Abstract
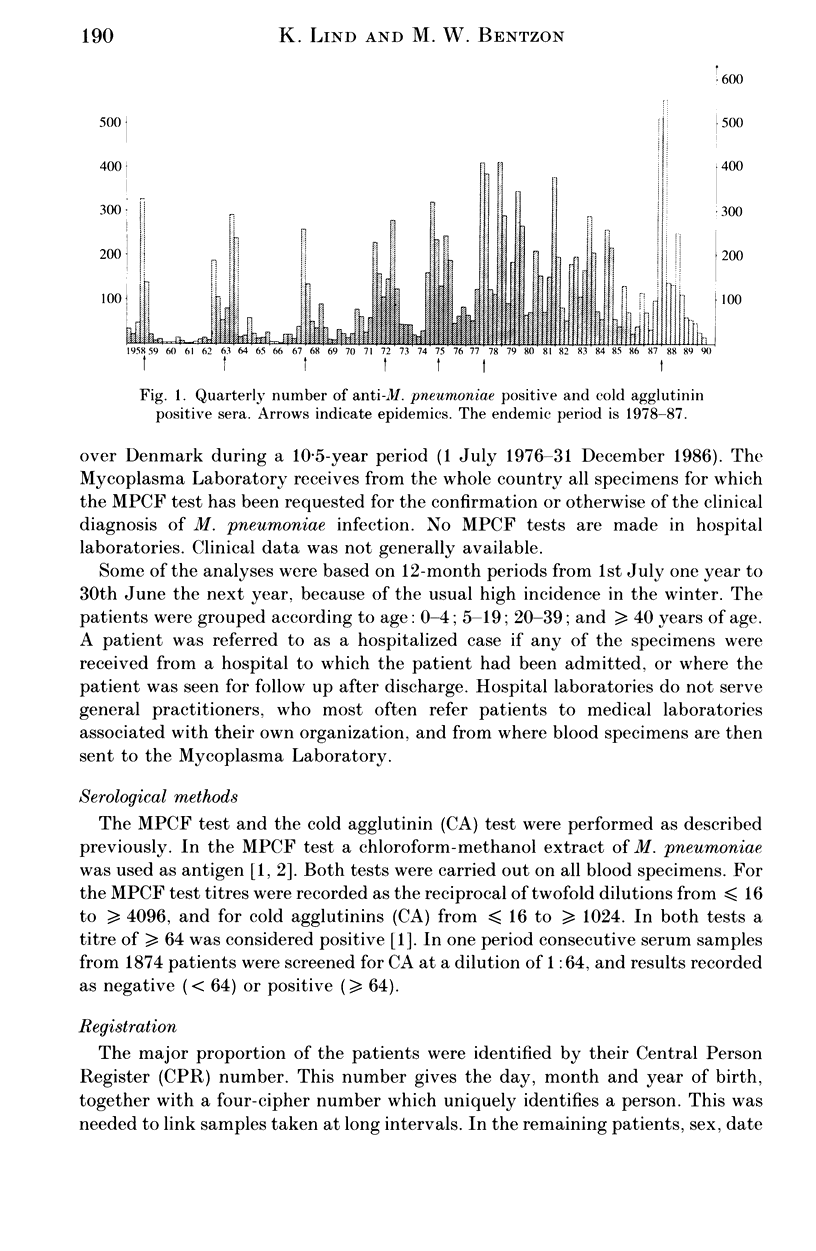
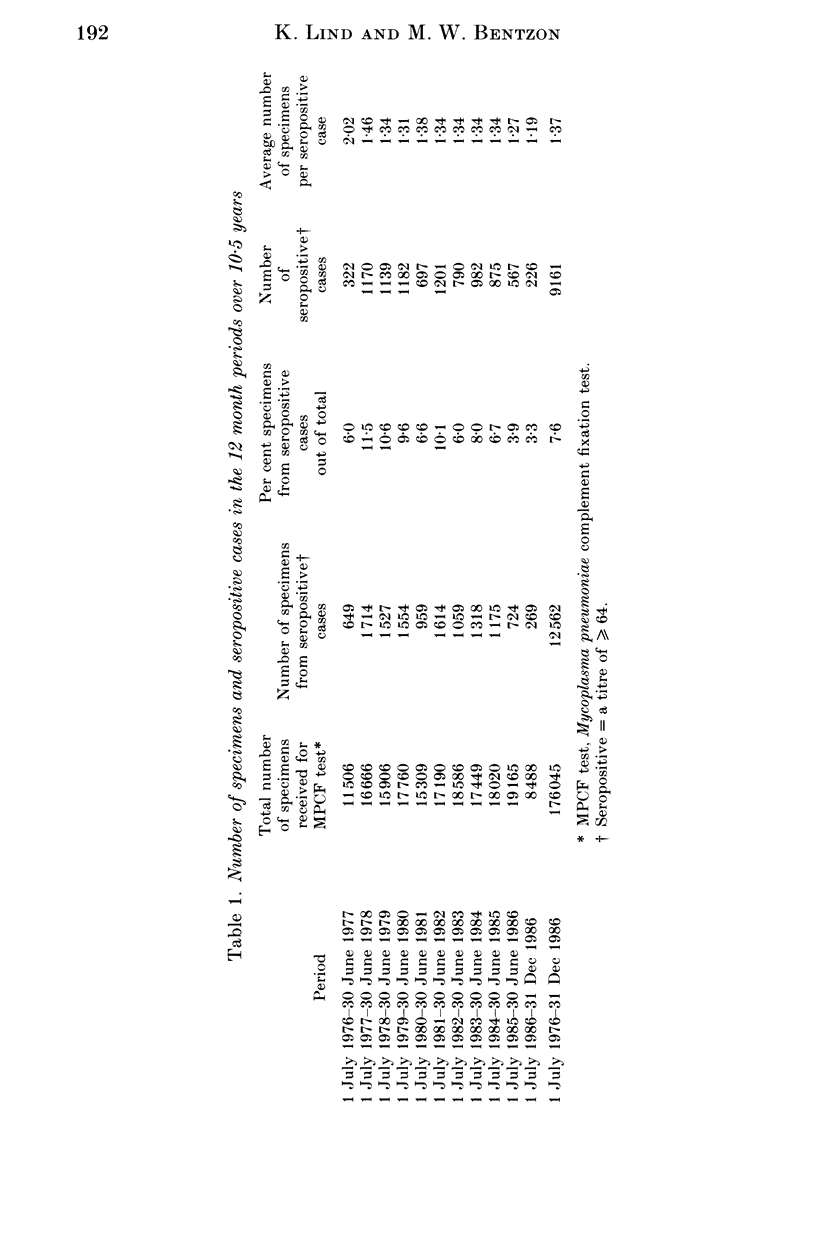
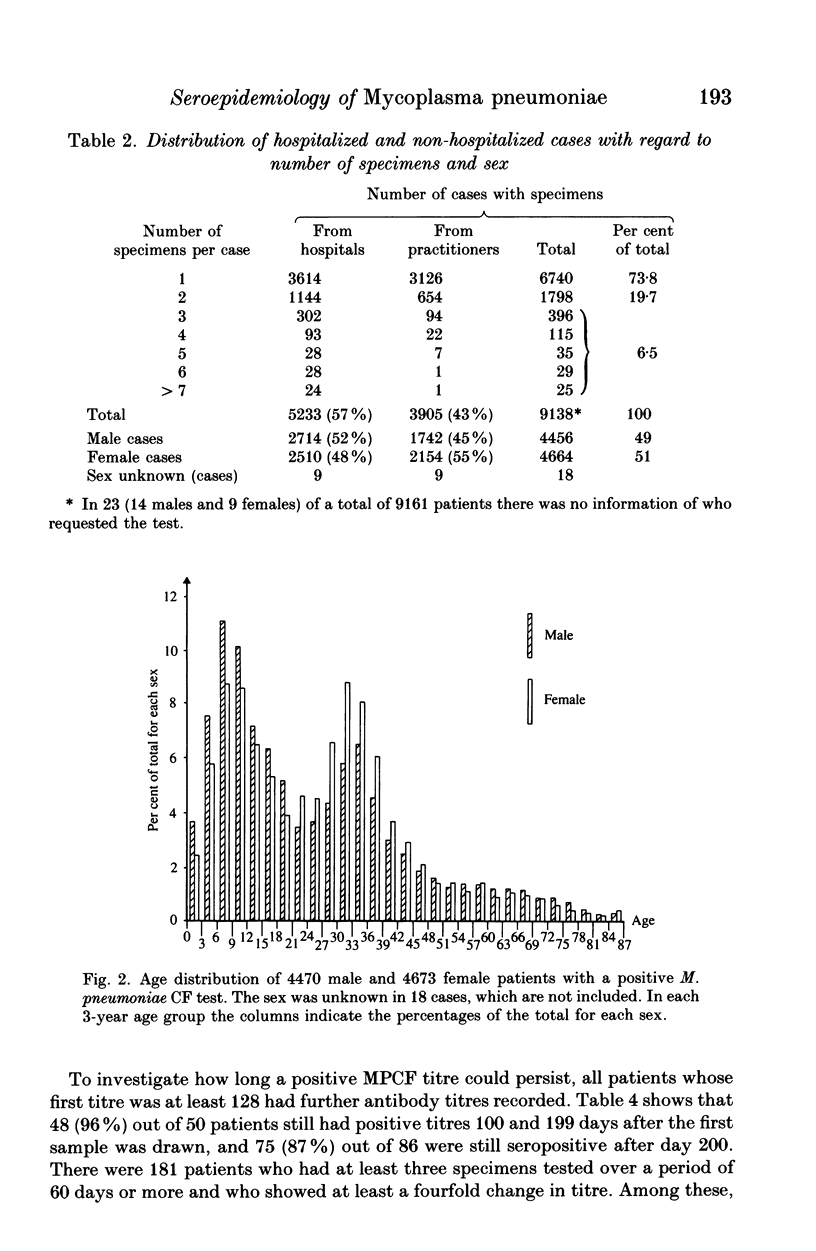
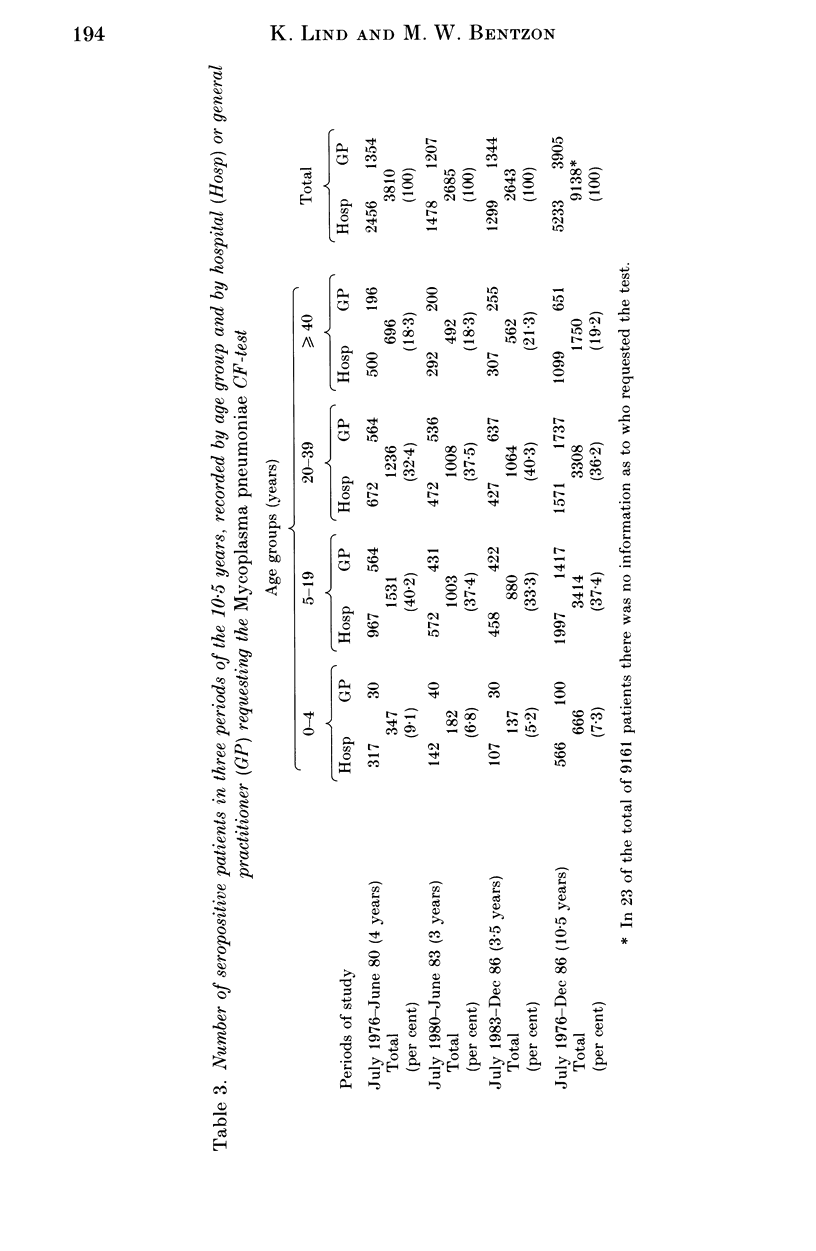
The study was based on a computerized card index of 9161 patients who had at least one positive blood specimen in the Mycoplasma pneumoniae complement fixation test. A total of 12,562 specimens from these patients had been sent to Statens Seruminstitut from hospitals and general practitioners during a 10.5-year period. The period encompassed a previously described endemic period in a 30-year study of the epidemiological pattern of M. pneumoniae infection in Denmark. The serological data presented support the hypothesis advanced here that a more than sixfold increase of children in day care might have contributed to a change in the epidemiological pattern. The correlation between age and level of specific antibodies, as well as persistence of seropositivity, were also investigated.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baseman J. B., Dallo S. F., Tully J. G., Rose D. L. Isolation and characterization of Mycoplasma genitalium strains from the human respiratory tract. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Nov;26(11):2266–2269. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.11.2266-2269.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner H., Prescott B., Greenberg H., James W. D., Horswood R. L., Chanock R. M. Unexpectedly high frequency of antibody to Mycoplasma pneumoniae in human sera as measured by sensitive techniques. J Infect Dis. 1977 Apr;135(4):524–530. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.4.524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denny F. W., Clyde W. A., Jr, Glezen W. P. Mycoplasma pneumoniae disease: clinical spectrum, pathophysiology, epidemiology, and control. J Infect Dis. 1971 Jan;123(1):74–92. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.1.74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENNY G. E., GRAYSTON J. T. EATON PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE ORGANISM (MYCOPLASMA PNEUMONIAE) COMPLEMENT-FIXING ANTIGEN: EXTRACTION WITH ORGANIC SOLVENTS. J Immunol. 1965 Jul;95:19–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernald G. W., Collier A. M., Clyde W. A., Jr Respiratory infections due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae in infants and children. Pediatrics. 1975 Mar;55(3):327–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foy H. M., Kenny G. E., McMahan R., Mansy A. M., Grayston J. T. Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in an urban area. Five years of surveillance. JAMA. 1970 Nov 30;214(9):1666–1672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foy H. M., Kenny G. E., Sefi R., Ochs H. D., Allan I. D. Second attacks of pneumonia due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Infect Dis. 1977 Apr;135(4):673–677. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.4.673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAYSTON J. T., ALEXANDER E. R., KENNY G. E., CLARKE E. R., FREMONT J. C., MACCOLL W. A. MYCOPLASMA PNEUMONIAE INFECTIONS. CLINICAL AND EPIDEMIOLOGIC STUDIES. JAMA. 1965 Feb 1;191:369–374. doi: 10.1001/jama.1965.03080050015004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny G. E., Kaiser G. G., Cooney M. K., Foy H. M. Diagnosis of Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia: sensitivities and specificities of serology with lipid antigen and isolation of the organism on soy peptone medium for identification of infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Sep;28(9):2087–2093. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.9.2087-2093.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lind K., Bentzon M. W. Changes in the epidemiological pattern of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections in Denmark. A 30 years survey. Epidemiol Infect. 1988 Oct;101(2):377–386. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800054327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lind K., Bentzon M. W. Epidemics of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in Denmark from 1958 to 1974. Int J Epidemiol. 1976 Sep;5(3):267–277. doi: 10.1093/ije/5.3.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lind K., Lindhardt B. O., Schütten H. J., Blom J., Christiansen C. Serological cross-reactions between Mycoplasma genitalium and Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Dec;20(6):1036–1043. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.6.1036-1043.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick D. P., Wenzel R. P., Senterfit L. B., Beam W. E., Jr Relationship of pre-existing antibody to subsequent infection by Mycoplasma pneumoniae in adults. Infect Immun. 1974 Jan;9(1):53–59. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.1.53-59.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S., Ebisawa I., Kitamoto O., Sato T. Persistence of serum antibody following Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1970 Apr;101(4):620–622. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1970.101.4.620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pönkä A., Ukkonen P. Age-related prevalence of complement-fixing antibody to Mycoplasma pneumoniae during an 8-year period. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Apr;17(4):571–575. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.4.571-575.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


