Abstract
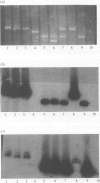
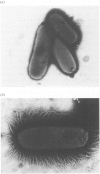
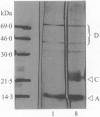
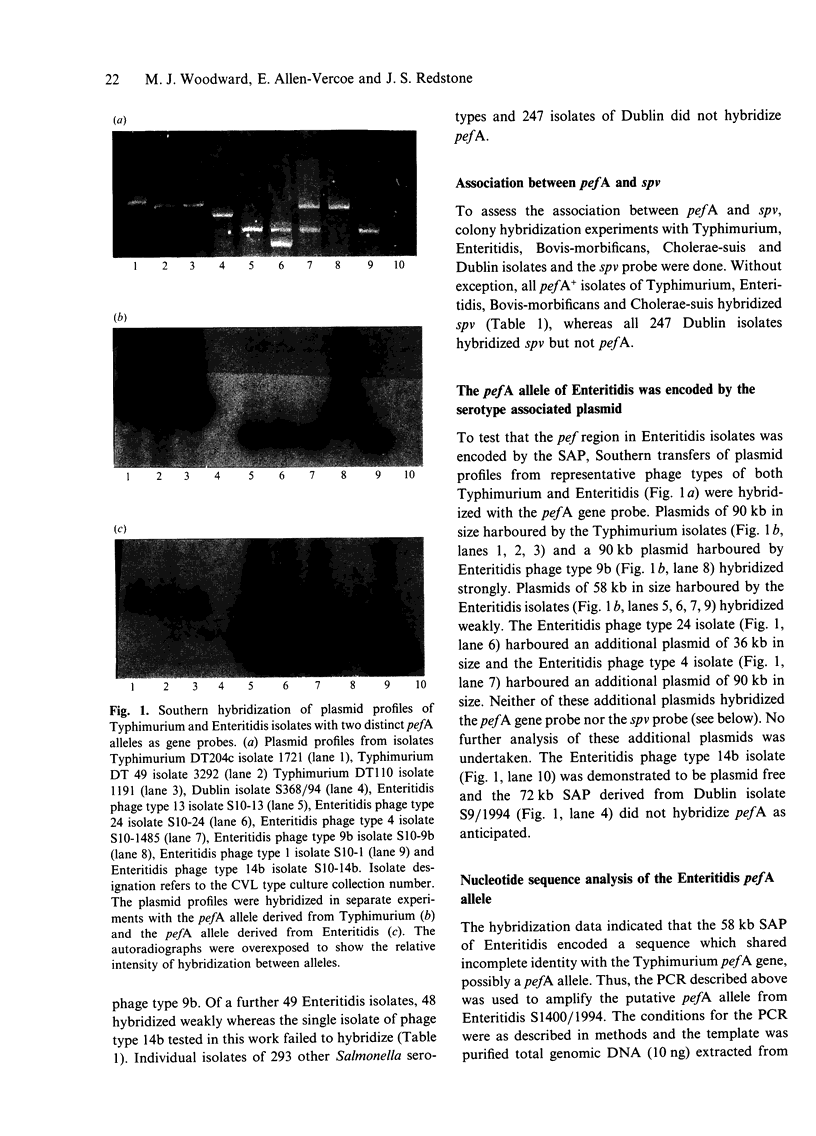
The pefA gene which encoded the serotype associated plasmid (SAP) mediated fimbrial major subunit antigen of Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium shared genetic identity with 128 of 706 salmonella isolates as demonstrated by dot (colony) hybridization. Seventy-seven of 113 isolates of Typhimurium and individual isolates of serotypes Bovis-morbificans, Cholerae-suis and Enteritidis phage type 9b hybridized pefA strongly, whereas 48 isolates of Enteritidis hybridized pefA weakly and one Enteritidis isolate of phage type 14b failed to hybridize. Individual isolates of 294 serotypes and 247 individual isolates of serotype Dublin did not hybridize pefA. Southern hybridization of plasmids extracted from Enteritidis demonstrated that the pefA gene probe hybridized strongly an atypical SAP of 80 kb in size harboured by one Enteritidis isolate of phage-type 9b, whereas the typical SAP of 58 kb in size harboured by 48 Enteritidis isolates hybridized weakly. One Enteritidis isolate of phage type 14b which failed to hybridize pefA in dot (colony) hybridization experiments was demonstrated to be plasmid free. A cosmid library of Enteritidis phage type 4 expressed in Escherichia coli K12 was screened by hybridization for the presence of pef sequences. Recombinant clones which were deduced to harbour the entire pef operon elaborated a PEF-like fimbrial structure at the cell surface. The PEF-like fimbrial antigen was purified from one cosmid clone and used in western blot experiments with sera from chickens infected with Enteritidis phage-type 4. Seroconversion to the fimbrial antigen was observed which indicated that the Enteritidis PEF-like fimbrial structure was expressed at some stage during infection. Nucleotide sequence analysis demonstrated that the pefA alleles of Typhimurium and Enteritidis phage-type 4 shared 76% DNA nucleotide and 82% deduced amino acid sequence identity.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnqvist A., Olsén A., Pfeifer J., Russell D. G., Normark S. The Crl protein activates cryptic genes for curli formation and fibronectin binding in Escherichia coli HB101. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Sep;6(17):2443–2452. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01420.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buisán M., Rodríguez-Peña J. M., Rotger R. Restriction map of the Salmonella enteritidis virulence plasmid and its homology with the plasmid of Salmonella typhimurium. Microb Pathog. 1994 Feb;16(2):165–169. doi: 10.1006/mpat.1994.1017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bäumler A. J., Heffron F. Identification and sequence analysis of lpfABCDE, a putative fimbrial operon of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1995 Apr;177(8):2087–2097. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.8.2087-2097.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bäumler A. J., Tsolis R. M., Bowe F. A., Kusters J. G., Hoffmann S., Heffron F. The pef fimbrial operon of Salmonella typhimurium mediates adhesion to murine small intestine and is necessary for fluid accumulation in the infant mouse. Infect Immun. 1996 Jan;64(1):61–68. doi: 10.1128/iai.64.1.61-68.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clouthier S. C., Collinson S. K., Kay W. W. Unique fimbriae-like structures encoded by sefD of the SEF14 fimbrial gene cluster of Salmonella enteritidis. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Jun;12(6):893–901. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb01077.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collinson S. K., Clouthier S. C., Doran J. L., Banser P. A., Kay W. W. Salmonella enteritidis agfBAC operon encoding thin, aggregative fimbriae. J Bacteriol. 1996 Feb;178(3):662–667. doi: 10.1128/jb.178.3.662-667.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collinson S. K., Doig P. C., Doran J. L., Clouthier S., Trust T. J., Kay W. W. Thin, aggregative fimbriae mediate binding of Salmonella enteritidis to fibronectin. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jan;175(1):12–18. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.1.12-18.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper G. L., Venables L. M., Woodward M. J., Hormaeche C. E. Invasiveness and persistence of Salmonella enteritidis, Salmonella typhimurium, and a genetically defined S. enteritidis aroA strain in young chickens. Infect Immun. 1994 Nov;62(11):4739–4746. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.11.4739-4746.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnenberg M. S., Girón J. A., Nataro J. P., Kaper J. B. A plasmid-encoded type IV fimbrial gene of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli associated with localized adherence. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Nov;6(22):3427–3437. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb02210.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doran J. L., Collinson S. K., Burian J., Sarlós G., Todd E. C., Munro C. K., Kay C. M., Banser P. A., Peterkin P. I., Kay W. W. DNA-based diagnostic tests for Salmonella species targeting agfA, the structural gene for thin, aggregative fimbriae. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Sep;31(9):2263–2273. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.9.2263-2273.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsinghorst E. A., Baron L. S., Kopecko D. J. Penetration of human intestinal epithelial cells by Salmonella: molecular cloning and expression of Salmonella typhi invasion determinants in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5173–5177. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich M. J., Kinsey N. E., Vila J., Kadner R. J. Nucleotide sequence of a 13.9 kb segment of the 90 kb virulence plasmid of Salmonella typhimurium: the presence of fimbrial biosynthetic genes. Mol Microbiol. 1993 May;8(3):543–558. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galán J. E., Curtiss R., 3rd Cloning and molecular characterization of genes whose products allow Salmonella typhimurium to penetrate tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6383–6387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginocchio C. C., Olmsted S. B., Wells C. L., Galán J. E. Contact with epithelial cells induces the formation of surface appendages on Salmonella typhimurium. Cell. 1994 Feb 25;76(4):717–724. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90510-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulig P. A., Danbara H., Guiney D. G., Lax A. J., Norel F., Rhen M. Molecular analysis of spv virulence genes of the Salmonella virulence plasmids. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Mar;7(6):825–830. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01172.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulig P. A. Virulence plasmids of Salmonella typhimurium and other salmonellae. Microb Pathog. 1990 Jan;8(1):3–11. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kukkonen M., Raunio T., Virkola R., Lähteenmäki K., Mäkelä P. H., Klemm P., Clegg S., Korhonen T. K. Basement membrane carbohydrate as a target for bacterial adhesion: binding of type I fimbriae of Salmonella enterica and Escherichia coli to laminin. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Jan;7(2):229–237. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01114.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lax A. J., Pullinger G. D., Baird G. D., Williamson C. M. The virulence plasmid of Salmonella dublin: detailed restriction map and analysis by transposon mutagenesis. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Jun;136(6):1117–1123. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-6-1117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. A., Jones B. D., Falkow S. Identification of a Salmonella typhimurium invasion locus by selection for hyperinvasive mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1847–1851. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppard K., Totty N., Waterfield M., Harlow E., Jenkins J., Crawford L. Purification and partial amino acid sequence analysis of the cellular tumour antigen, p53, from mouse SV40-transformed cells. EMBO J. 1983;2(11):1993–1999. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01690.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockman H. A., Curtiss R., 3rd Virulence of non-type 1-fimbriated and nonfimbriated nonflagellated Salmonella typhimurium mutants in murine typhoid fever. Infect Immun. 1992 Feb;60(2):491–496. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.2.491-496.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michiels T., Popoff M. Y., Durviaux S., Coynault C., Cornelis G. A new method for the physical and genetic mapping of large plasmids: application to the localisation of the virulence determinants on the 90 kb plasmid of Salmonella typhimurium. Microb Pathog. 1987 Aug;3(2):109–116. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsén A., Arnqvist A., Hammar M., Sukupolvi S., Normark S. The RpoS sigma factor relieves H-NS-mediated transcriptional repression of csgA, the subunit gene of fibronectin-binding curli in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Feb;7(4):523–536. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01143.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardon P., Popoff M. Y., Coynault C., Marly J., Miras I. Virulence-associated plasmids of Salmonella serotype Typhimurium in experimental murine infection. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1986 Jul-Aug;137B(1):47–60. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(86)80093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pullinger G. D., Lax A. J. A Salmonella dublin virulence plasmid locus that affects bacterial growth under nutrient-limited conditions. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Jun;6(12):1631–1643. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb00888.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rankin S. C., Benson C. E., Platt D. J. The distribution of serotype-specific plasmids among different subgroups of strains of Salmonella enterica serotype Enteritidis: characterization of molecular variants by restriction enzyme fragmentation patterns. Epidemiol Infect. 1995 Feb;114(1):25–40. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800051888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhen M., Riikonen P., Taira S. Transcriptional regulation of Salmonella enterica virulence plasmid genes in cultured macrophages. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Oct;10(1):45–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb00902.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sizemore D. R., Fink P. S., Ou J. T., Baron L., Kopecko D. J., Warren R. L. Tn5 mutagenesis of the Salmonella typhimurium 100 kb plasmid: definition of new virulence regions. Microb Pathog. 1991 Jun;10(6):493–499. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(91)90116-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sohel I., Puente J. L., Murray W. J., Vuopio-Varkila J., Schoolnik G. K. Cloning and characterization of the bundle-forming pilin gene of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli and its distribution in Salmonella serotypes. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Feb;7(4):563–575. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01147.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi A. Electron microscope studies of experimental Salmonella infection. I. Penetration into the intestinal epithelium by Salmonella typhimurium. Am J Pathol. 1967 Jan;50(1):109–136. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorns C. J., Sojka M. G., Chasey D. Detection of a novel fimbrial structure on the surface of Salmonella enteritidis by using a monoclonal antibody. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Nov;28(11):2409–2414. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.11.2409-2414.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorns C. J., Sojka M. G., Mclaren I. M., Dibb-Fuller M. Characterisation of monoclonal antibodies against a fimbrial structure of Salmonella enteritidis and certain other serogroup D salmonellae and their application as serotyping reagents. Res Vet Sci. 1992 Nov;53(3):300–308. doi: 10.1016/0034-5288(92)90130-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorns C. J., Turcotte C., Gemmell C. G., Woodward M. J. Studies into the role of the SEF14 fimbrial antigen in the pathogenesis of Salmonella enteritidis. Microb Pathog. 1996 Apr;20(4):235–246. doi: 10.1006/mpat.1996.0022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turcotte C., Woodward M. J. Cloning, DNA nucleotide sequence and distribution of the gene encoding the SEF14 fimbrial antigen of Salmonella enteritidis. J Gen Microbiol. 1993 Jul;139(7):1477–1485. doi: 10.1099/00221287-139-7-1477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis T. S., Paulin S. M., Plested J. S., Watson P. R., Jones P. W. The Salmonella dublin virulence plasmid mediates systemic but not enteric phases of salmonellosis in cattle. Infect Immun. 1995 Jul;63(7):2755–2761. doi: 10.1128/iai.63.7.2755-2761.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward M. J., McLaren I., Wray C. Distribution of virulence plasmids within Salmonellae. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Mar;135(3):503–511. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-3-503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]