Abstract
Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease type 4B (CMT4B) is a severe, demyelinating peripheral neuropathy characterized by slowed nerve conduction velocity, axon loss, and distinctive myelin outfolding and infolding. CMT4B is caused by recessive mutations in either myotubularin-related protein 2 (MTMR2; CMT4B1) or MTMR13 (CMT4B2). Myotubularins are phosphoinositide (PI) 3-phosphatases that dephosphorylate phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate (PtdIns3P) and PtdIns(3,5)P2, two phosphoinositides that regulate endosomal–lysosomal membrane traffic. Interestingly, nearly half of the metazoan myotubularins are predicted to be catalytically inactive. Both active and inactive myotubularins have essential functions in mammals and in Caenorhabditis elegans. MTMR2 and MTMR13 are active and inactive PI 3-phosphatases, respectively, and the two proteins have been shown to directly associate, although the functional significance of this association is not well understood. To establish a mouse model of CMT4B2, we disrupted the Mtmr13 gene. Mtmr13-deficient mice develop a peripheral neuropathy characterized by reduced nerve conduction velocity and myelin outfoldings and infoldings. Dysmyelination is evident in Mtmr13-deficient nerves at 14 days and worsens throughout life. Thus, loss of Mtmr13 in mice leads to a peripheral neuropathy with many of the key features of CMT4B2. Although myelin outfoldings and infoldings occur most frequently at the paranode, our morphological analyses indicate that the ultrastructure of the node of Ranvier and paranode is intact in Mtmr13-deficient nerve fibers. We also found that Mtmr2 levels are decreased by ≈50% in Mtmr13-deficient sciatic nerves, suggesting a mode of Mtmr2 regulation. Mtmr13-deficient mice will be an essential tool for studying how the loss of MTMR13 leads to CMT4B2.
Keywords: MTMR2; myelin; PtdIns3P; PtdIns(3,5)P2; endosomal traffic
Charcot–Marie–Tooth (CMT) disease (also called hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy) describes a group of inherited peripheral neuropathies that are both clinically and genetically heterogeneous (1). With a worldwide incidence of ≈1 in 2,500, CMT is one of the most common inherited neurological disorders (www.charcot-marie-tooth.org). CMT leads to progressive degeneration of the muscles of the extremities and loss of sensory function (2). Patients with demyelinating CMT (types 1, 3, and 4) show reduced nerve conduction velocity (NCV) (<38 m/s). In contrast, the axonal forms of CMT (type 2) are associated with normal or near normal NCVs and decreased compound muscle action potential amplitudes. Nerve biopsies from patients with demyelinating CMT show axonal loss and evidence of demyelination/remyelination, whereas nerves from axonal CMT patients show axonal loss without signs of demyelination and remyelination (2). Genetic studies have identified CMT-causing mutations in ≈30 distinct genes of diverse function (1). However, the cellular mechanisms by which these mutations lead to disease are generally poorly understood (1–4). In general, demyelinating and axonal forms of CMT are caused by mutations in genes expressed in Schwann cells and neurons, respectively (1).
CMT type 4B (CMT4B) is a severe, autosomal-recessive form of demyelinating CMT characterized by slowed NCV (9–35 m/s) and an early-childhood onset (5–8). Sural nerve biopsies from CMT4B patients show evidence of segmental demyelination/remyelination, severe axon loss, and distinctive myelin outfoldings and infoldings (5–7). Aberrant myelin folding of this nature has been reported in only a few other forms of CMT, and such folding is considered the pathological hallmark of CMT4B (9–12). CMT4B is caused by mutations in either myotubularin-related protein 2 (MTMR2; CMT4B1) or MTMR13 (CMT4B2) (13–16).
The myotubularins are a large family of phosphoinositide (PI) 3-phosphatases; 14 members have been identified in the human genome (17–21). Myotubularins are members of the protein tyrosine phosphatase superfamily (22), which catalyze phosphoester hydrolysis using a nucleophilic cysteine and an arginine that coordinates oxygens of the substrate phosphate (23). These two residues are found within a conserved Cys-x5-Arg motif. Myotubularins selectively hydrolyze the 3-phosphate of phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate (PtdIns3P) and PtdIns(3,5)P2, two PIs that regulate endosomal–lysosomal membrane traffic (24–28). Both PtdIns3P and PtdIns(3,5)P2 serve as inducible, membrane-anchored binding sites for effector proteins that bind selectively to the inositol head groups (29, 30). Most PtdIns3P effector proteins contain FYVE or PX domains that bind selectively to PtdIns3P (29, 30). PtdIns3P has also been shown to activate the calcium-activated potassium channel KCa3.1, an ion channel that plays a key role in T lymphocyte activation (31).
In addition to MTMR2 and MTMR13, MTM1 and MTMR5 have been shown to play critical roles in mammalian physiology (32, 33). In Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Caenorhabditis elegans, loss-of-function mutations in myotubularins lead to endosomal trafficking defects, consistent with a substrate specificity for PtdIns3P and PtdIns(3,5)P2 (34, 35).
Interestingly, nearly half of the metazoan myotubularins are predicted to be catalytically inactive (21). Inactive myotubularins contain phylogenetically conserved substitutions of the catalytically essential Cys and Arg residues of the Cys-x5-Arg motif. Despite lacking enzymatic function, inactive myotubularins have been found to have essential cellular functions in mammals and in C. elegans (14, 15, 33, 34). Although the functions of the inactive myotubularins are not well understood, it is clear that inactive family members oligomerize with active myotubularins (34, 36–41). Through oligomerization, inactive myotubularins have been reported to regulate the enzymatic activity and cellular localization of active myotubularin PI 3-phosphatases (36–38, 40).
Recessive mutations in either MTMR2 or MTMR13 lead to nearly indistinguishable forms of CMT4B (13–15), suggesting that the two proteins have related functions. Consistent with this hypothesis, MTMR2 and MTMR13 physically associate (39, 40). The catalytically inactive MTMR13 is expected to regulate MTMR2. Indeed, MTMR13 has been reported to directly stimulate the PI 3-phosphatase activity of MTMR2 in vitro (40). However, the large, multidomain nature of Mtmr13 suggests that it may have a multifaceted and complex function (Fig. 1A). To establish a disease-relevant model in which to study the function of Mtmr13, we generated Mtmr13-deficent mice. Here we describe a CMT4B2-like peripheral neuropathy that results from the loss of Mtmr13.
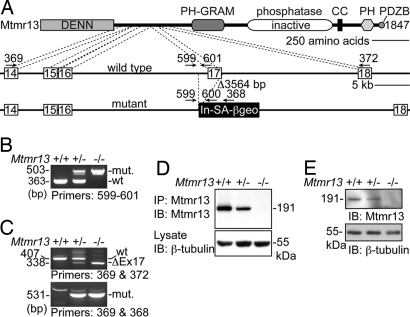
Fig. 1.
Disruption of Mtmr13. (A) A representation of the manner in which Mtmr13 is disrupted in ES cell line RRF511. The Mtmr13 protein is depicted with indicated protein domains. Cell line RRF511 contains a 3,564-bp deletion that spans exon 17 and the preceding intronic sequence. The gene-trap plasmid pGT0lxf is integrated immediately after the deletion. Gene-trap vector pGT0lxf contains an intron and splice acceptor (In-SA) followed by the βgeo cDNA, a stop codon, and a polyA addition signal (pA). The positions of oligonucleotide primers within genomic and vector sequences are indicated. (B) Mtmr13 genotyping using primers 599, 600, and 601 in a three-primer PCR. (C) RT-PCR analysis of Mtmr13 mRNAs using brain RNA from wild-type, heterozygous, and Mtmr13−/− mice. Primer pairs were designed to detect either the wild-type (primers 369 and 372) or mutant (primers 369 and 368) Mtmr13 mRNA. ΔEx17 is an mRNA message that results from splicing of exon 16 to exon 18. (D and E) Mtmr13 protein analysis in brain and sciatic nerve, respectively. Immunoprecipitates (IP) and extracts were analyzed by SDS/PAGE and immunoblotting (IB).
Results
Disruption of Mtmr13.
To confirm that MTMR13 is the causative gene for CMT4B2, and in hopes of establishing a mouse model for this condition, we generated Mtmr13 mutant mice. BayGenomics ES cell line RRF511 contains a gene-trap plasmid integrated within intron 16–17 of the Mtmr13 gene (Fig. 1A). We obtained heterozygous RRF511 mice via blastocyst injection and subsequently generated RRF511 homozygous animals. RT-PCR analysis and DNA sequencing confirmed the predicted disruption of the Mtmr13 mRNA (Fig. 1C). Immunoblotting of brain and sciatic nerve extracts demonstrated the absence of Mtmr13 protein in Mtmr13−/− mice (Fig. 1 D and E).
Peripheral Neuropathy in Mtmr13-Deficient Mice.
Mtmr13−/− mice are viable and are represented among weaned animals at close to the expected Mendelian frequency (35 of 163 animals or 21.5%). Both male and female Mtmr13−/− mice are fertile, appear broadly normal, and do not show obvious behavioral abnormalities. However, some Mtmr13−/− adult animals transiently show a wide placement of the hind paws when placed on a flat surface, suggesting neuromuscular abnormality [supporting information (SI) Fig. 5 A and B].
Because CMT4B2 patients display substantially slowed NCV (median motor NCV ≈ 19 m/s) (16), we evaluated motor (M) NCV in Mtmr13−/− mice. At 8 months these animals possess significantly slowed MNCV (22.5 ± 2.2 m/s vs. 39.6 ± 1.8 m/s for wild type; P < 0.0001) (SI Fig. 5C), consistent with a demyelinating neuropathy.
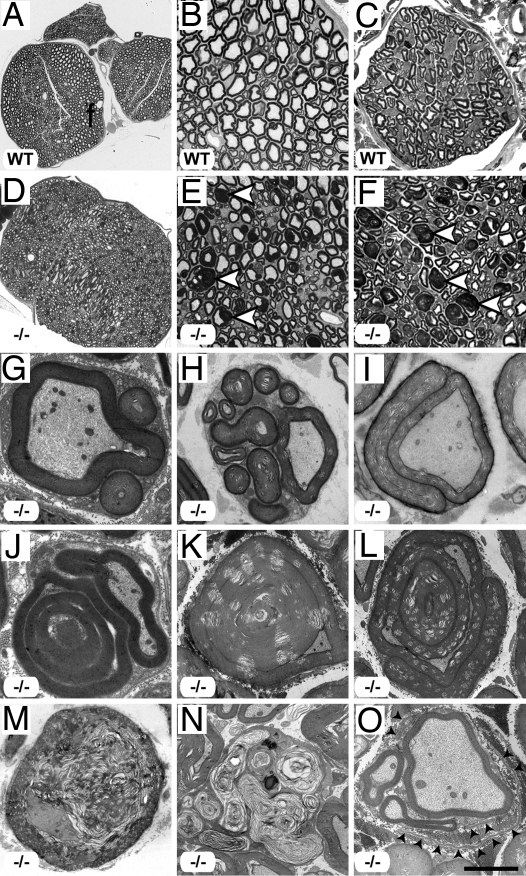
Upon histological examination, sciatic nerves from Mtmr13−/− mice appeared dramatically different from those of wild-type or heterozygous animals (Fig. 2 and SI Fig. 5). Mtmr13−/− nerve fibers contained myelin outfoldings and infoldings (Fig. 2E). Outfoldings were observed in both large- and small-caliber Mtmr13−/− nerve fibers (Fig. 2E and not depicted). Myelin outfoldings and infoldings were also prominent in a purely sensory nerve (saphenous) (Fig. 2 C and F).
Fig. 2.
Peripheral neuropathy in Mtmr13-deficient mice. (A–F) Abnormal myelin morphology in Mtmr13−/− peripheral nerves. Sciatic (A, B, D, and E) and saphenous (C and F) nerves were analyzed at 7 and 2 months, respectively. Sciatic nerves from Mtmr13−/− mice (D and E) contain numerous fibers with extensive redundant loops of myelin (arrowheads in E), which are not observed in wild-type (A and B) or heterozygous (SI Fig. 5) mice. (C and F) Sensory (saphenous) nerves from Mtmr13−/− mice show dysmyelination similar to that of sciatic nerves (arrowheads in F). (G–O) Myelin morphology in sciatic nerves of Mtmr13−/− mice examined by EM (see Materials and Methods) at 14 days (G and J), 7 months (H, I, and M), or 14 months (K, L, N, and O). (G–L) Examples of abnormal myelin morphologies observed in Mtmr13−/− sciatic nerves (see Results for description). (M and N) Two Mtmr13−/− nerve fibers in distinct phases of axonal degeneration. (O) A putative regenerating cluster of axons in an Mtmr13−/− nerve. Please note the relatively thin myelin, supernumerary Schwann cell processes, and redundant basal lamina elements (arrowheads) surrounding the cluster of axons. [Scale bar: 173 μm (A), 34.5 μm (B), 16.6 μm (C), 173 μm (D), 34.5 μm (E), 16.6 μm (F), 2.8 μm (G), 3 μm (H), 4.3 μm (I), 2.1 μm (J), 4.9 μm (K and L), 3.6 μm (M), 4.9 μm (N), and 3 μm (O).]
EM of Mtmr13−/− sciatic nerves provided further insight into the nature of dysmyelination. First, outfolds are observed that consist of one or more satellite loops of myelin that sometimes contain axoplasm-like material (Fig. 2 G and H). In some cases, a redundant myelin loop is manifested as a flattened sheet that surrounds much or all of the primary sheath (Fig. 2I). Myelin outfoldings containing internal loops of myelin are also observed (Fig. 2J), as are fibers in which myelin is folded into the axon (Fig. 2K). Such infolds often dramatically alter the profile of the axon (Fig. 2K). Less frequently, fibers containing both an infold and an outfold are observed (Fig. 2L). Myelin outfolds are bounded by the Schwann cell plasma membrane, and the surrounding basal lamina appears morphologically normal (Fig. 2 G and H and SI Fig. 6 A and B). Myelin thickness in redundant loops is usually similar to that of the primary myelin sheath, suggesting that they are extensions of the primary sheath (Fig. 2 G–L and not depicted). The compaction and periodicity of myelin appeared normal in Mtmr13−/− nerves, suggesting that the underlying defect is one of myelin homeostasis rather than structure (SI Fig. 6 C and D). Nonmyelinating Schwann cells in Mtmr13−/− nerves appeared morphologically similar to those of wild-type nerves (SI Fig. 6 E and F).
In addition to myelin outfolding and infolding, biopsies from CMT4B2 patients show evidence of segmental demyelination/remyelination (“onion bulbs”), hypomyelination, and a severe loss of large caliber axons (5, 42, 43). However, in Mtmr13−/− mid-sciatic nerves, degenerating axons are observed only rather rarely, mostly in older mice (Fig. 2 M and N). Significant axon loss is not apparent in sciatic nerves from Mtmr13−/− mice, even at 14 months of age. Only very rarely did we observe thinly myelinated axons or putative regenerating clusters of axons (Fig. 2O). Onion bulb formations as developed as those found in sural nerves of CMT4B2 patients are not observed in Mtmr13−/− sciatic nerves (5, 42, 43). Finally, decreased myelin thickness was not apparent in Mtmr13−/− sciatic nerve fibers (data not shown).
We also examined the onset and progression of dysmyelination in Mtmr13−/− animals. Myelin infoldings and outfoldings were present in mutant sciatic nerves at postnatal day 14 (P14) (Fig. 2 G and J and SI Fig. 7), suggesting that misfolding occurs concomitantly with myelination. The percentage of nerve fibers with myelin infoldings/outfoldings increased steadily with age. By 14 months, approximately half of sciatic nerve fibers contain myelin infoldings or outfoldings (SI Fig. 7). The complexity of myelin outfoldings and infoldings also increased with age; multiply outfolded/infolded fibers (Fig. 2 K and L) were more common in older mice (7 or 14 months), although such structures are observed in young mice (P14 and P28) (Fig. 2J and SI Fig. 7).
Ultrastructure of Mtmr13-Deficient Nerve Fibers.
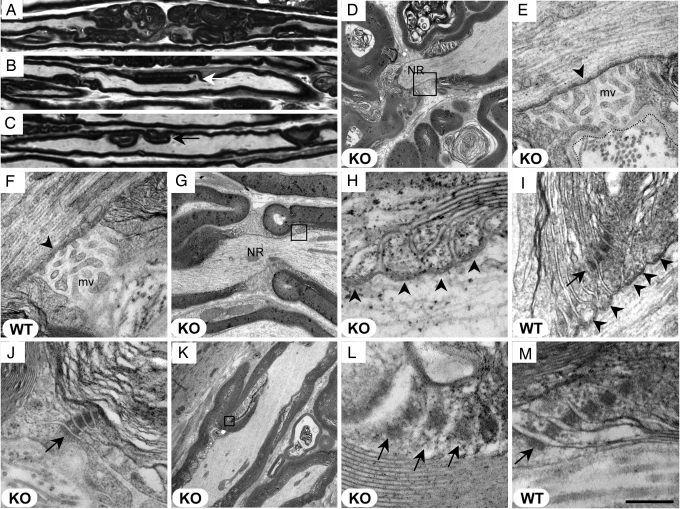
Given the profound dysmyelination and reduced MNCV observed in Mtmr13−/− mice, we performed an ultrastructural analysis to assess how specific subcellular domains of myelinating Schwann cells might be affected by the loss of Mtmr13. Myelin infoldings and outfoldings are most prominent adjacent to nodes of Ranvier (Fig. 3A), although they are also observed within internodal regions (Fig. 3 B and C), sometimes at Schmidt–Lanterman incisures. Several additional findings are consistent with both Mtmr13 and Mtmr2 having key functions within the paranodal region of the Schwann cell. First, our immunofluorescence experiments suggest that Mtmr13 is enriched at the paranode (data not shown). In addition, the Mtmr13 binding partner Mtmr2 is reported to be enriched at the paranode (44, 45). Indeed, loss of Mtmr2 leads to a failed recruitment of the MAGUK family scaffold protein Dlg1/Sap97 to the paranode (44, 45), suggesting that Mtmr2 may help to organize cell polarity protein complexes within this domain of Schwann cells. Finally, endosomes and lysosomes, organelles that contain and are regulated by the Mtmr2–Mtmr13 substrates PtdIns3P and PtdIns(3,5)P2, are found within the Schwann cell cytoplasm of the paranode (44, 46).
Fig. 3.
Ultrastructure of the node of Ranvier, paranode, and Schmidt–Lanterman incisures in Mtmr13-deficient nerve fibers. Wild-type (F, I, and M) and Mtmr13−/− (A–E, G, H, and J–L) mice were analyzed at 2 (A–C) or 7 (D–M) months. Longitudinal sections (0.5 μm and 70 nm in A–C and D–M, respectively) of sciatic nerves were analyzed by light microscopy (A–C) or EM (D–M). (A–C) Myelin misfolding is most prominent near nodes of Ranvier (A) but also occurs in internodal regions (arrows in B and C). (D) Myelin outfoldings adjacent to a node of Ranvier (NR) in an Mtmr13−/− nerve fiber. Note that the Schwann cell on either side of the node is affected. (E and F) Nodal microvilli (mv) appear morphologically normal in Mtmr13−/− Schwann cells. E is a magnification of the indicated portion of D. The electron-dense undercoating of the nodal axolemma (arrowhead) appears morphologically normal in Mtmr13−/− Schwann cells. The overlaying basal lamina is intact in nodes of Ranvier in Mtmr13−/− nerve fibers (a dotted line traces the outer edge of the basal lamina in E). (G–I) Paranodal, septate-like axo-glial junctions (arrowheads) are intact in Mtmr13−/− nerve fibers. H is a magnification of the indicated portion of G. (I and J) Autotypic adherens junctions (arrows) within paranodal loops are intact in Mtmr13−/− Schwann cells. (K–M) Autotypic adherens junctions (arrows) within Schmidt–Lanterman incisures are intact and in register in Mtmr13−/− Schwann cells. L is a magnification of the indicated portion of K. [Scale bar: 29 μm (A–C), 3.9 μm (D), 523 nm (E and F), 2 μm (G), 200 nm (H), 327 nm (I), 391 nm (J), 5.2 μm (K), 169 nm (L), and 200 nm (M).]
We examined the ultrastructure of the node of Ranvier and paranode in Mtmr13−/− nerves. By 7 months of age, all nodes of Ranvier examined in Mtmr13−/− nerves contained substantial myelin infoldings/outfoldings on both sides of the node (13 of 13 nodes) (Fig. 3 A, D, and G). Such myelin accumulations often dramatically alter the shape of the node (Fig. 3 A and D). However, nodal organization appears broadly intact in Mtmr13−/− nerves. The nodal microvilli appear morphologically normal, as does the electron-dense undercoating of the nodal axolemma (Fig. 3 E and F). The basal lamina that overlays the nodal microvilli also appears normal in Mtmr13−/− nerve fibers (Fig. 3E).
Paranodal ultrastructure also appears broadly normal in Mtmr13−/− nerve fibers. Paranodal axo-glial junctions appear intact and are morphologically similar to those of wild-type nerves (Fig. 3 H and I). In addition, the “autotypic” or “reflexive” adherens junctions formed between paranodal Schwann cell membrane loops appear intact in Mtmr13−/− nerves (Fig. 3 I and J) (47, 48). The analogous adherens junctions within Schmidt–Lanterman incisures also appear morphologically normal (Fig. 3 K–M) (49). Thus, despite the striking accumulations of myelin adjacent to nodes of Ranvier, all of the ultrastructural elements of the node and paranode that we have examined appeared intact.
Mtmr2 Abundance in Mtmr13-Deficient Nerves.
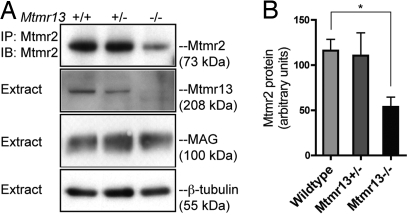
Mtmr13 is a large, multidomain protein that contains a catalytically inactive phosphatase domain and is associated with cellular membranes (39) (Fig. 1A). Mtmr13 associates with the active Mtmr2 phosphatase in a manner that requires coiled-coil sequences found in both proteins (39, 40). Via this interaction, Mtmr13 has been reported to directly stimulate the PI 3-phosphatase activity of Mtmr2 in vitro (40). Inactive myotubularins have also been proposed to regulate the cellular localization of active myotubularins (36, 37, 40). We investigated whether the loss of Mtmr13 might alter Mtmr2 protein levels in sciatic nerves. Mtmr2 was immunoprecipitated from wild-type and Mtmr13−/− nerves, and protein levels were assessed by immunoblotting. We consistently found Mtmr2 protein levels to be reduced in Mtmr13−/− nerves (Fig. 4A). Densitometric quantification of these findings indicated a decrease of ≈50% relative to wild-type nerves (Fig. 4B). The levels of myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG), a marker of noncompact myelin, were not significantly altered in Mtmr13−/− sciatic nerves (Fig. 4A). Thus, the loss of Mtmr13 leads to a reduced abundance of Mtmr2 in sciatic nerve, suggesting a possible mechanism for regulation of Mtmr2.
Fig. 4.
Mtmr2 protein levels in Mtmr13-deficient nerves. (A) Mtmr2 was immunoprecipitated (IP) from sciatic nerve extracts from mice of the indicated genotypes (see Materials and Methods). Immunoprecipitates and extracts were analyzed by SDS/PAGE and immunoblotting (IB) with antibodies specific for the indicated proteins. (B) Quantification of Mtmr2 abundance in sciatic nerve. Mtmr2 immunoblots (n = 3) were analyzed by using densitometry. Data presented are the relative abundance of Mtmr2 in arbitrary units (mean ± standard error). *, P = 0.020 (unpaired t test).
Discussion
Mtmr13-Deficient Mice as a Model of CMT4B2.
We describe a new mouse model of CMT4B2 peripheral neuropathy, in which many of the key characteristics of the human condition are well modeled. First, Mtmr13−/− mice possess substantially slowed NCV. Second, the myelin outfoldings and infoldings observed in Mtmr13−/− nerves are remarkably similar to those found in the nerves of CMT4B2 patients (5, 8, 42, 43). Third, as in CMT4B2, both motor and sensory nerves are affected. Finally, the early onset and progressive nature of the phenotype described here correlate well with the clinical picture of CMT4B2 (5, 8, 42, 43). The neuropathy observed in Mtmr13−/− animals is also very similar to that of mice lacking Mtmr2, an active PI 3-phosphatase that associates with Mtmr13 (44, 45, 50).
Our model of CMT4B2 also differs from the human condition in several ways. Nerve biopsies from CMT4B2 patients show severe axon loss, hypomyelination of axons, and evidence of demyelination/remyelination (onion bulbs) (5, 8, 42, 43). However, these features are rather limited in Mtmr13−/− sciatic nerves, even those from mice 14 months of age. Significant axon loss is not apparent in sciatic nerves, and degenerating axons are only occasionally observed. These differences may result from the relative shortness of both lifespan and nerve length in mice (3). Axon loss might also be more pronounced in more distal portions of Mtmr13−/− nerves, as was observed in Mtmr2−/− nerves (45).
Relationship Between Mtmr2 and Mtmr13.
Our study provides insight into the relationship between Mtmr13 and its binding partner, the active PI 3-phosphatase Mtmr2. First, the similarity between the neuropathy described here and that described for Mtmr2−/− mice (44, 45, 50) is consistent with the hypothesis that these two proteins function together or at least in the same pathway. Second, we demonstrate here that Mtmr2 protein levels are reduced by ≈50% in Mtmr13−/− sciatic nerves, raising the possibility that Mtmr2 phosphatase activity is reduced in the absence of Mtmr13. However, a 50% reduction in Mtmr2 protein levels seems unlikely to be the sole cause of the observed phenotype, because Mtmr2-heterozygous mice are phenotypically normal (44, 45, 50). Further studies of Mtmr2−/− and Mtmr13−/− mice will be required to understand the likely complex relationship between the two proteins. For example, it will be important to evaluate the localization and phosphatase activity of Mtmr2 in Mtmr13−/− nerves.
Effect of Loss of Mtmr13 on Schwann Cell Ultrastructure.
It is unclear how the loss of either Mtmr13 or Mtmr2 leads to the dramatic myelin morphology abnormalities observed in mice and patients. In Mtmr13−/− nerves, myelin outfoldings and infoldings are most prominent in the paranodal domain of the Schwann cell, and the same has been observed in Mtmr2−/− mice (44, 45, 50). Therefore, we investigated whether the ultrastructure of the node of Ranvier and the paranode is altered in Mtmr13−/− nerve fibers. Despite massive myelin accumulations adjacent to the node of Ranvier, all of the ultrastructural elements of the node and paranode that we examined appeared morphologically similar to those of the wild type. Thus, aberrant myelin accumulations are unlikely to result from an overt structural defect within the paranode or node of Ranvier. An attractive alternate hypothesis is that the loss of Mtmr13 deranges myelin membrane turnover within the paranode, leading to excessive accumulation. Such a model has been proposed for Mtmr2−/− mice (44). Mtmr2–Mtmr13-mediated regulation of PtdIns3P, PtdIns(3,5)P2, and endosomal–lysosomal membrane traffic at the paranode would be broadly consistent with the functions of myotubularins in S. cerevisiae and C. elegans (34, 35, 51). It is notable that paranodes are sites of myelin membrane remodeling during early postnatal development (52).
3-Phosphoinositide Dysregulation and Peripheral Neuropathy.
Recent genetic studies have highlighted the importance of the regulation of PtdIns3P and PtdIns(3,5)P2 in the peripheral nervous system. First, the PtdIns(3,5)P2 5-phosphatase FIG4 was recently shown to be the protein deficient in CMT4J (53). Second, mutations in Frabin/FGD4 have been found to cause CMT4H (11, 12). Frabin/FGD4 encodes a Rho GTPase guanine nucleotide exchange factor that activates Cdc42 (54). Interestingly, Frabin also contains a FYVE domain, which may bind to PtdIns3P. Nerve biopsies from CMT4H patients show myelin outfoldings and infoldings similar to those observed in CMT4B1/2 patients (12). To speculate, MTMR2, MTMR13, and Frabin might function in a signaling pathway that involves regulation of PtdIns3P and Cdc42-mediated changes in cell shape and polarity. The CMT4B2 mouse model that we have described here will be an essential tool for future investigations of the function of 3-phosphoinositides in peripheral nerve.
While we were preparing our manuscript, a paper by Tersar et al. describing the characterization of a line of Mtmr13/Sbf2-deficient mice was published (55). The authors used a gene-trapping approach distinct from ours to disrupt Mtmr13. The independent use of two distinct gene-trap disruptions of Mtmr13 to produce mouse models of CMT4B2 firmly validates Mtmr13 deficiency as a model of this human condition.
Materials and Methods
Disruption of Mtmr13.
A full description of our gene-trap disruption of Mtmr13 is available in SI Materials and Methods. ES cell line RRF511 contains an exon-trapping plasmid (pGT0lxf) integrated within intron 16–17 of the Mtmr13 gene. The resulting mutant mRNA is predicted to contain exons 1–16 followed by an in-frame βgeo ORF, a stop codon, and a poly(A) signal. The resulting protein is predicted to consist of Mtmr13 residues 1–620 fused to βgeo. The genomic site of pGT0lxf integration was identified by using PCR to scan through intron 16–17 with various 5′ primers of intronic sequence and a 3′ primer specific for pGT0lxf (primer 541). All animal work was approved by the University of California at San Diego Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee.
Protein Analysis.
Protein extracts were prepared by homogenizing fresh brains from 6-month-old animals in ice-cold lysis buffer (see SI Materials and Methods) and clearing the extract by centrifugation at 17,000 × g. Sciatic nerves (from sciatic notch to knee) were frozen by using liquid nitrogen. Nerves from two 10-month-old mice were pooled and ground to a powder in a nitrogen-chilled mortar and pestle. This material was suspended in lysis buffer, homogenized, and clarified by centrifugation. Mtmr13 and Mtmr2 were immunoprecipitated from brain or sciatic nerve extracts as described previously (39), except that either 10 mg of extracted brain protein or 0.4 mg of sciatic nerve protein was used for immunoprecipitation (IP). Immunoprecipitates and extracts were analyzed by SDS/PAGE, immunoblotting, and densitometry as described previously (39). Antibodies used were rabbit anti-MTMR2 and anti-MTMR13 (39), rabbit anti-MAG, and mouse anti-β-tubulin (Santa Cruz Biotechnology).
NCV.
NCV was examined by using a previously described procedure (56) (see SI Materials and Methods).
Morphological Analysis.
Mice were perfused with 4% paraformaldehyde/1.5% glutaraldehyde in 0.1 M sodium cacodylate buffer (pH 7.4). Nerves were removed, fixed overnight in the same buffer, and prepared for EM by postfixation with OsO4 and en bloc staining with uranyl acetate. Ultrathin (70-nm) sections were cut and contrasted further with uranyl acetate and lead nitrate, and grids were examined by EM (see SI Materials and Methods). For semithin morphological analysis, nerves were processed as described above except that 0.5 μm were stained with toluidine blue. Mid-sciatic nerve sections were examined by light microscopy or EM. Mid-sciatic nerve sections from heterozygous mice were examined at 7 and 14 months and were indistinguishable from those of wild-type mice when examined by either light microscopy or EM.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments.
We thank Dr. Marilyn Farquhar and Timo Meerloo for training and use of the Immunoelectron Microscopy Core Facility, which is supported in part by National Institutes of Health Grants CA100768 and DK17780 (to Dr. Farquhar). We thank Drs. Ryan A. Adams, Katerina Akassoglou, Nigel A. Calcutt, Mathew S. Gentry, Andrew P. Mizisin, Anne N. Murphy, and Gregory S. Taylor for helpful discussions. We also thank Drs. Calcutt and Mizisin for critically reading the manuscript, for the use of equipment, and for assistance in the interpretation of NCV data. This work was supported by Muscular Dystrophy Association Grant MDA4266 (to F.L.R.), National Institutes of Health Grant R37DK018024 (to J.E.D.), and National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke Grant K99NS057903 (to F.L.R.).
Footnotes
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
This article contains supporting information online at www.pnas.org/cgi/content/full/0800742105/DC1.
References
- 1.Scherer SS. Finding the causes of inherited neuropathies. Arch Neurol. 2006;63:812–816. doi: 10.1001/archneur.63.6.812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Saifi GM, Szigeti K, Snipes GJ, Garcia CA, Lupski JR. Molecular mechanisms, diagnosis, and rational approaches to management of and therapy for Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and related peripheral neuropathies. J Invest Med. 2003;51:261–283. doi: 10.1136/jim-51-05-14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Suter U, Scherer SS. Disease mechanisms in inherited neuropathies. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2003;4:714–726. doi: 10.1038/nrn1196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Shy ME. Therapeutic strategies for the inherited neuropathies. Neuromol Med. 2006;8:255–278. doi: 10.1385/nmm:8:1-2:255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Othmane KB, et al. Identification of a new locus for autosomal recessive Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease with focally folded myelin on chromosome 11p15. Genomics. 1999;62:344–349. doi: 10.1006/geno.1999.6028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ohnishi A, et al. Autosomal recessive motor and sensory neuropathy with excessive myelin outfolding. Muscle Nerve. 1989;12:568–575. doi: 10.1002/mus.880120707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Quattrone A, et al. Autosomal recessive hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy with focally folded myelin sheaths: Clinical, electrophysiologic, and genetic aspects of a large family. Neurology. 1996;46:1318–1324. doi: 10.1212/wnl.46.5.1318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Previtali SC, Quattrini A, Bolino A. Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 4B demyelinating neuropathy: Deciphering the role of MTMR phosphatases. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2007;9:1–16. doi: 10.1017/S1462399407000439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Fabrizi GM, et al. Focally folded myelin in Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy type 1B with Ser49Leu in the myelin protein zero. Acta Neuropathol (Berlin) 2000;100:299–304. doi: 10.1007/s004019900175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kochanski A, Drac H, Jedrzejowska H, Hausmanowa-Petrusewicz I. Focally folded myelin in Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 1B disease is associated with Asn131Lys mutation in myelin protein zero gene: Short report. Eur J Neurol. 2003;10:547–549. doi: 10.1046/j.1468-1331.2003.00640.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Delague V, et al. Mutations in FGD4 encoding the Rho GDP/GTP exchange factor FRABIN cause autosomal recessive Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 4H. Am J Hum Genet. 2007;81:1–16. doi: 10.1086/518428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Stendel C, et al. Peripheral nerve demyelination caused by a mutant Rho GTPase guanine nucleotide exchange factor, frabin/FGD4. Am J Hum Genet. 2007;81:158–164. doi: 10.1086/518770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Bolino A, et al. Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 4B is caused by mutations in the gene encoding myotubularin-related protein-2. Nat Genet. 2000;25:17–19. doi: 10.1038/75542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Senderek J, et al. Mutation of the SBF2 gene, encoding a novel member of the myotubularin family, in Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy type 4B2/11p15. Hum Mol Genet. 2003;12:349–356. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddg030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Azzedine H, et al. Mutations in MTMR13, a new pseudophosphatase homologue of MTMR2 and Sbf1, in two families with an autosomal recessive demyelinating form of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease associated with early-onset glaucoma. Am J Hum Genet. 2003;72:1141–1153. doi: 10.1086/375034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hirano R, et al. SET binding factor 2 (SBF2) mutation causes CMT4B with juvenile onset glaucoma. Neurology. 2004;63:577–580. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000133211.40288.9a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Wishart MJ, Dixon JE. PTEN and myotubularin phosphatases: From 3-phosphoinositide dephosphorylation to disease. Trends Cell Biol. 2002;12:579–585. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(02)02412-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Taylor GS, Dixon JE. PTEN and myotubularins: Families of phosphoinositide phosphatases. Methods Enzymol. 2003;366:43–56. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(03)66004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Laporte J, Bedez F, Bolino A, Mandel JL. Myotubularins, a large disease-associated family of cooperating catalytically active and inactive phosphoinositides phosphatases. Hum Mol Genet. 2003;12(Suppl 2):R285–R292. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddg273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Clague MJ, Lorenzo O. The myotubularin family of lipid phosphatases. Traffic. 2005;6:1063–1069. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2005.00338.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Robinson FL, Dixon JE. Myotubularin phosphatases: Policing 3-phosphoinositides. Trends Cell Biol. 2006;16:403–412. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2006.06.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Tonks NK. Protein tyrosine phosphatases: From genes, to function, to disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7:833–846. doi: 10.1038/nrm2039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Zhang ZY, et al. The Cys(X)5Arg catalytic motif in phosphoester hydrolysis. Biochemistry. 1994;33:15266–15270. doi: 10.1021/bi00255a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Taylor GS, Maehama T, Dixon JE. Myotubularin, a protein tyrosine phosphatase mutated in myotubular myopathy, dephosphorylates the lipid second messenger, phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000;97:8910–8915. doi: 10.1073/pnas.160255697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Blondeau F, et al. Myotubularin, a phosphatase deficient in myotubular myopathy, acts on phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate pathway. Hum Mol Genet. 2000;9:2223–2229. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.hmg.a018913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Walker DM, et al. Characterization of MTMR3, an inositol lipid 3-phosphatase with novel substrate specificity. Curr Biol. 2001;11:1600–1605. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(01)00501-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Efe JA, Botelho RJ, Emr SD. The Fab1 phosphatidylinositol kinase pathway in the regulation of vacuole morphology. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2005;17:402–408. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2005.06.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lindmo K, Stenmark H. Regulation of membrane traffic by phosphoinositide 3-kinases. J Cell Sci. 2006;119:605–614. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kutateladze TG. Phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate recognition and membrane docking by the FYVE domain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1761:868–877. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2006.03.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Michell RH, Heath VL, Lemmon MA, Dove SK. Phosphatidylinositol 3,5-bisphosphate: Metabolism and cellular functions. Trends Biochem Sci. 2006;31:52–63. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2005.11.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Srivastava S, et al. Phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate indirectly activates KCa3.1 via 14 amino acids in the carboxy terminus of KCa3.1. Mol Biol Cell. 2006;17:146–154. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E05-08-0763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Laporte J, et al. A gene mutated in X-linked myotubular myopathy defines a new putative tyrosine phosphatase family conserved in yeast. Nat Genet. 1996;13:175–182. doi: 10.1038/ng0696-175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Firestein R, et al. Male infertility, impaired spermatogenesis, and azoospermia in mice deficient for the pseudophosphatase Sbf1. J Clin Invest. 2002;109:1165–1172. doi: 10.1172/JCI12589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Dang H, Li Z, Skolnik EY, Fares H. Disease-related myotubularins function in endocytic traffic in Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol Biol Cell. 2004;15:189–196. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E03-08-0605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Parrish WR, Stefan CJ, Emr SD. Essential role for the myotubularin-related phosphatase Ymr1p and the synaptojanin-like phosphatases Sjl2p and Sjl3p in regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate in yeast. Mol Biol Cell. 2004;15:3567–3579. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E04-03-0209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Kim SA, Vacratsis PO, Firestein R, Cleary ML, Dixon JE. Regulation of myotubularin-related (MTMR)2 phosphatidylinositol phosphatase by MTMR5, a catalytically inactive phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:4492–4497. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0431052100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Nandurkar HH, et al. Identification of myotubularin as the lipid phosphatase catalytic subunit associated with the 3-phosphatase adapter protein, 3-PAP. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:8660–8665. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1033097100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Mochizuki Y, Majerus PW. Characterization of myotubularin-related protein 7 and its binding partner, myotubularin-related protein 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:9768–9773. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1333958100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Robinson FL, Dixon JE. The phosphoinositide-3-phosphatase MTMR2 associates with MTMR13, a membrane-associated pseudophosphatase also mutated in type 4B Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:31699–31707. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M505159200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Berger P, et al. Multi-level regulation of myotubularin-related protein-2 phosphatase activity by myotubularin-related protein-13/set-binding factor-2. Hum Mol Genet. 2006;15:569–579. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddi473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Lorenzo O, Urbe S, Clague MJ. Systematic analysis of myotubularins: Heteromeric interactions, subcellular localisation and endosome related functions. J Cell Sci. 2006;119:2953–2959. doi: 10.1242/jcs.03040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Gambardella A, et al. Genetic heterogeneity in autosomal recessive hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy with focally folded myelin sheaths (CMT4B) Neurology. 1998;50:799–801. doi: 10.1212/wnl.50.3.799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Kiwaki T, et al. Hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy with myelin folding and juvenile onset glaucoma. Neurology. 2000;55:392–397. doi: 10.1212/wnl.55.3.392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Bolino A, et al. Disruption of Mtmr2 produces CMT4B1-like neuropathy with myelin outfolding and impaired spermatogenesis. J Cell Biol. 2004;167:711–721. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200407010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Bolis A, et al. Loss of Mtmr2 phosphatase in Schwann cells but not in motor neurons causes Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 4B1 neuropathy with myelin outfoldings. J Neurosci. 2005;25:8567–8577. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2493-05.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Fortun J, et al. Alterations in degradative pathways and protein aggregation in a neuropathy model based on PMP22 overexpression. Neurobiol Dis. 2005;22:153–164. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2005.10.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Fannon AM, et al. Novel E-cadherin-mediated adhesion in peripheral nerve: Schwann cell architecture is stabilized by autotypic adherens junctions. J Cell Biol. 1995;129:189–202. doi: 10.1083/jcb.129.1.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Balice-Gordon RJ, Bone LJ, Scherer SS. Functional gap junctions in the schwann cell myelin sheath. J Cell Biol. 1998;142:1095–1104. doi: 10.1083/jcb.142.4.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Hall SM, Williams PL. Studies on the “incisures” of Schmidt and Lanterman. J Cell Sci. 1970;6:767–791. doi: 10.1242/jcs.6.3.767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Bonneick S, et al. An animal model for Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 4B1. Hum Mol Genet. 2005;14:3685–3695. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddi400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Xue Y, et al. Genetic analysis of the myotubularin family of phosphatases in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:34380–34386. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M303259200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Berthold CH, Nilsson RI. De- and remyelination in spinal roots during normal perinatal development in the cat: A brief summary of structural observations and a conceptual hypothesis. J Anat. 2002;200:391–403. doi: 10.1046/j.1469-7580.2002.00042.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Chow CY, et al. Mutation of FIG4 causes neurodegeneration in the pale tremor mouse and patients with CMT4J. Nature. 2007;448:68–72. doi: 10.1038/nature05876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Umikawa M, et al. Association of frabin with the actin cytoskeleton is essential for microspike formation through activation of Cdc42 small G protein. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:25197–25200. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.36.25197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Tersar K, et al. Mtmr13/Sbf2-deficient mice: An animal model for CMT4B2. Hum Mol Genet. 2007;16:2991–3001. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddm257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Garcia ML, et al. NF-M is an essential target for the myelin-directed “outside-in” signaling cascade that mediates radial axonal growth. J Cell Biol. 2003;163:1011–1020. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200308159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.