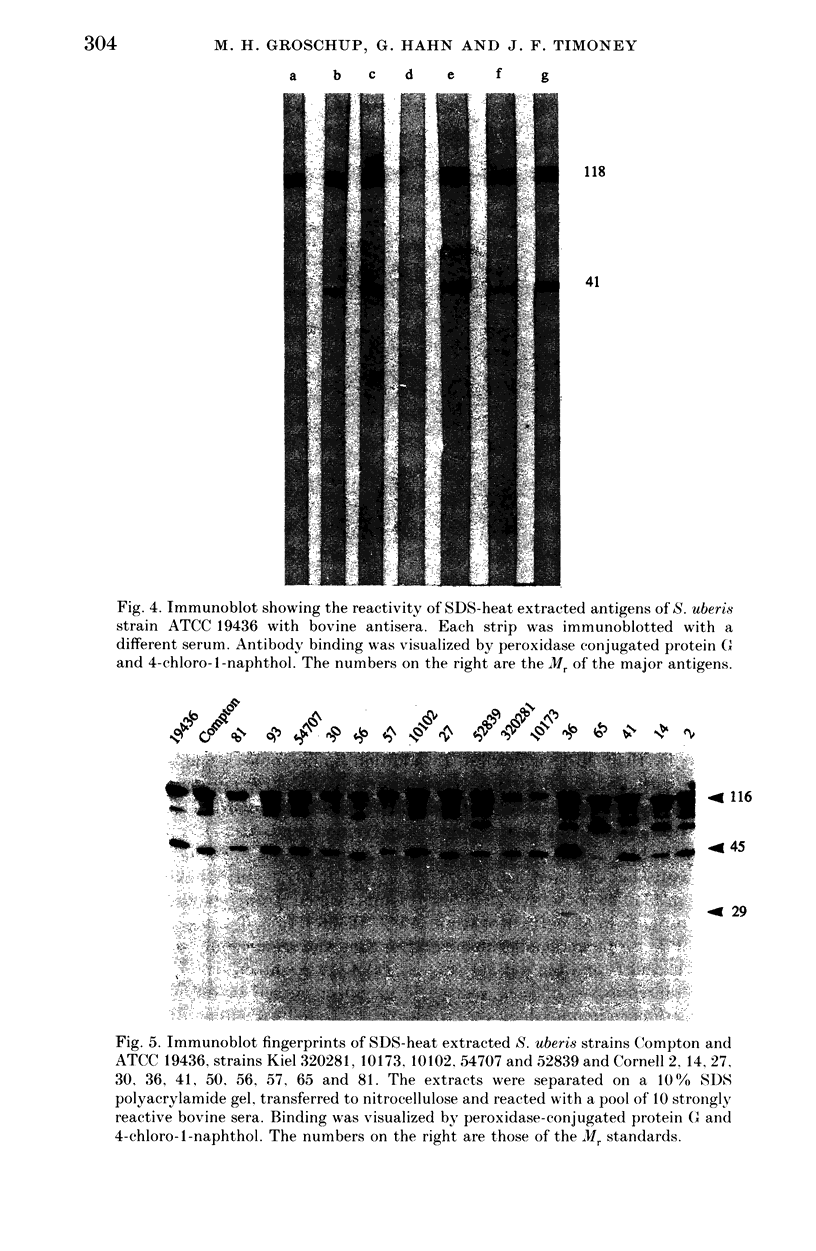
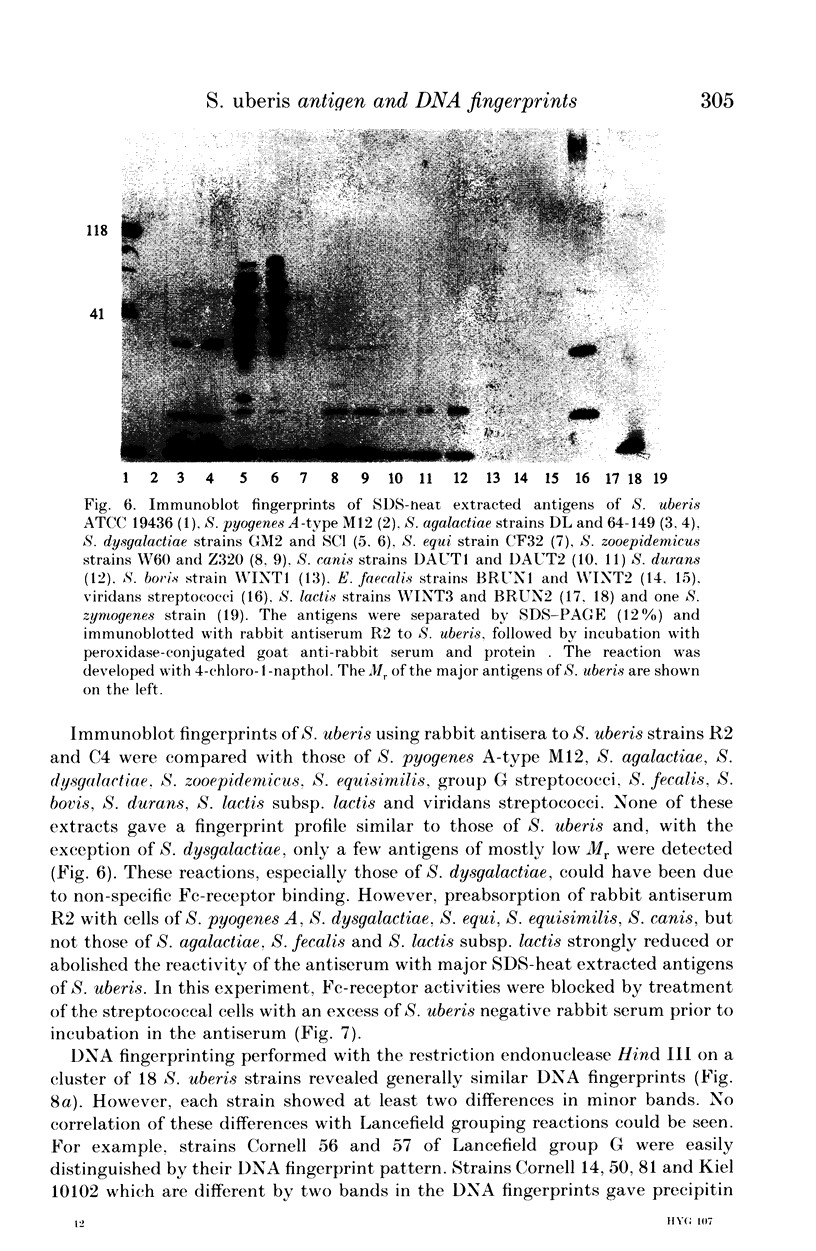
Abstract
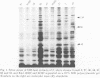
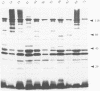
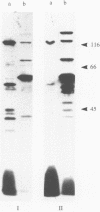
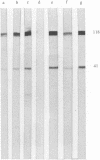
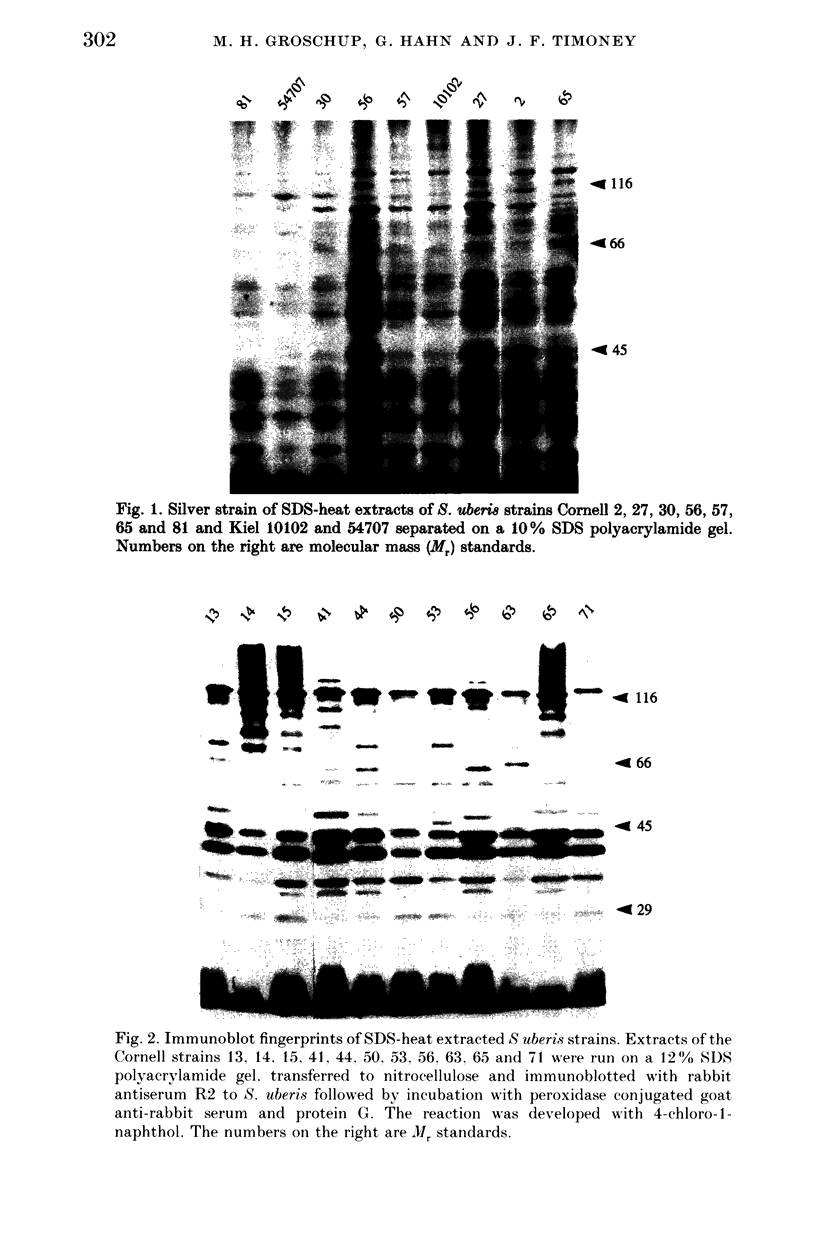
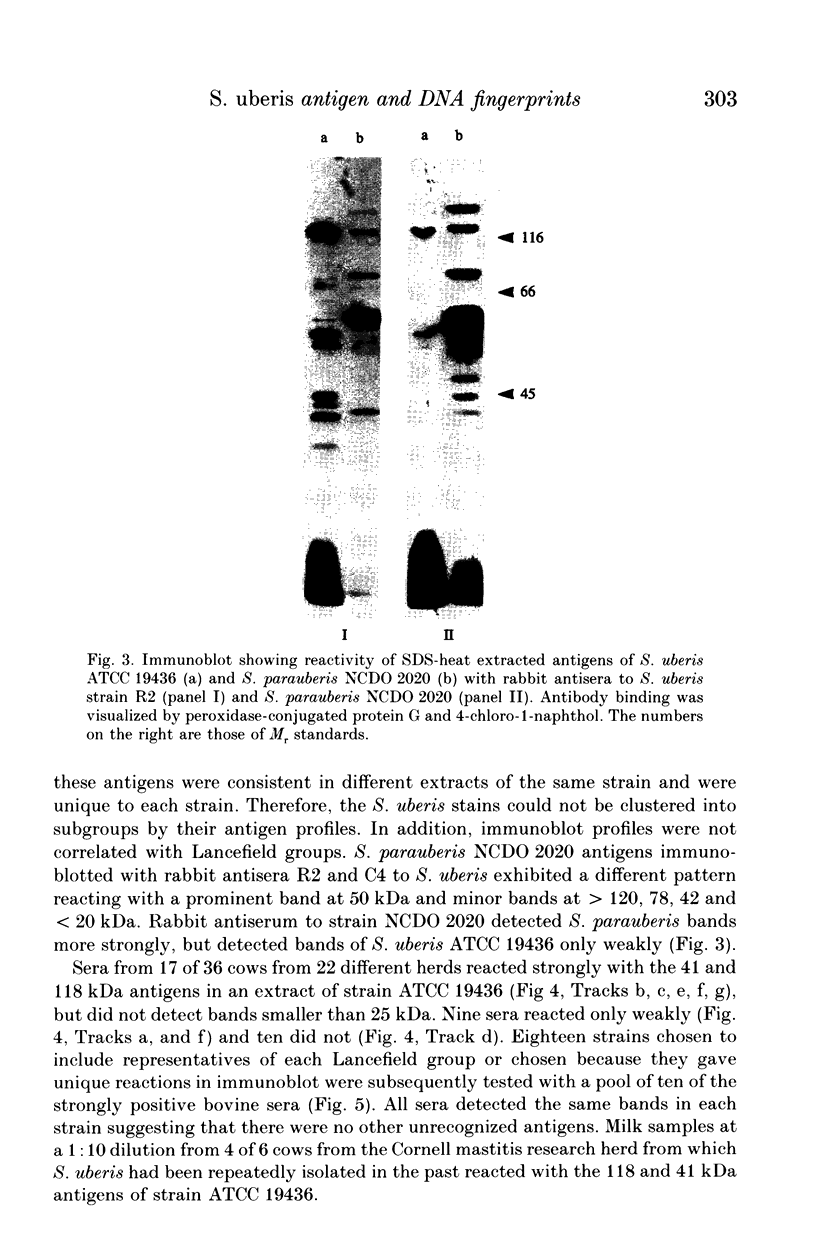
DNA- fingerprints (Hind III) of Streptococcus uberis field isolates from New York State and Europe showed substantial homogeneity, but were different to those of the type strain of the newly proposed psychrophilic species S. parauberis. S. uberis strains had major SDS-heat extracted antigens of molecular masses (Mr) less than 14, 40-41, 42-43, 59-61, 80-86 and 118-122 kDa following immunoblotting with rabbit hyperimmune sera. Bovine sera and milk reacted with the 40-41 and 118-122 kDa antigens. Variations in the Mr of particular bands were too unevenly distributed to permit formation of subgroups. Although cross reactive, the sizes of the antigens of S. parauberis strain NCDO 2020 were substantially different to those of S. uberis, the most prominent antigen having a Mr of 50 kDa. The antigenic and genetic data therefore strongly support the introduction of S. parauberis as a distinct species. S. uberis strains reacted with antiserum to Lancefield groups B, E, G and P, their grouping reactions showing no correlation with DNA and immunoblot fingerprints. Lancefield grouping of S. uberis therefore appears to have little value in identification.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bialkowska-Hobrzanska H., Jaskot D., Hammerberg O. Evaluation of restriction endonuclease fingerprinting of chromosomal DNA and plasmid profile analysis for characterization of multiresistant coagulase-negative staphylococci in bacteremic neonates. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Feb;28(2):269–275. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.2.269-275.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bramley A. J., Dodd F. H. Reviews of the progress of dairy science: mastitis control--progress and prospects. J Dairy Res. 1984 Aug;51(3):481–512. doi: 10.1017/s0022029900023797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnie J. P., Lee W. A comparison of DNA and immunoblot fingerprinting of the SII biotype of coagulase negative staphylococci. Epidemiol Infect. 1988 Oct;101(2):203–212. doi: 10.1017/s095026880005411x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnie J. P., Matthews R. C., Clark I., Milne L. J. Immunoblot fingerprinting Aspergillus fumigatus. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Mar 31;118(2):179–186. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90004-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnie J. P., Matthews R., Lee W., Philpott-Howard J., Brown R., Damani N., Breuer J., Honeywell K., Jordans Z. Four outbreaks of nosocomial systemic candidiasis. Epidemiol Infect. 1987 Aug;99(1):201–211. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800067030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caufield P. W., Walker T. M. Genetic diversity within Streptococcus mutans evident from chromosomal DNA restriction fragment polymorphisms. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Feb;27(2):274–278. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.2.274-278.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleary P. P., Kaplan E. L., Livdahl C., Skjold S. DNA fingerprints of Streptococcus pyogenes are M type specific. J Infect Dis. 1988 Dec;158(6):1317–1323. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.6.1317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischetti V. A., Jarymowycz M., Jones K. F., Scott J. R. Streptococcal M protein size mutants occur at high frequency within a single strain. J Exp Med. 1986 Oct 1;164(4):971–980. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.4.971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis P. G., Wilesmith J. W., Wilson C. D. Observations on the incidence of clinical bovine mastitis in non-lactating cows in England and Wales. Vet Rec. 1986 May 17;118(20):549–552. doi: 10.1136/vr.118.20.549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill A. W., Brady C. A. A note on the isolation and propagation of lytic phages from Streptococcus uberis and their potential for strain typing. J Appl Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;67(4):425–431. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1989.tb02513.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill A. W., Leigh J. A. DNA fingerprinting of Streptococcus uberis: a useful tool for epidemiology of bovine mastitis. Epidemiol Infect. 1989 Aug;103(1):165–171. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800030466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. F., Norcross N. L. Immunochemical detection of a common antigen among Streptococcus uberis isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 May;17(5):892–897. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.5.892-897.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King J. S. Streptococcus uberis: a review of its role as a causative organism of bovine mastitis. I. Characteristics of the organism. Br Vet J. 1981 Jan;137(1):36–52. doi: 10.1016/s0007-1935(17)31786-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King J. S. Streptococcus uberis: a review of its role as a causative organism of bovine mastitis. II. Control of infection. Br Vet J. 1981 Mar-Apr;137(2):160–165. doi: 10.1016/s0007-1935(17)31733-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krikler S. J., Pennington T. H., Petrie D. Typing of strains of Staphylococcus aureus by Western Blot analysis of culture supernates. J Med Microbiol. 1986 Mar;21(2):169–171. doi: 10.1099/00222615-21-2-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Burnie J. P. Fingerprinting methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by the immunoblot technique. J Med Microbiol. 1988 Apr;25(4):261–268. doi: 10.1099/00222615-25-4-261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald T. J., McDonald J. S. Streptococci isolated from bovine intramammary infections. Am J Vet Res. 1976 Apr;37(4):377–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poxton I. R., Aronsson B., Möllby R., Nord C. E., Collee J. G. Immunochemical fingerprinting of Clostridium difficile strains isolated from an outbreak of antibiotic-associated colitis and diarrhoea. J Med Microbiol. 1984 Jun;17(3):317–324. doi: 10.1099/00222615-17-3-317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANTZ L. A., RANDALL E. Use of autoclaved extracts of hemolytic streptococci for serological grouping. Stanford Med Bull. 1955 May;13(2):290–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roguinsky M. Caractères biochimiques et sérologiques de Streptococcus uberis. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1971 Feb;120(2):154–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roguinsky M. Réactions de Streptococcus uberis avec les sérums G et P. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1969 Oct;117(4):529–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp J., Poxton I. R. An immunochemical method for fingerprinting Clostridium difficile. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Nov 7;83(2):241–248. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90246-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skjold S. A., Quie P. G., Fries L. A., Barnham M., Cleary P. P. DNA fingerprinting of Streptococcus zooepidemicus (Lancefield group C) as an aid to epidemiological study. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jun;155(6):1145–1150. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.6.1145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viering T. P., Fine D. P. Genetic analysis of Streptococcus pneumoniae serotypes with the use of DNA fingerprinting. J Infect Dis. 1989 Jul;160(1):76–82. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.1.76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilesmith J. W., Francis P. G., Wilson C. D. Incidence of clinical mastitis in a cohort of British dairy herds. Vet Rec. 1986 Feb 22;118(8):199–204. doi: 10.1136/vr.118.8.199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. M., Collins M. D. Molecular taxonomic studies on Streptococcus uberis types I and II. Description of Streptococcus parauberis sp. nov. J Appl Bacteriol. 1990 May;68(5):485–490. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1990.tb02900.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]