Abstract
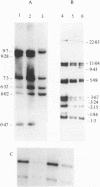
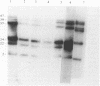
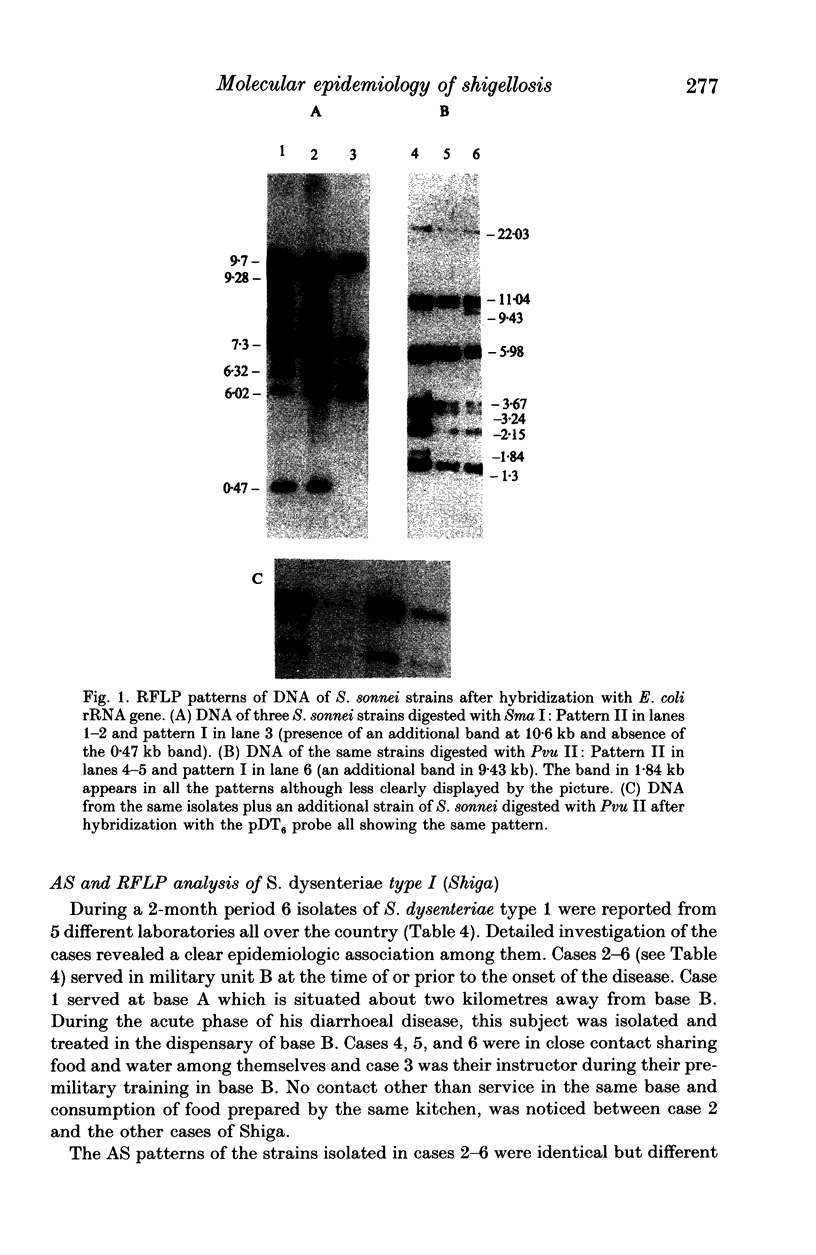
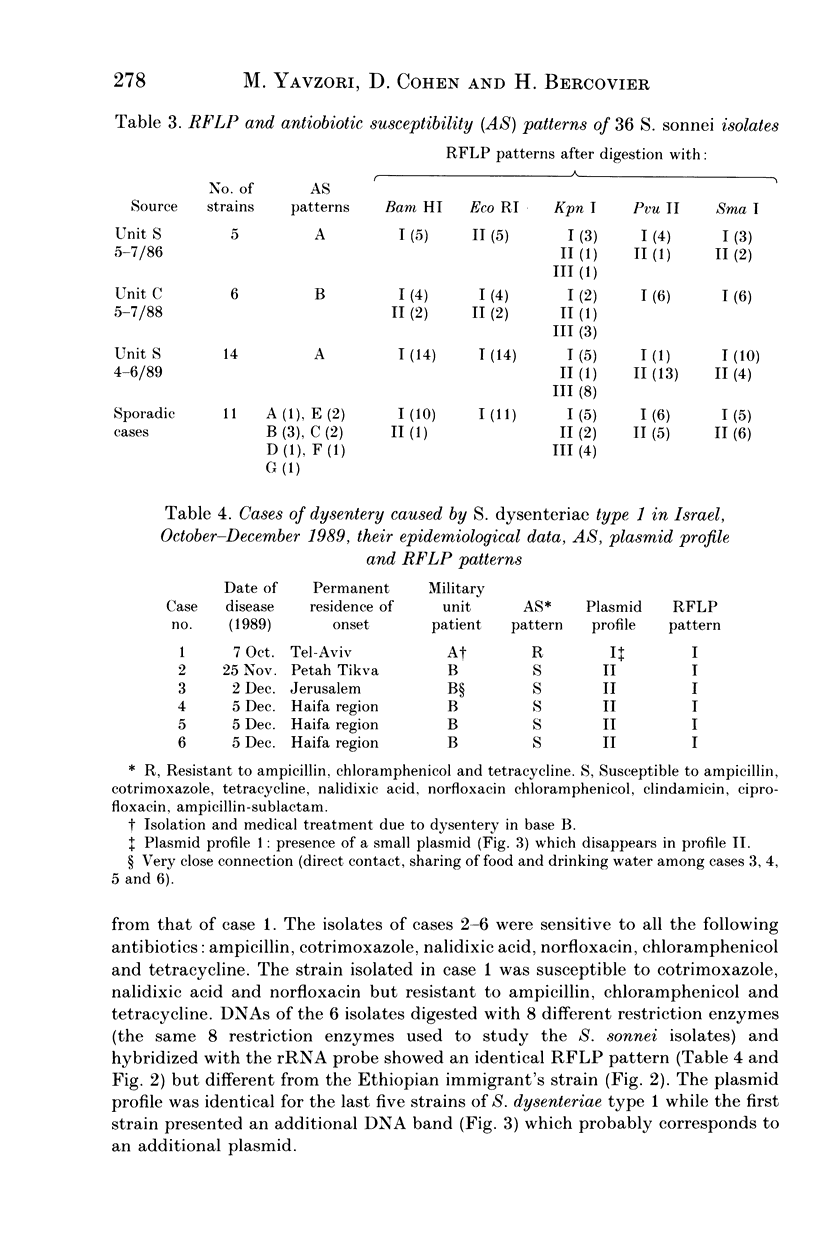
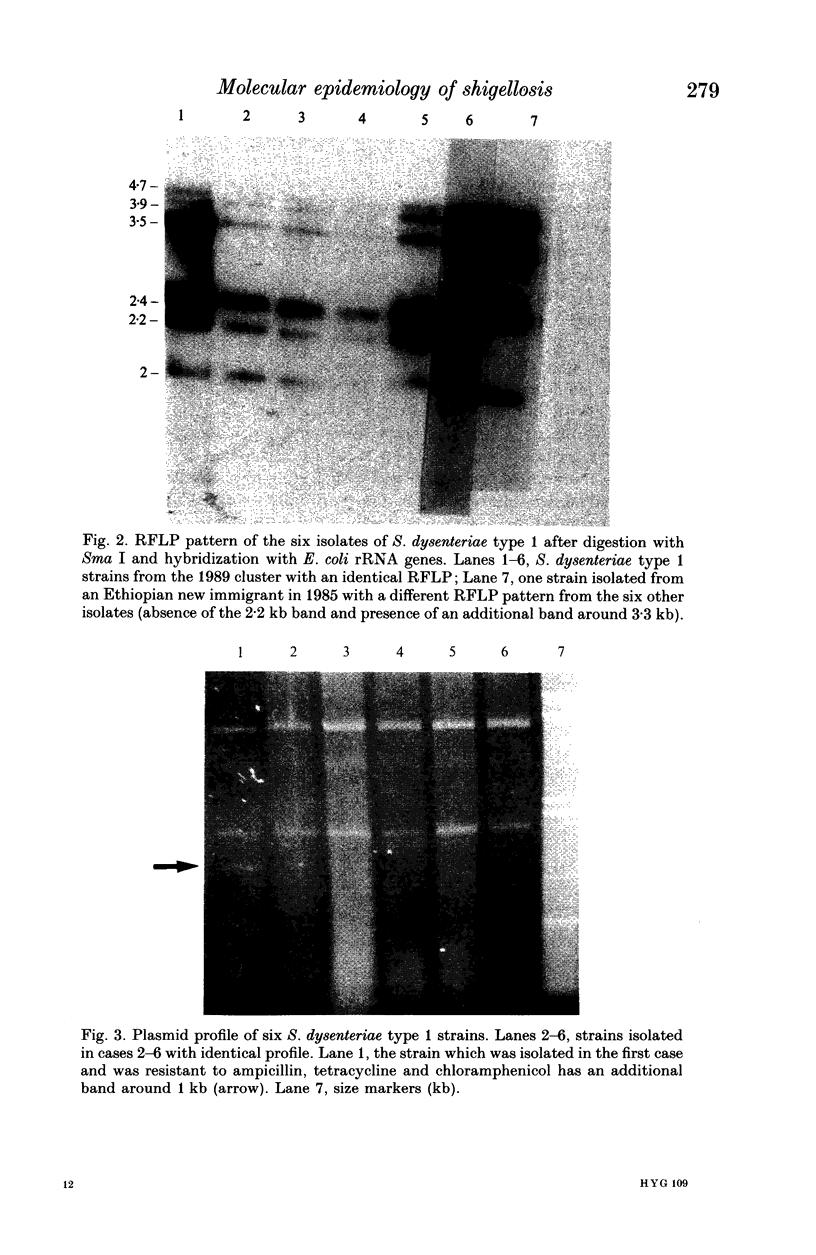
The DNAs of Shigella sonnei or Shigella dysenteriae type 1 strains isolated in outbreaks of shigellosis or in sporadic cases were analysed by restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP). Southern blots of the DNAs of 36 S. sonnei isolates digested by 8 restriction enzymes were hybridized with an Escherichia coli rRNA probe. The S. sonnei strains were unexpectedly diverse in their RFLP. Antibiotypes of the same isolates showed clusters of strains corresponding to the various outbreaks. On the other hand, RFLP analysis suggested concomitant multiple sources of infection rather than a common source and thereby introduced a new insight in the epidemiology of shigellosis. RFLP was also used to trace S. dysenteriae type 1 transmission in a recent cluster of clinical cases. Although antibiotic resistance patterns indicated the presence of more than one strain, RFLP analysis showed that the six isolates were identical clones and suggested the loss of an R episome after one person-to-person passage.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. J., McWhorter A. C., Knutson J. K., Steigerwalt A. G. Escherichia vulneris: a new species of Enterobacteriaceae associated with human wounds. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):1133–1140. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.1133-1140.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Ullrich A., Raker M. A., Gray A., Dull T. J., Gutell R. R., Noller H. F. Construction and fine mapping of recombinant plasmids containing the rrnB ribosomal RNA operon of E. coli. Plasmid. 1981 Jul;6(1):112–118. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(81)90058-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein B. I. New molecular techniques for microbial epidemiology and the diagnosis of infectious diseases. J Infect Dis. 1990 Apr;161(4):595–602. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.4.595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost J. A., Rowe B., Vandepitte J., Threlfall E. J. Plasmid characterisation in the investigation of an epidemic caused by multiply resistant Shigella dysenteriae type 1 in Central Africa. Lancet. 1981 Nov 14;2(8255):1074–1076. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91277-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. S., Block C., Cohen D., Slater P. E. Four decades of shigellosis in Israel: epidemiology of a growing public health problem. Rev Infect Dis. 1991 Mar-Apr;13(2):248–253. doi: 10.1093/clinids/13.2.248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinojosa-Ahumada M., Swaminathan B., Hunter S. B., Cameron D. N., Kiehlbauch J. A., Wachsmuth I. K., Strockbine N. A. Restriction fragment length polymorphisms in rRNA operons for subtyping Shigella sonnei. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Nov;29(11):2380–2384. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.11.2380-2384.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpel R., Olami Y., Taglicht D., Schuldiner S., Padan E. Sequencing of the gene ant which affects the Na+/H+ antiporter activity in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10408–10414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LiPuma J. J., Stull T. L., Dasen S. E., Pidcock K. A., Kaye D., Korzeniowski O. M. DNA polymorphisms among Escherichia coli isolated from bacteriuric women. J Infect Dis. 1989 Mar;159(3):526–532. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.3.526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litwin C. M., Ryan K. J., Chipowsky S., Storm A., McCombie S. Molecular epidemiology of Shigella sonnei in Pima County, Arizona: evidence for a Mexico-related plasmid. J Infect Dis. 1990 Apr;161(4):797–800. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.4.797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendoza M. C., Gonzalez A. J., Mendez F. J., Hardisson C. Plasmid typing of Shigella sonnei epidemic strains and molecular relationship of their R-plasmids. Eur J Epidemiol. 1988 Jun;4(2):158–163. doi: 10.1007/BF00144744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaberg D. R., Rubens C. E., Alford R. H., Farrar W. E., Schaffner W., McGee Z. A. Evolution of antimicrobial resistance and nosocomial infection. Lessons from the Vanderbilt experience. Am J Med. 1981 Feb;70(2):445–448. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90786-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shlaes D. M., Currie-McCumber C. A. Plasmid analysis in molecular epidemiology: a summary and future directions. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Sep-Oct;8(5):738–746. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.5.738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strockbine N. A., Parsonnet J., Greene K., Kiehlbauch J. A., Wachsmuth I. K. Molecular epidemiologic techniques in analysis of epidemic and endemic Shigella dysenteriae type 1 strains. J Infect Dis. 1991 Feb;163(2):406–409. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.2.406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stull T. L., LiPuma J. J., Edlind T. D. A broad-spectrum probe for molecular epidemiology of bacteria: ribosomal RNA. J Infect Dis. 1988 Feb;157(2):280–286. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.2.280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tacket C. O., Shahid N., Huq M. I., Alim A. R., Cohen M. L. Usefulness of plasmid profiles for differentiation of Shigella isolates in Bangladesh. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Aug;20(2):300–301. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.2.300-301.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]