Abstract
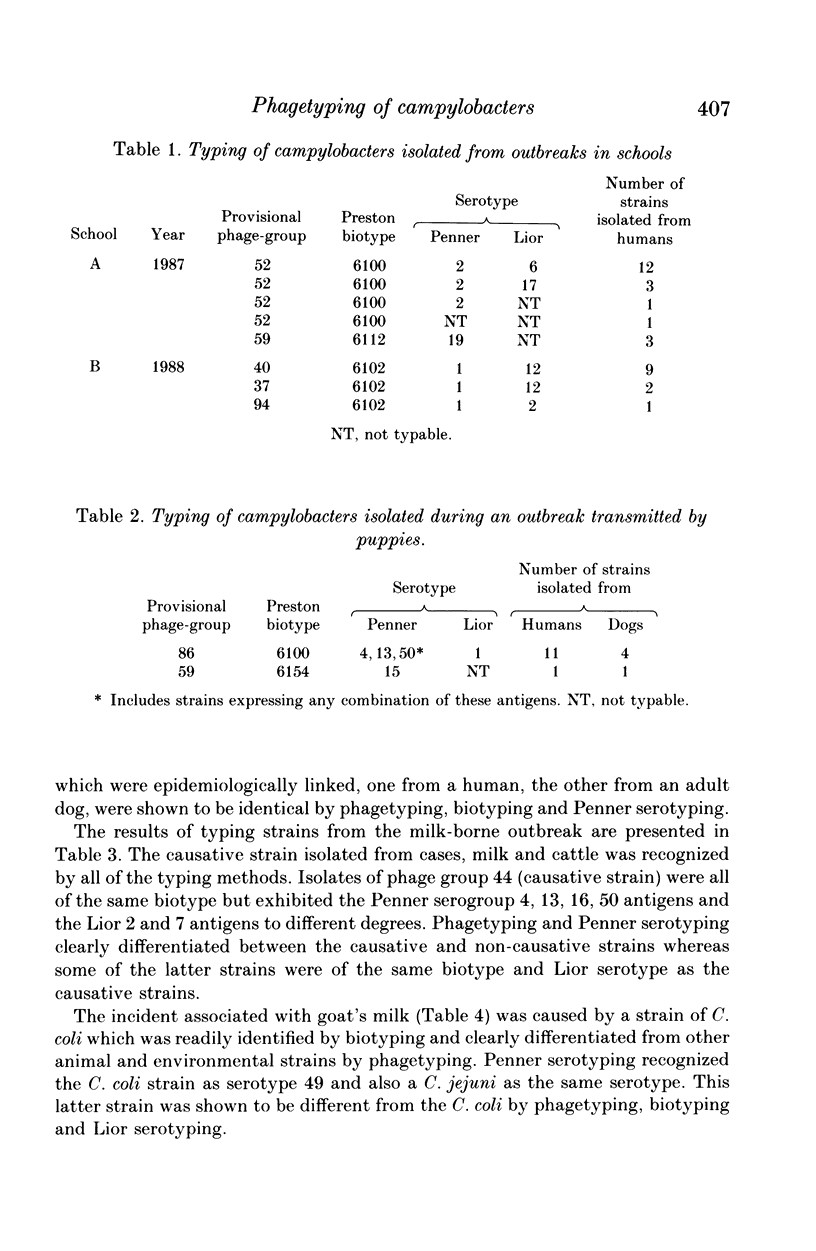
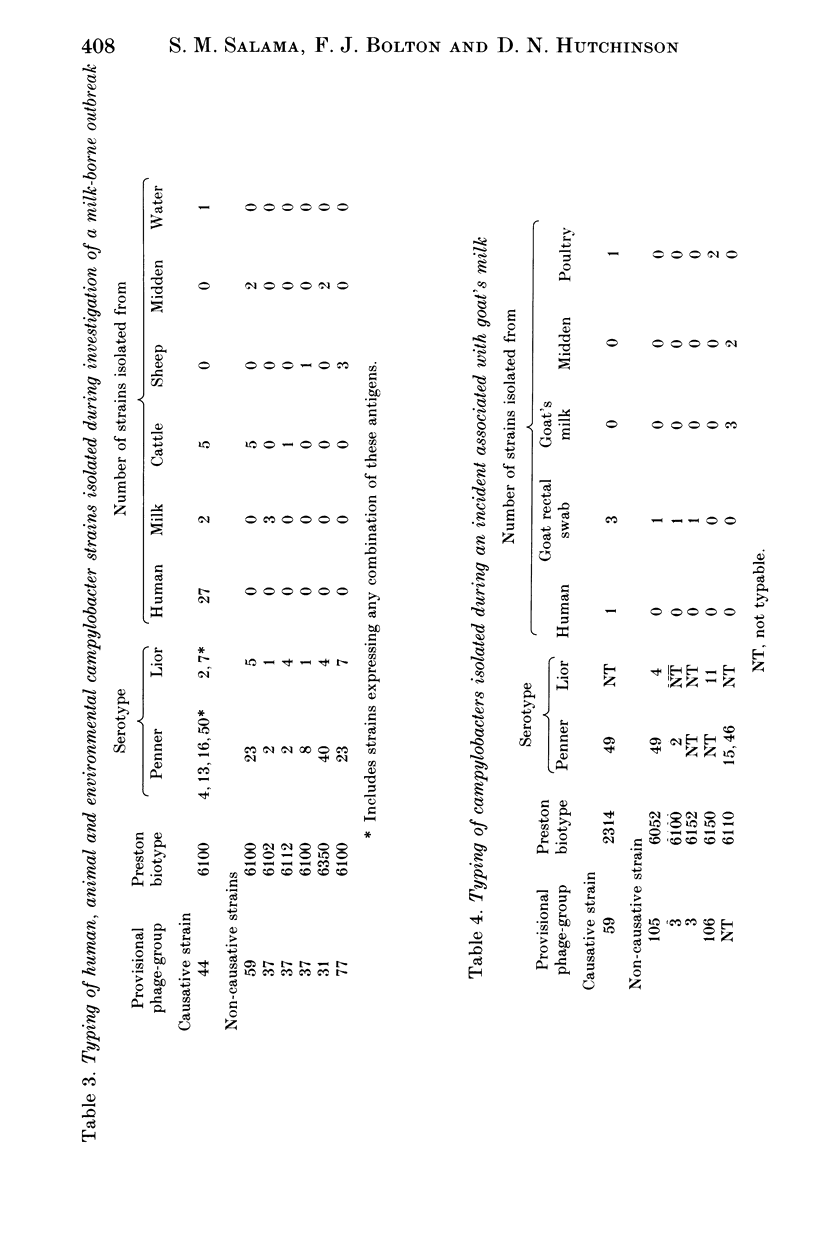
A new scheme for phagetyping campylobacters has been evaluated using strains isolated from five outbreaks. The phagetyping results have been compared with the results of Penner serotyping, Lior serotyping and Preston biotyping. Phagetyping recognized the causative strains in all of the incidents and also differentiated these strains from animal and environmental strains isolated during these investigations. In some outbreaks phagetyping proved to be more discriminatory than serotyping or biotyping, e.g. strains of Penner serotype 2, and serogroup 4, 13, 16, 50 were subdivided by this method. Phagetyping is to be recommended for typing strains from outbreaks and although the results indicate that it may be used alone we advocate that it should be used in conjunction with one of the established typing methods.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolton F. J., Holt A. V., Hutchinson D. N. Campylobacter biotyping scheme of epidemiological value. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Jun;37(6):677–681. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.6.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury W. C., Marko M. A., Hennessy J. N., Penner J. L. Occurrence of plasmid DNA in serologically defined strains of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):460–463. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.460-463.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grajewski B. A., Kusek J. W., Gelfand H. M. Development of a bacteriophage typing system for Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jul;22(1):13–18. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.1.13-18.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson D. N., Bolton F. J., Hinchliffe P. M., Dawkins H. C., Horsley S. D., Jessop E. G., Robertshaw P. A., Counter D. E. Evidence of udder excretion of Campylobacter jejuni as the cause of milk-borne campylobacter outbreak. J Hyg (Lond) 1985 Apr;94(2):205–215. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400061416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson D. N., Bolton F. J., Jelley W. C., Mathews W. G., Telford D. R., Counter D. E., Jessop E. G., Horsley S. D. Campylobacter enteritis associated with consumption of raw goat's milk. Lancet. 1985 May 4;1(8436):1037–1038. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91632-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson D. N., Bolton F. J., Jones D. M., Sutcliffe E. M., Abbott J. D. Application of three typing schemes (Penner, Lior, Preston) to strains of Campylobacter spp. isolated from three outbreaks. Epidemiol Infect. 1987 Apr;98(2):139–144. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800061847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. M., Abbott J. D., Painter M. J., Sutcliffe E. M. A comparison of biotypes and serotypes of Campylobacter sp. isolated from patients with enteritis and from animal and environmental sources. J Infect. 1984 Jul;9(1):51–58. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(84)94498-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakoyiannis C. K., Winter P. J., Marshall R. B. Identification of Campylobacter coli isolates from animals and humans by bacterial restriction endonuclease DNA analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Sep;48(3):545–549. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.3.545-549.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lior H. New, extended biotyping scheme for Campylobacter jejuni, Campylobacter coli, and "Campylobacter laridis". J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Oct;20(4):636–640. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.4.636-640.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lior H., Woodward D. L., Edgar J. A., Laroche L. J., Gill P. Serotyping of Campylobacter jejuni by slide agglutination based on heat-labile antigenic factors. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 May;15(5):761–768. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.5.761-768.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner J. L., Hennessy J. N. Passive hemagglutination technique for serotyping Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni on the basis of soluble heat-stable antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Dec;12(6):732–737. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.6.732-737.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skirrow M. B., Benjamin J. Differentiation of enteropathogenic Campylobacter. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Nov;33(11):1122–1122. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.11.1122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenover F. C., Williams S., Gordon K. P., Harris N., Nolan C., Plorde J. J. Utility of plasmid fingerprinting for epidemiological studies of Campylobacter jejuni infections. J Infect Dis. 1984 Feb;149(2):279–279. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.2.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


