Abstract
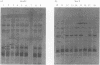
Strains of Salmonella enterica serovar berta (S. berta) from Denmark and seven other countries have been characterized with the aim of developing a rational typing strategy in connection with outbreak investigations. Biotyping divided the strains into H2S-positive (90%) and H2S-negative (10%) biovars. Six percent of the strains were resistant to one or more antimicrobial agents. Eighty-eight percent of the strains carried plasmids and 52 different plasmid profiles were recognized. Six of the common plasmid sizes in these profiles were shown by restriction enzyme analyses to contain more than one plasmid species. More than 90% of the strains had the same ribotype with the restriction enzymes Sma I and EcoR I and the same whole cell protein profile. Outer membrane protein profiles and isoenzyme profiles were identical in all S. berta analysed. Plasmid profiling in combination with restriction enzyme analysis of plasmids seemed to be the most rational typing strategy for S. berta. The results indicated that S. berta strains regardless of geographical source or host are possibly clonal in nature.
Full text
PDF

















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achtman M., Mercer A., Kusecek B., Pohl A., Heuzenroeder M., Aaronson W., Sutton A., Silver R. P. Six widespread bacterial clones among Escherichia coli K1 isolates. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):315–335. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.315-335.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altwegg M., Hickman-Brenner F. W., Farmer J. J., 3rd Ribosomal RNA gene restriction patterns provide increased sensitivity for typing Salmonella typhi strains. J Infect Dis. 1989 Jul;160(1):145–149. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.1.145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson E. S., Ward L. R., Saxe M. J., de Sa J. D. Bacteriophage-typing designations of Salmonella typhimurium. J Hyg (Lond) 1977 Apr;78(2):297–300. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400056187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker R. M., Old D. C. The usefulness of biotyping in studying the epidemiology and phylogeny of salmonellae. J Med Microbiol. 1989 Jun;29(2):81–88. doi: 10.1099/00222615-29-2-81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beltran P., Musser J. M., Helmuth R., Farmer J. J., 3rd, Frerichs W. M., Wachsmuth I. K., Ferris K., McWhorter A. C., Wells J. G., Cravioto A. Toward a population genetic analysis of Salmonella: genetic diversity and relationships among strains of serotypes S. choleraesuis, S. derby, S. dublin, S. enteritidis, S. heidelberg, S. infantis, S. newport, and S. typhimurium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7753–7757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisgaard M. Characterization of atypical Actinobacillus lignieresii isolated from ducks with salpingitis and peritonitis. Nord Vet Med. 1975 Jul-Aug;27(7-8):378–383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisgaard M., Heltberg O., Frederiksen W. Isolation of Pasteurella caballi from an infected wound on a veterinary surgeon. APMIS. 1991 Mar;99(3):291–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner F., Margadant A., Peduzzi R., Piffaretti J. C. The plasmid pattern as an epidemiologic tool for Salmonella typhimurium epidemics: comparison with the lysotype. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jul;148(1):7–11. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.1.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. L., Tauxe R. V. Drug-resistant Salmonella in the United States: an epidemiologic perspective. Science. 1986 Nov 21;234(4779):964–969. doi: 10.1126/science.3535069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costas M., Cookson B. D., Talsania H. G., Owen R. J. Numerical analysis of electrophoretic protein patterns of methicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Nov;27(11):2574–2581. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.11.2574-2581.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costas M., Holmes B., Sloss L. L. Numerical analysis of electrophoretic protein patterns of Providencia rustigianii strains from human diarrhoea and other sources. J Appl Bacteriol. 1987 Oct;63(4):319–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1987.tb02709.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox N. A., Bailey J. S., Mauldin J. M., Blankenship L. C. Presence and impact of Salmonella contamination in commercial broiler hatcheries. Poult Sci. 1990 Sep;69(9):1606–1609. doi: 10.3382/ps.0691606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox N. A., Bailey J. S., Mauldin J. M., Blankenship L. C., Wilson J. L. Extent of salmonellae contamination in breeder hatcheries. Poult Sci. 1991 Feb;70(2):416–418. doi: 10.3382/ps.0700416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimont F., Grimont P. A. Ribosomal ribonucleic acid gene restriction patterns as potential taxonomic tools. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1986 Sep-Oct;137B(2):165–175. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(86)80105-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmuth R., Stephan R., Bunge C., Hoog B., Steinbeck A., Bulling E. Epidemiology of virulence-associated plasmids and outer membrane protein patterns within seven common Salmonella serotypes. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):175–182. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.175-182.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hintermann G., Fischer H. M., Crameri R., Hütter R. Simple procedure for distinguishing CCC, OC, and L forms of plasmid DNA by agarose gel electrophoresis. Plasmid. 1981 May;5(3):371–373. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(81)90012-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg S. D., Wachsmuth I. K., Hickman-Brenner F. W., Cohen M. L. Comparison of plasmid profile analysis, phage typing, and antimicrobial susceptibility testing in characterizing Salmonella typhimurium isolates from outbreaks. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):100–104. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.100-104.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter P. R. Reproducibility and indices of discriminatory power of microbial typing methods. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Sep;28(9):1903–1905. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.9.1903-1905.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapperud G., Lassen J., Dommarsnes K., Kristiansen B. E., Caugant D. A., Ask E., Jahkola M. Comparison of epidemiological marker methods for identification of Salmonella typhimurium isolates from an outbreak caused by contaminated chocolate. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Sep;27(9):2019–2024. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.9.2019-2024.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Minor L. Typing of Salmonella species. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;7(2):214–218. doi: 10.1007/BF01963091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Minor L., Véron M., Popoff M. Proposition pour une nomenclature des Salmonella. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1982 Sep-Oct;133(2):245–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Kopecko D. J., Jones K. R., Ayers D. J., McCowen S. M. A multiple plasmid-containing Escherichia coli strain: convenient source of size reference plasmid molecules. Plasmid. 1978 Jun;1(3):417–420. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClelland M., Hanish J., Nelson M., Patel Y. KGB: a single buffer for all restriction endonucleases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 11;16(1):364–364. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.1.364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLellan T. Molecular charge and electrophoretic mobility in cetacean myoglobins of known sequence. Biochem Genet. 1984 Feb;22(1-2):181–200. doi: 10.1007/BF00499297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J. Duplication and amplification of toxin genes in Vibrio cholerae. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):253–263. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90228-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen J. E. An improved method for rapid isolation of plasmid DNA from wild-type gram-negative bacteria for plasmid restriction profile analysis. Lett Appl Microbiol. 1990 May;10(5):209–212. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-765x.1990.tb01335.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen J. E., Baggesen D. L., Nielsen B. B., Larsen H. E. The prevalence of plasmids in Danish bovine and human isolates of Salmonella dublin. APMIS. 1990 Aug;98(8):735–740. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1990.tb04994.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt D. J., Brown D. J., Old D. C., Barker R. M., Munro D. S., Taylor J. Old and new techniques together resolve a problem of infection by Salmonella typhimurium. Epidemiol Infect. 1987 Aug;99(1):137–142. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800066942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt D. J., Chesham J. S., Brown D. J., Kraft C. A., Taggart J. Restriction enzyme fingerprinting of enterobacterial plasmids: a simple strategy with wide application. J Hyg (Lond) 1986 Oct;97(2):205–210. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400065281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves M. W., Evins G. M., Heiba A. A., Plikaytis B. D., Farmer J. J., 3rd Clonal nature of Salmonella typhi and its genetic relatedness to other salmonellae as shown by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis, and proposal of Salmonella bongori comb. nov. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Feb;27(2):313–320. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.2.313-320.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders N. A., Harrison T. G., Kachwalla N., Taylor A. G. Identification of species of the genus Legionella using a cloned rRNA gene from Legionella pneumophila. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Aug;134(8):2363–2374. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-8-2363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., Caugant D. A., Ochman H., Musser J. M., Gilmour M. N., Whittam T. S. Methods of multilocus enzyme electrophoresis for bacterial population genetics and systematics. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 May;51(5):873–884. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.5.873-884.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw C. R., Prasad R. Starch gel electrophoresis of enzymes--a compilation of recipes. Biochem Genet. 1970 Apr;4(2):297–320. doi: 10.1007/BF00485780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen M., Brown D. J., Bisgaard M., Hansen H. C., Olsen J. E. Plasmid profiles of Salmonella enterica serovar berta isolated from broilers in Denmark. APMIS. 1991 Jul;99(7):609–614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R., Hughes S. G., Broda P. Plasmid identification using specific endonucleases. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;133(2):141–149. doi: 10.1007/BF00264835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Threlfall E. J., Brown D. J., Rowe B., Ward L. R. Occurrence of S typhimurium DT204c in poultry in England and Wales. Vet Rec. 1990 Sep 1;127(9):234–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Threlfall E. J., Frost J. A. The identification, typing and fingerprinting of Salmonella: laboratory aspects and epidemiological applications. J Appl Bacteriol. 1990 Jan;68(1):5–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1990.tb02542.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Threlfall E. J., Frost J. A., Ward L. R., Rowe B. Plasmid profile typing can be used to subdivide phage-type 49 of Salmonella typhimurium in outbreak investigations. Epidemiol Infect. 1990 Apr;104(2):243–251. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800059410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Threlfall E. J., Rowe B., Ferguson J. L., Ward L. R. Characterization of plasmids conferring resistance to gentamicin and apramycin in strains of Salmonella typhimurium phage type 204c isolated in Britain. J Hyg (Lond) 1986 Dec;97(3):419–426. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400063609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tompkins L. S., Troup N., Labigne-Roussel A., Cohen M. L. Cloned, random chromosomal sequences as probes to identify Salmonella species. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jul;154(1):156–162. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.1.156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward L. R., Threlfall E. J., Rowe B. Multiple drug resistance in salmonellae in England and Wales: a comparison between 1981 and 1988. J Clin Pathol. 1990 Jul;43(7):563–566. doi: 10.1136/jcp.43.7.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward L. R., de Sa J. D., Rowe B. A phage-typing scheme for Salmonella enteritidis. Epidemiol Infect. 1987 Oct;99(2):291–294. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800067765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]