Abstract
Esterase electrophoretic typing and restriction fragment length polymorphism of ribosomal DNA regions (ribotyping) were used to differentiate 102 Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolates obtained from chronic lung infection in 23 patients with cystic fibrosis (CF) and two reference strains (including the type strain ATCC 10145). Twenty-five zymotypes were obtained with the former method and 16 ribotypes with the latter. Combination of the two typing systems led to the finding of 30 different types. Our data highlights the physiopathological complexity of P. aeruginosa infection in CF as, in six individual cases, several types were found among isolates from a given patient. On the other hand, two unique types were found in two and three patients respectively, raising the possibility of cross-infections.
Full text
PDF


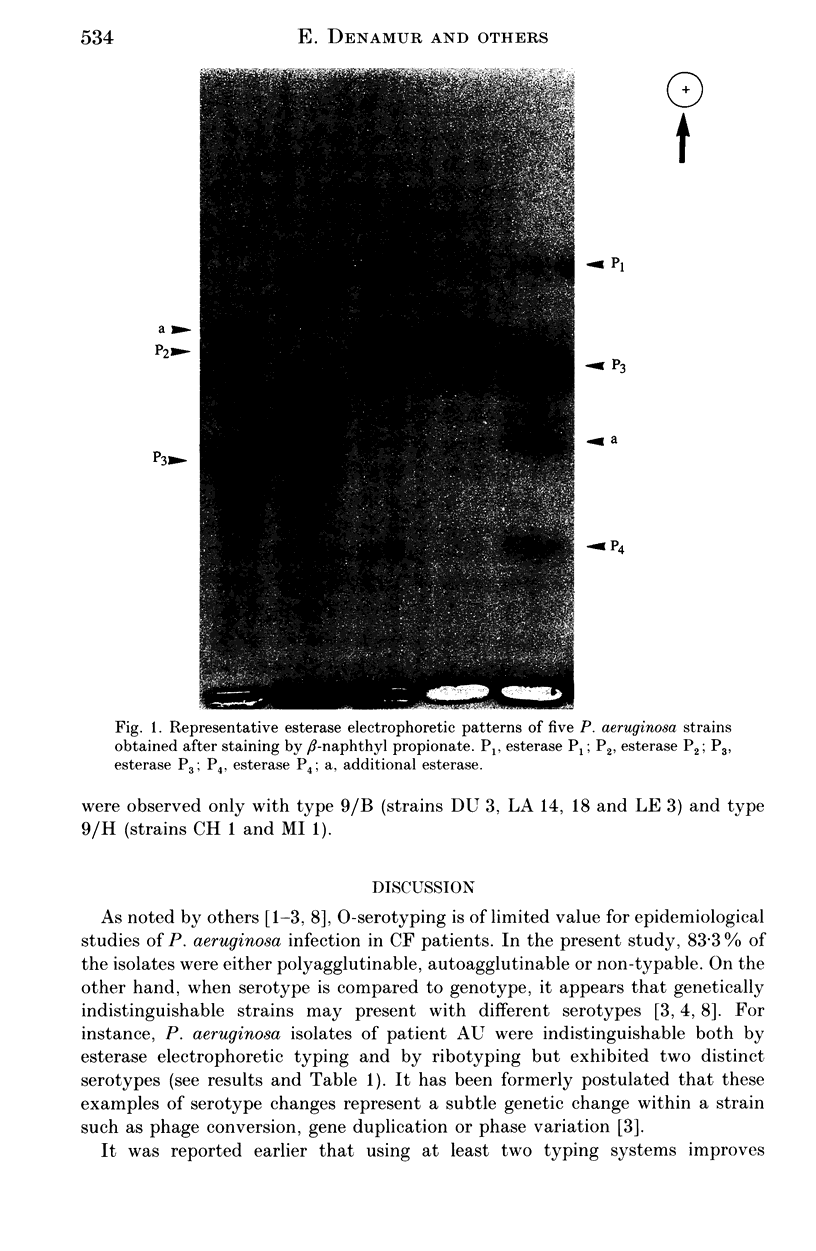





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Branger C., Goullet P. Esterase electrophoretic polymorphism of methicillin-sensitive and methicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus. J Med Microbiol. 1987 Nov;24(3):275–281. doi: 10.1099/00222615-24-3-275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conroy J. V., Baltch A. L., Smith R. P., Hammer M. C., Griffin P. E. Bacteremia due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa: use of a combined typing system in an eight-year study. J Infect Dis. 1983 Sep;148(3):603–603. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.3.603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Döring G., Bareth H., Gairing A., Wolz C., Botzenhart K. Genotyping of Pseudomonas aeruginosa sputum and stool isolates from cystic fibrosis patients: evidence for intestinal colonization and spreading into toilets. Epidemiol Infect. 1989 Dec;103(3):555–564. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800030958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goullet P. An esterase zymogram of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Jul;77(1):27–35. doi: 10.1099/00221287-77-1-27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goullet P., Picard B. Typage électrophorétique des estérases d'Escherichia coli au cours de septicémies. Presse Med. 1984 Apr 21;13(17):1079–1081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith S. J., Nathan C., Selander R. K., Chamberlin W., Gordon S., Kabins S., Weinstein R. A. The epidemiology of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in oncology patients in a general hospital. J Infect Dis. 1989 Dec;160(6):1030–1036. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.6.1030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimont F., Grimont P. A. Ribosomal ribonucleic acid gene restriction patterns as potential taxonomic tools. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1986 Sep-Oct;137B(2):165–175. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(86)80105-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grothues D., Koopmann U., von der Hardt H., Tümmler B. Genome fingerprinting of Pseudomonas aeruginosa indicates colonization of cystic fibrosis siblings with closely related strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Oct;26(10):1973–1977. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.10.1973-1977.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoiby N., Flensborg E. W., Beck B., Friis B., Jacobsen S. V., Jacobsen L. Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in cystic fibrosis. Diagnostic and prognostic significance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa precipitins determined by means of crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Scand J Respir Dis. 1977 Apr;58(2):65–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAWRENCE S. H., MELNICK P. J., WEIMER H. E. A species comparison of serum proteins and enzymes by starch gel electrophoresis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Dec;105:572–575. doi: 10.3181/00379727-105-26180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LENNOX E. S. Transduction of linked genetic characters of the host by bacteriophage P1. Virology. 1955 Jul;1(2):190–206. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(55)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin M. H., Weinstein R. A., Nathan C., Selander R. K., Ochman H., Kabins S. A. Association of infection caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa serotype O11 with intravenous abuse of pentazocine mixed with tripelennamine. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Oct;20(4):758–762. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.4.758-762.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogle J. W., Janda J. M., Woods D. E., Vasil M. L. Characterization and use of a DNA probe as an epidemiological marker for Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jan;155(1):119–126. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.1.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasloske B. L., Joffe A. M., Sun Q., Volpel K., Paranchych W., Eftekhar F., Speert D. P. Serial isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from a cystic fibrosis patient have identical pilin sequences. Infect Immun. 1988 Mar;56(3):665–672. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.3.665-672.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattyn S., Mertens G. Esterase iso-enzyme electrophoresis for epidemiological surveillance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa hospital infections. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1988 Dec;7(6):821–822. doi: 10.1007/BF01975063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard-Pasquier N., Ouagued M., Picard B., Goullet P., Krishnamoorthy R. A simple, sensitive method of analyzing bacterial ribosomal DNA polymorphism. Electrophoresis. 1989 Mar;10(3):186–189. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150100306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard B., Bruneau B., Goullet P. Demonstration of an outbreak of Serratia marcescens infections in a medical intensive care unit by esterase electrophoretic typing. J Hosp Infect. 1988 Feb;11(2):194–195. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(88)90064-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard B., Goullet P., Denamur E., Suermondt G. Esterase electrophoresis: a molecular tool for studying the epidemiology of Branhamella catarrhalis nosocomial infection. Epidemiol Infect. 1989 Dec;103(3):547–554. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800030946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard B., Goullet P. Epidemiological complexity of hospital aeromonas infections revealed by electrophoretic typing of esterases. Epidemiol Infect. 1987 Feb;98(1):5–14. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800061665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitt T. L. Epidemiological typing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;7(2):238–247. doi: 10.1007/BF01963095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitt T. L., Livermore D. M., Pitcher D., Vatopoulos A. C., Legakis N. J. Multiresistant serotype O 12 Pseudomonas aeruginosa: evidence for a common strain in Europe. Epidemiol Infect. 1989 Dec;103(3):565–576. doi: 10.1017/s095026880003096x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speert D. P., Campbell M. E., Farmer S. W., Volpel K., Joffe A. M., Paranchych W. Use of a pilin gene probe to study molecular epidemiology of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Nov;27(11):2589–2593. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.11.2589-2593.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stull T. L., LiPuma J. J., Edlind T. D. A broad-spectrum probe for molecular epidemiology of bacteria: ribosomal RNA. J Infect Dis. 1988 Feb;157(2):280–286. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.2.280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- URIEL J. [Characterization of cholinesterase and other carboxylic esterases after electrophoresis and immunoelectrophoresis on agar. I. Application to the study of esterases of normal human serum]. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1961 Jul;101:104–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uriel J. Méthode d'électrophorèse dans des gels d'acrylamide-agarose. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1966;48(8):969–982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R. Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):221–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.221-271.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolz C., Kiosz G., Ogle J. W., Vasil M. L., Schaad U., Botzenhart K., Döring G. Pseudomonas aeruginosa cross-colonization and persistence in patients with cystic fibrosis. Use of a DNA probe. Epidemiol Infect. 1989 Apr;102(2):205–214. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800029873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




