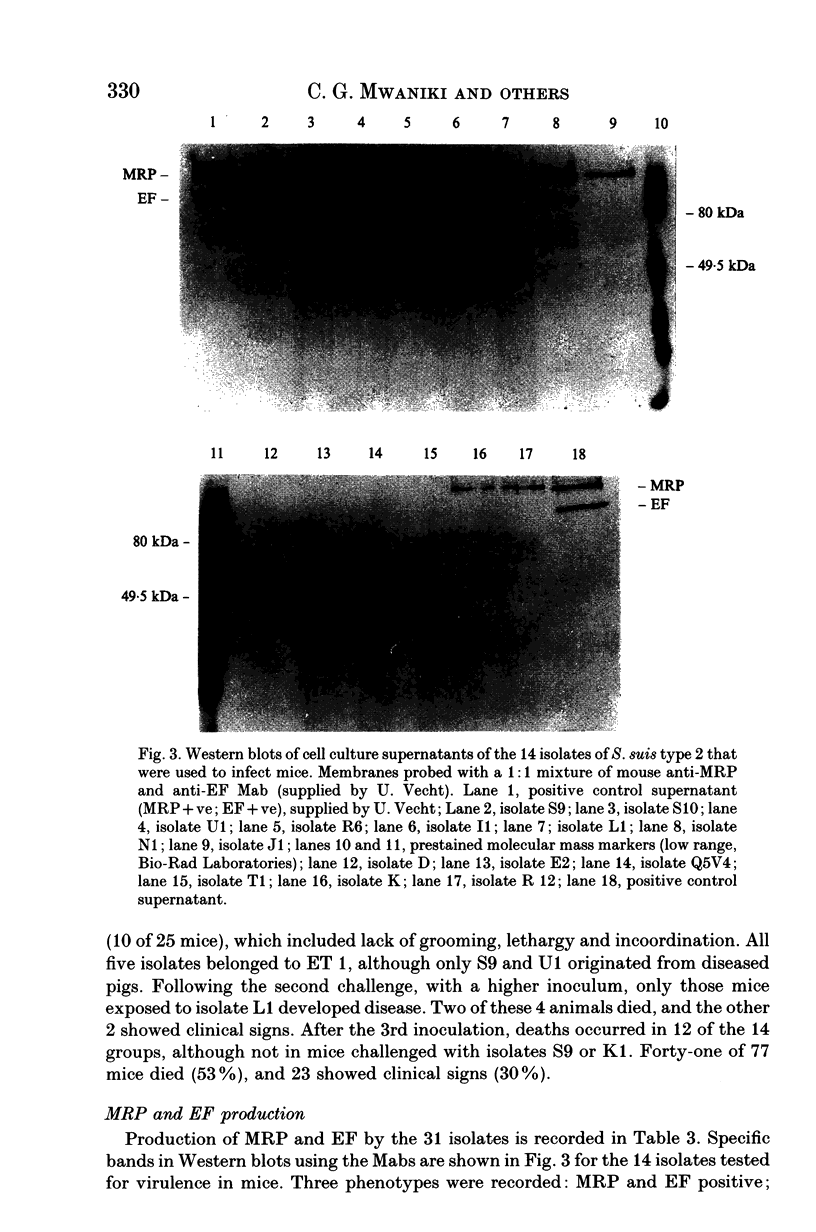
Multilocus enzyme electrophoresis was used to divide 124 Australian isolates of Streptococcus suis type 2 into 17 electrophoretic types (ETs). Isolates in ET 1 were the most frequent cause of disease amongst Western Australian pigs, but isolates of ET 8 were more commonly associated with disease in other Australian states. Multiple isolates from 10 of 19 farms all belonged to the same ET, whilst isolates from the other farms belonged to between 2 and 4 different ETs. Some isolates could be differentiated further by DNA restriction endonuclease analysis, whilst others with the same restriction pattern were located in different, but closely-related ETs. Fourteen isolates were tested for their virulence in mice. Most caused disease if given in high numbers, but isolates in ET 1 were virulent at lower dose rates. This virulent clone also was distinguished by the fact that 80% of isolates produced extracellular factor (EF).
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beaudoin M., Harel J., Higgins R., Gottschalk M., Frenette M., MacInnes J. I. Molecular analysis of isolates of Streptococcus suis capsular type 2 by restriction-endonuclease-digested DNA separated on SDS-PAGE and by hybridization with an rDNA probe. J Gen Microbiol. 1992 Dec;138(12):2639–2645. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-12-2639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clifton-Hadley F. A., Alexander T. J., Enright M. R., Guise J. Monitoring herds for Streptococcus suis type 2 by sampling tonsils of slaughter pigs. Vet Rec. 1984 Dec 1;115(22):562–564. doi: 10.1136/vr.115.22.562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clifton-Hadley F. A., Alexander T. J. The carrier site and carrier rate of Streptococcus suis type II in pigs. Vet Rec. 1980 Jul 12;107(2):40–41. doi: 10.1136/vr.107.2.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P. R., Ossowicz C. J. Evaluation of methods used for detecting Streptococcus suis type 2 in tonsils, and investigation of the carrier state in pigs. Res Vet Sci. 1991 Mar;50(2):190–194. doi: 10.1016/0034-5288(91)90104-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschalk M., Higgins R., Jacques M., Beaudoin M., Henrichsen J. Characterization of six new capsular types (23 through 28) of Streptococcus suis. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Nov;29(11):2590–2594. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.11.2590-2594.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschalk M., Higgins R., Jacques M., Mittal K. R., Henrichsen J. Description of 14 new capsular types of Streptococcus suis. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2633–2636. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2633-2636.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampson D. J., Trott D. J., Clarke I. L., Mwaniki C. G., Robertson I. D. Population structure of Australian isolates of Streptococcus suis. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Nov;31(11):2895–2900. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.11.2895-2900.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins R., Gottschalk M. An update on Streptococcus suis identification. J Vet Diagn Invest. 1990 Jul;2(3):249–252. doi: 10.1177/104063879000200324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kebede M., Chengappa M. M., Stuart J. G. Isolation and characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of Streptococcus suis: efficacy trial of the mutant vaccine in mice. Vet Microbiol. 1990 Apr;22(2-3):249–257. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(90)90112-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamont M. H., Edwards P. T., Windsor R. S. Streptococcal meningitis in pigs: results of a five-year survey. Vet Rec. 1980 Nov 15;107(20):467–469. doi: 10.1136/vr.107.20.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogollon J. D., Pijoan C., Murtaugh M. P., Collins J. E., Cleary P. P. Identification of epidemic strains of Streptococcus suis by genomic fingerprinting. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Apr;29(4):782–787. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.4.782-787.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogollon J. D., Pijoan C., Murtaugh M. P., Kaplan E. L., Collins J. E., Cleary P. P. Characterization of prototype and clinically defined strains of Streptococcus suis by genomic fingerprinting. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Nov;28(11):2462–2466. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.11.2462-2466.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau A., Higgins R., Bigras-Poulin M., Nadeau M. Rapid detection of Streptococcus suis serotype 2 in weaned pigs. Am J Vet Res. 1989 Oct;50(10):1667–1671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei M. Estimation of average heterozygosity and genetic distance from a small number of individuals. Genetics. 1978 Jul;89(3):583–590. doi: 10.1093/genetics/89.3.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perch B., Pedersen K. B., Henrichsen J. Serology of capsulated streptococci pathogenic for pigs: six new serotypes of Streptococcus suis. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jun;17(6):993–996. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.6.993-996.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson I. D., Blackmore D. K. Experimental studies on the comparative infectivity and pathogenicity of Streptococcus suis type 2. II. Porcine and human isolates in laboratory animals. Epidemiol Infect. 1990 Dec;105(3):479–484. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800048093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson I. D., Blackmore D. K., Hampson D. J., Fu Z. F. A longitudinal study of natural infection of piglets with Streptococcus suis types 1 and 2. Epidemiol Infect. 1991 Aug;107(1):119–126. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800048743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson I. D., Blackmore D. K. Prevalence of Streptococcus suis types 1 and 2 in domestic pigs in Australia and New Zealand. Vet Rec. 1989 Apr 15;124(15):391–394. doi: 10.1136/vr.124.15.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., Caugant D. A., Ochman H., Musser J. M., Gilmour M. N., Whittam T. S. Methods of multilocus enzyme electrophoresis for bacterial population genetics and systematics. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 May;51(5):873–884. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.5.873-884.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sihvonen L., Kurl D. N., Henrichsen J. Streptococcus suis isolated from pigs in Finland. Acta Vet Scand. 1988;29(1):9–13. doi: 10.1186/BF03548386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touil F., Higgins R., Nadeau M. Isolation of Streptococcus suis from diseased pigs in Canada. Vet Microbiol. 1988 Jun;17(2):171–177. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(88)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vecht U., Arends J. P., van der Molen E. J., van Leengoed L. A. Differences in virulence between two strains of Streptococcus suis type II after experimentally induced infection of newborn germ-free pigs. Am J Vet Res. 1989 Jul;50(7):1037–1043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vecht U., Wisselink H. J., Jellema M. L., Smith H. E. Identification of two proteins associated with virulence of Streptococcus suis type 2. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):3156–3162. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.3156-3162.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vecht U., Wisselink H. J., van Dijk J. E., Smith H. E. Virulence of Streptococcus suis type 2 strains in newborn germfree pigs depends on phenotype. Infect Immun. 1992 Feb;60(2):550–556. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.2.550-556.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. E., Blakemore W. F., Alexander T. J. A murine model of Streptococcus suis type 2 meningitis in the pig. Res Vet Sci. 1988 Nov;45(3):394–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
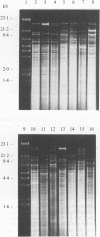
- Windsor R. S., Elliott S. D. Streptococcal infection in young pigs. IV. An outbreak of streptococcal meningitis in weaned pigs. J Hyg (Lond) 1975 Aug;75(1):69–78. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400047070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]