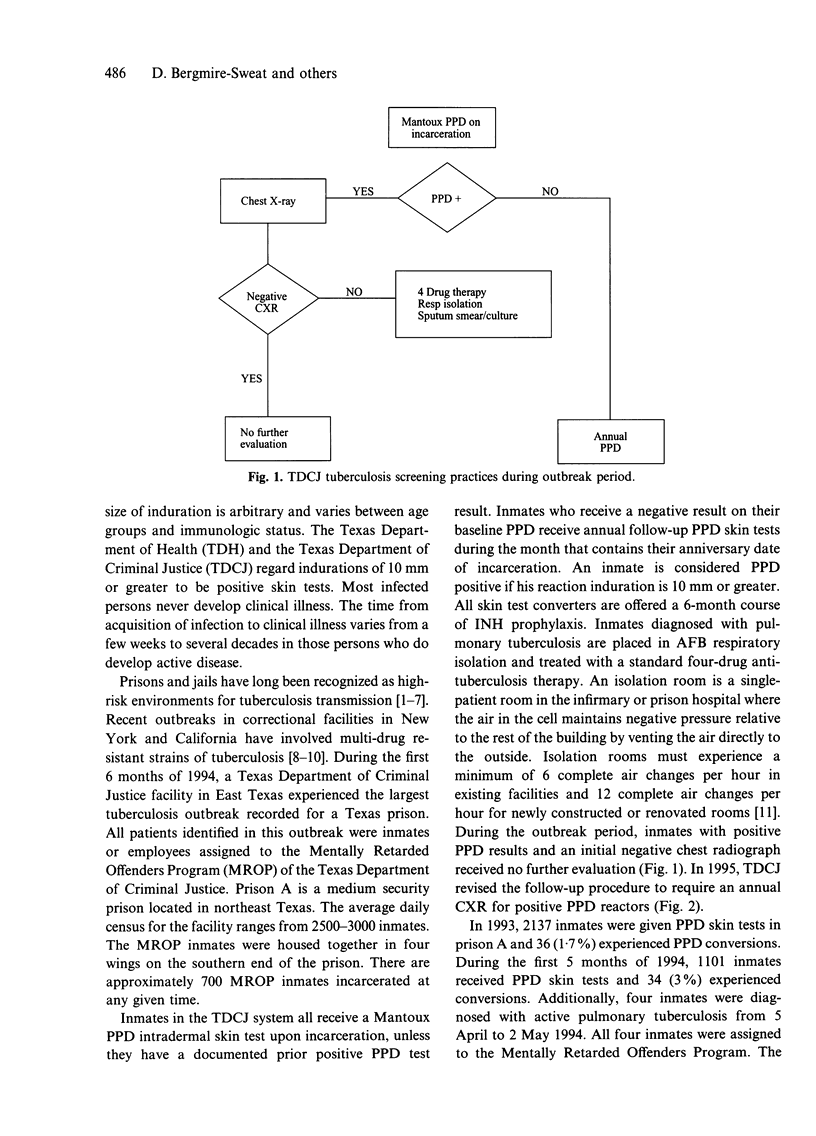
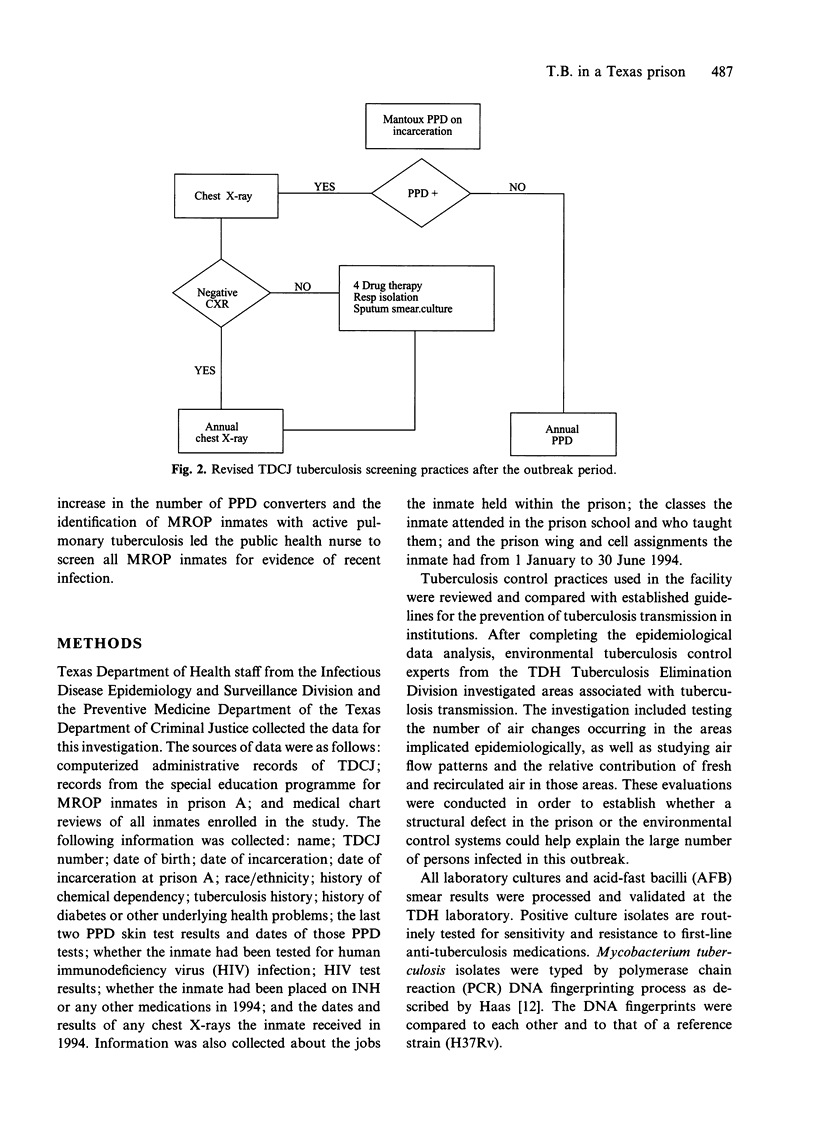
Abstract
In 1994 a Texas prison containing a population of mentally retarded inmates experienced a large tuberculosis outbreak. Fifteen cases of tuberculosis were identified (8 confirmed by positive cultures for Mycobacterium tuberculosis) and more than 100 inmates became infected. The culture-confirmed patients were infected with an identical strain of tuberculosis as demonstrated by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) based DNA fingerprinting technique. The prison followed standard tuberculosis infection control policies, but these controls were inadequate to prevent tuberculosis transmission in this special population. Two hundred and thirty inmates (119 inmates showing evidence of new tuberculosis infection or active disease and 111 healthy controls) were enrolled in the investigation. Inmate cell assignments, job duties, and educational classes were identified and medical chart reviews were conducted on all inmates. Tuberculosis transmission was associated with residing on the D Wing of the prison (OR = 25.84, P < 0.01), attending school in Classroom A (OR = 8.34, P = 0.01) and working on the prison utility work crew (OR = 2.52, P < 0.01). The index case in the outbreak had been prescribed 6 months of isoniazid (INH) chemoprophylaxis in 1988.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abeles H., Feibes H., Mandel E., Girard J. A. The large city prison--a reservoir of tuberculosis. Tuberculosis control among sentenced male prisoners in New York City. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1970 May;101(5):706–709. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1970.101.5.706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellin E. Y., Fletcher D. D., Safyer S. M. Association of tuberculosis infection with increased time in or admission to the New York City jail system. JAMA. 1993 May 5;269(17):2228–2231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun M. M., Truman B. I., Maguire B., DiFerdinando G. T., Jr, Wormser G., Broaddus R., Morse D. L. Increasing incidence of tuberculosis in a prison inmate population. Association with HIV infection. JAMA. 1989 Jan 20;261(3):393–397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredin C. P., Godfrey M., McKiernan J. A school microepidemic of tuberculosis. Thorax. 1991 Dec;46(12):922–923. doi: 10.1136/thx.46.12.922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control (CDC) Prevention and control of tuberculosis in correctional institutions: recommendations of the Advisory Committee for the Elimination of Tuberculosis. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1989 May 12;38(18):313-20, 325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Probable transmission of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in a correctional facility--California. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1993 Jan 29;42(3):48–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly K., Murphy C. A school outbreak of tuberculosis. Ir Med J. 1987 Dec;80(12):415–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drobniewski F. Tuberculosis in prisons--forgotten plague. Lancet. 1995 Oct 7;346(8980):948–949. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(95)91562-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas W. H., Butler W. R., Woodley C. L., Crawford J. T. Mixed-linker polymerase chain reaction: a new method for rapid fingerprinting of isolates of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 May;31(5):1293–1298. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.5.1293-1298.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoge C. W., Fisher L., Donnell H. D., Jr, Dodson D. R., Tomlinson G. V., Jr, Breiman R. F., Bloch A. B., Good R. C. Risk factors for transmission of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in a primary school outbreak: lack of racial difference in susceptibility to infection. Am J Epidemiol. 1994 Mar 1;139(5):520–530. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a117035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King L., Geis G. Tuberculosis transmission in a large urban jail. JAMA. 1977 Feb 21;237(8):791–792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier A. R., DiFerdinando G. T., Jr, Greenberg A. J., Sosin D. M., Jones W. D., Jr, Bloch A. B., Woodley C. L. Tuberculosis in a correctional facility. Arch Intern Med. 1993 Dec 13;153(23):2692–2695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks J. J., Brenner E. R., Breeden D. C., Anders H. M., Parker R. L. Epidemiology of a tuberculosis outbreak in a South Carolina junior high school. Am J Public Health. 1985 Apr;75(4):361–365. doi: 10.2105/ajph.75.4.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stead W. W. Special problems in tuberculosis. Tuberculosis in the elderly and in residents of nursing homes, correctional facilities, long-term care hospitals, mental hospitals, shelters for the homeless, and jails. Clin Chest Med. 1989 Sep;10(3):397–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valway S. E., Greifinger R. B., Papania M., Kilburn J. O., Woodley C., DiFerdinando G. T., Dooley S. W. Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in the New York State prison system, 1990-1991. J Infect Dis. 1994 Jul;170(1):151–156. doi: 10.1093/infdis/170.1.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valway S. E., Richards S. B., Kovacovich J., Greifinger R. B., Crawford J. T., Dooley S. W. Outbreak of multi-drug-resistant tuberculosis in a New York State prison, 1991. Am J Epidemiol. 1994 Jul 15;140(2):113–122. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a117222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wales J. M., Buchan A. R., Cookson J. B., Jones D. A., Marshall B. S. Tuberculosis in a primary school: the Uppingham outbreak. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 Oct 12;291(6501):1039–1040. doi: 10.1136/bmj.291.6501.1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]