Abstract
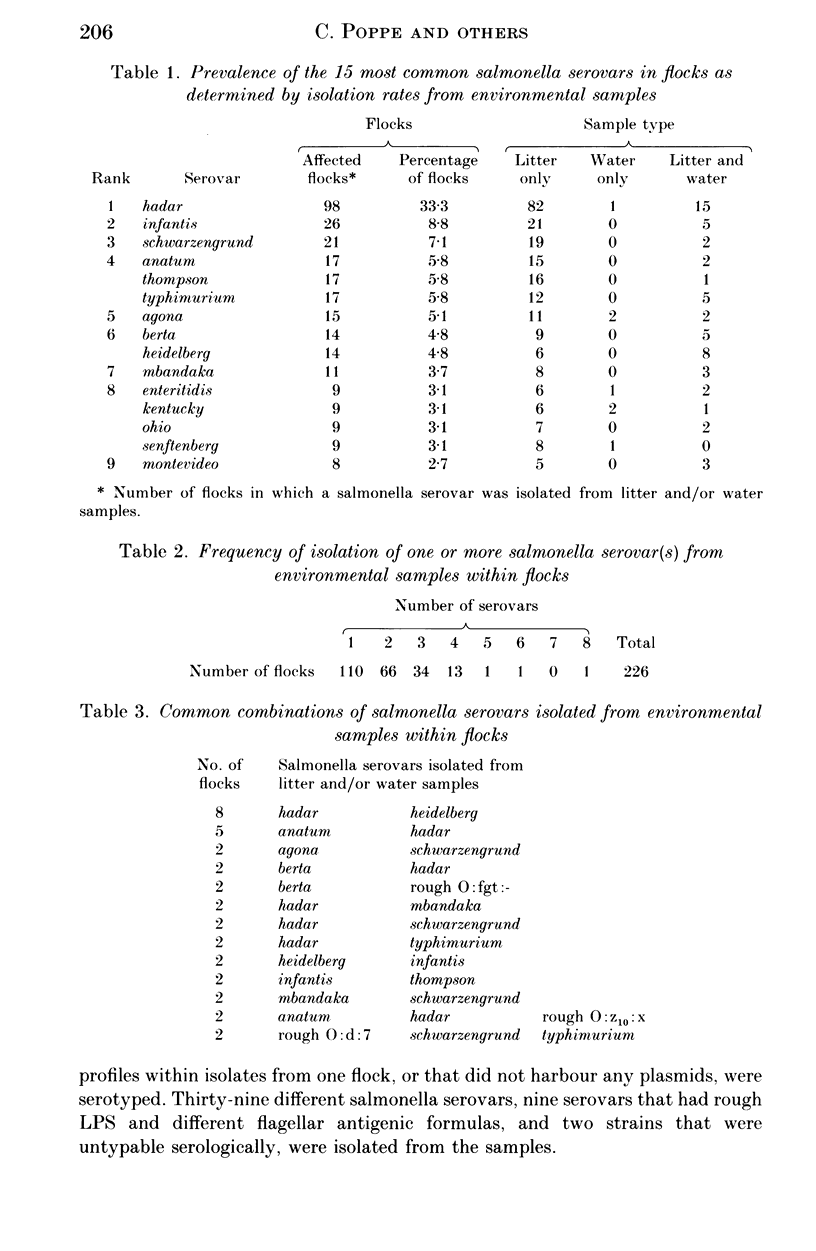
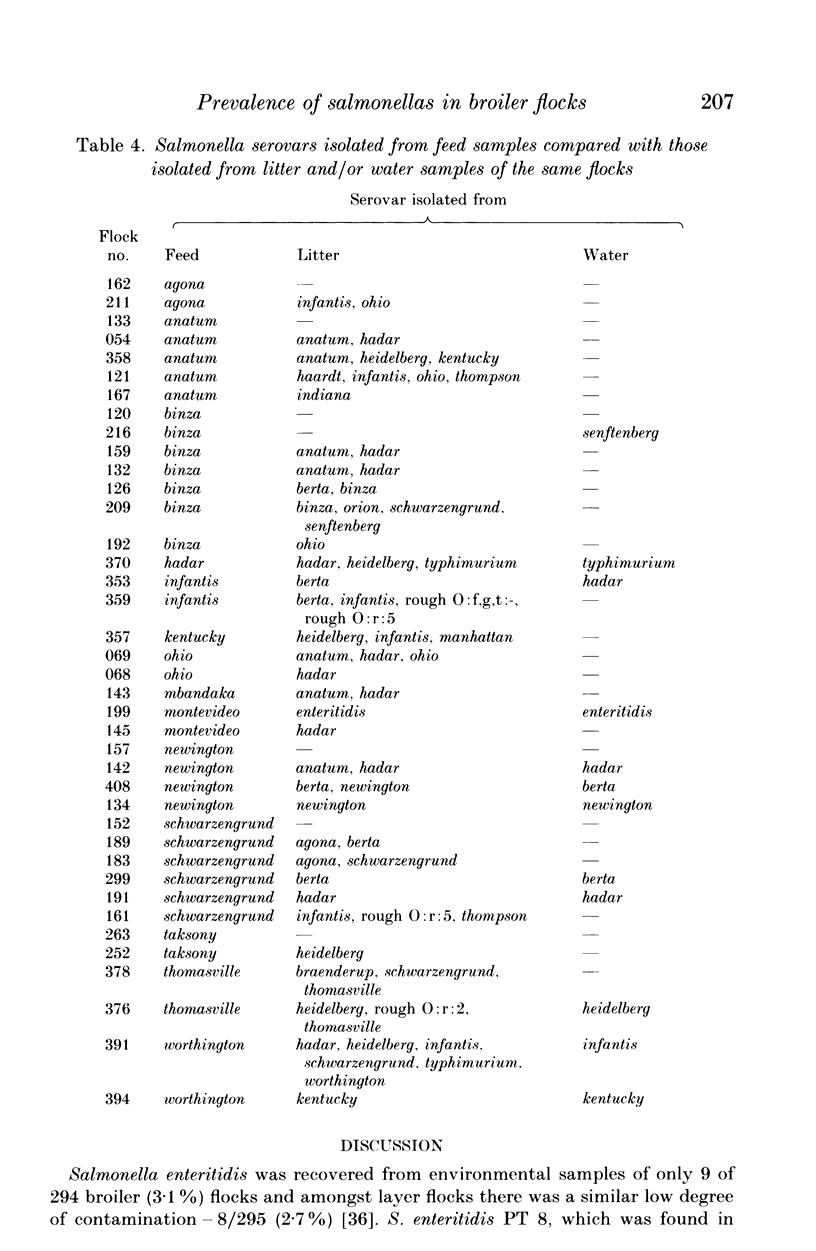
A nation-wide survey was conducted to estimate the prevalence of Salmonella enteritidis and other salmonellas among Canadian commercial broiler flocks. Environmental (litter and/or water) samples from 226 of 294 (76.9%) randomly selected flocks were contaminated with salmonellas. Litter samples were more often contaminated with salmonellas than water samples (47.4 v. 12.3%). Fifty different salmonella serovars were isolated. The most prevalent serovars were S. hadar, S. infantis, and S. schwarzengrund; they were isolated from samples of 98/294 (33.3%), 26/294 (8.8%), and 21/294 (7.1%) flocks, respectively. Feed samples of 39/290 (13.4%) flocks were contaminated with salmonellas. Salmonella enteritidis was isolated from the environmental samples of 9/294 (3.1%) flocks. Salmonella enteritidis phage type (PT) 8 was isolated from seven flocks, and PT 13a from two flocks.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Centers for Disease Control (CDC) Update: Salmonella enteritidis infections and grade A shell eggs--United States, 1989. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1990 Jan 5;38(51-52):877–880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowden J. M., Chisholm D., O'Mahony M., Lynch D., Mawer S. L., Spain G. E., Ward L., Rowe B. Two outbreaks of Salmonella enteritidis phage type 4 infection associated with the consumption of fresh shell-egg products. Epidemiol Infect. 1989 Aug;103(1):47–52. doi: 10.1017/s095026880003034x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowden J. M., Lynch D., Joseph C. A., O'Mahony M., Mawer S. L., Rowe B., Bartlett C. L. Case-control study of infections with Salmonella enteritidis phage type 4 in England. BMJ. 1989 Sep 23;299(6702):771–773. doi: 10.1136/bmj.299.6702.771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fey H., Bürgi E., Margadant A., Boller E. An economic and rapid diagnostic procedure for the detection of salmonella/shigella using the polyvalent salmonella phage O-1. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1978 Jan;240(1):7–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost J. A., Ward L. R., Rowe B. Acquisition of a drug resistance plasmid converts Salmonella enteritidis phage type 4 to phage type 24. Epidemiol Infect. 1989 Oct;103(2):243–248. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800030594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Güdel K., Fey H. Improvement of the polyvalent Salmonella phage's O-1 diagnostic value by addition of a phage specific for the O groups E1-E4. Zentralbl Bakteriol A. 1981;249(2):220–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins R., Malo R., René-Roberge E., Gauthier R. Studies on the dissemination of Salmonella in nine broiler-chicken flocks. Avian Dis. 1982 Jan-Mar;26(1):26–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinton M., Pearson G. R., Threlfall E. J., Rowe B., Woodward M., Wray C. Experimental Salmonella enteritidis infection in chicks. Vet Rec. 1989 Mar 4;124(9):223–223. doi: 10.1136/vr.124.9.223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. Y., Morris J. G., Jr, Trump D., Tilghman D., Wood P. K., Jackman N., Israel E., Libonati J. P. Investigation of an outbreak of Salmonella enteritidis gastroenteritis associated with consumption of eggs in a restaurant chain in Maryland. Am J Epidemiol. 1988 Oct;128(4):839–844. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a115037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lister S. A. Salmonella enteritidis infection in broilers and broiler breeders. Vet Rec. 1988 Sep 24;123(13):350–350. doi: 10.1136/vr.123.13.350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long J. R., DeWitt W. F., Ruet J. L. Studies on Salmonella from floor litter of 60 broiler chicken houses in Nova Scotia. Can Vet J. 1980 Mar;21(3):91–94. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Kopecko D. J., Jones K. R., Ayers D. J., McCowen S. M. A multiple plasmid-containing Escherichia coli strain: convenient source of size reference plasmid molecules. Plasmid. 1978 Jun;1(3):417–420. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGarr C., Mitchell W. R., Carlson H. C., Fish N. A. An epidemiological study of Salmonellae in broiler chicken production. Can J Public Health. 1980 Jan-Feb;71(1):47–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien J. D. Salmonella enteritidis infection in broiler chickens. Vet Rec. 1988 Feb 27;122(9):214–214. doi: 10.1136/vr.122.9.214-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne D. J., Scudamore J. M. Outbreaks of salmonella food-poisoning over a period of eight years from a common source. Lancet. 1977 Jun 11;1(8024):1249–1250. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92453-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perales I., Audicana A. Salmonella enteritidis and eggs. Lancet. 1988 Nov 12;2(8620):1133–1133. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90542-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poppe C., Barnum D. A., Mitchell W. R. Effect of chlorination of drinking water on experimental salmonella infection in poultry. Avian Dis. 1986 Apr-Jun;30(2):362–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poppe C., Irwin R. J., Forsberg C. M., Clarke R. C., Oggel J. The prevalence of Salmonella enteritidis and other Salmonella spp. among Canadian registered commercial layer flocks. Epidemiol Infect. 1991 Apr;106(2):259–270. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800048408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rampling A., Anderson J. R., Upson R., Peters E., Ward L. R., Rowe B. Salmonella enteritidis phage type 4 infection of broiler chickens: a hazard to public health. Lancet. 1989 Aug 19;2(8660):436–438. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90604-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby C. E., Pettit J. R., Papp-Vid G., Spencer J. L., Willis N. G. The isolation of salmonellae, Newcastle disease virus and other infectious agents from quarantined imported birds in Canada. Can J Comp Med. 1981 Oct;45(4):366–370. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe B., Hall M. L., Ward L. R., de Sa J. D. Epidemic spread of Salmonella hadar in England and Wales. Br Med J. 1980 Apr 19;280(6221):1065–1066. doi: 10.1136/bmj.280.6221.1065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler W. W., Brownell J. R., Fanelli M. J. Influence of age and inoculum level on shed pattern of Salmonella typhimurium in chickens. Avian Dis. 1969 Nov;13(4):793–803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E., Kadam S. K., MacLachlan P. R. Derepression of F factor function in Salmonella typhimurium. Can J Microbiol. 1983 Sep;29(9):1205–1212. doi: 10.1139/m83-184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp J. C. Salmonellosis and eggs. BMJ. 1988 Dec 17;297(6663):1557–1558. doi: 10.1136/bmj.297.6663.1557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipp C. R., Rowe B. A mechanised microtechnique for salmonella serotyping. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Jun;33(6):595–597. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.6.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snoeyenbos G. H., Carlson V. L., Smyser C. F., Olesiuk O. M. Dynamics of salmonella infection in chicks reared on litter. Avian Dis. 1969 Feb;13(1):72–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snoeyenbos G. H., McKie B. A., Smyser C. F., Weston C. R. Progress in identifying and maintaining salmonella-free commercial chicken breeding flocks. 1. 1967-1969. Avian Dis. 1970 Nov;14(4):683–696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snoeyenbos G. H., Smyser C. F., Van Roekel H. Salmonella infections of the ovary and peritoneum of chickens. Avian Dis. 1969 Aug;13(3):668–670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Louis M. E., Morse D. L., Potter M. E., DeMelfi T. M., Guzewich J. J., Tauxe R. V., Blake P. A. The emergence of grade A eggs as a major source of Salmonella enteritidis infections. New implications for the control of salmonellosis. JAMA. 1988 Apr 8;259(14):2103–2107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timoney J. F., Shivaprasad H. L., Baker R. C., Rowe B. Egg transmission after infection of hens with Salmonella enteritidis phage type 4. Vet Rec. 1989 Dec 9;125(24):600–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward L. R., de Sa J. D., Rowe B. A phage-typing scheme for Salmonella enteritidis. Epidemiol Infect. 1987 Oct;99(2):291–294. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800067765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


