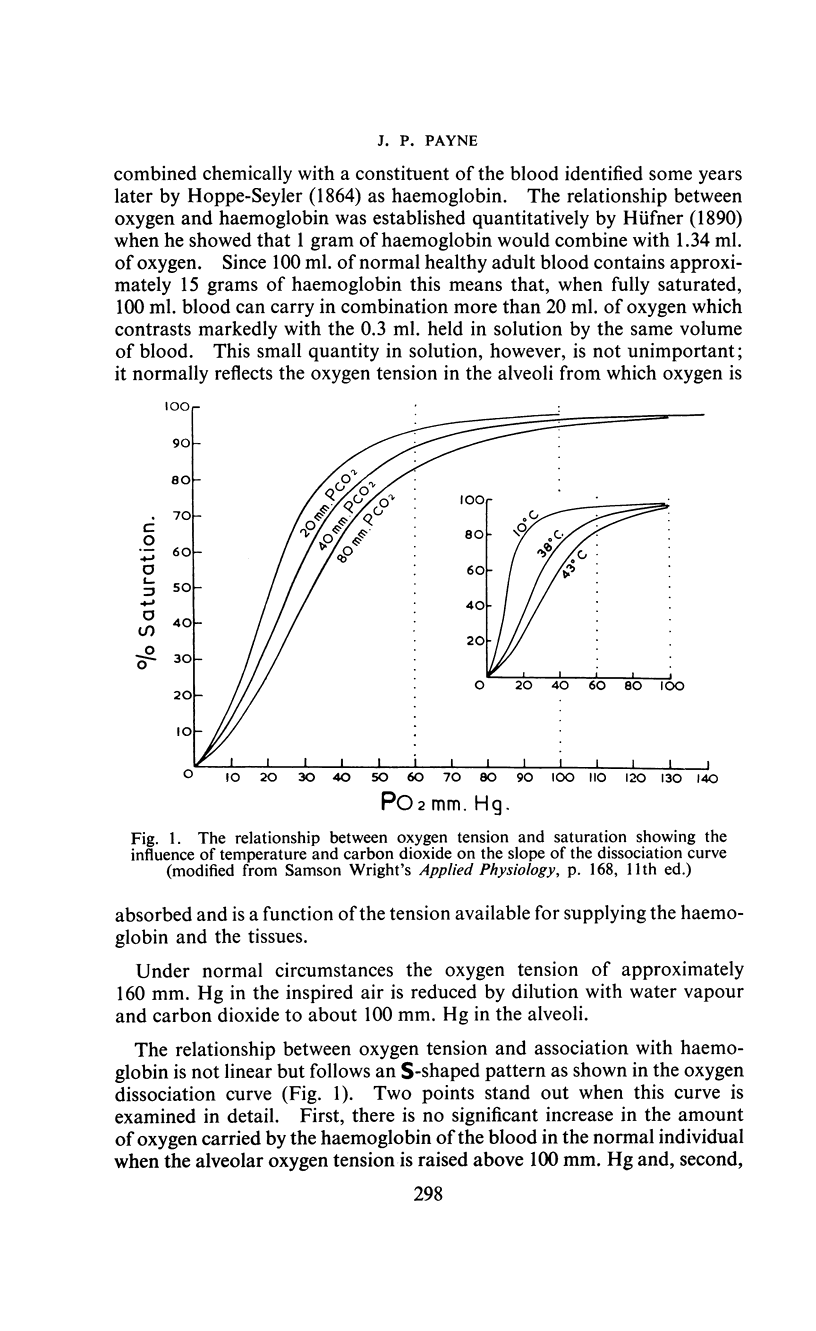
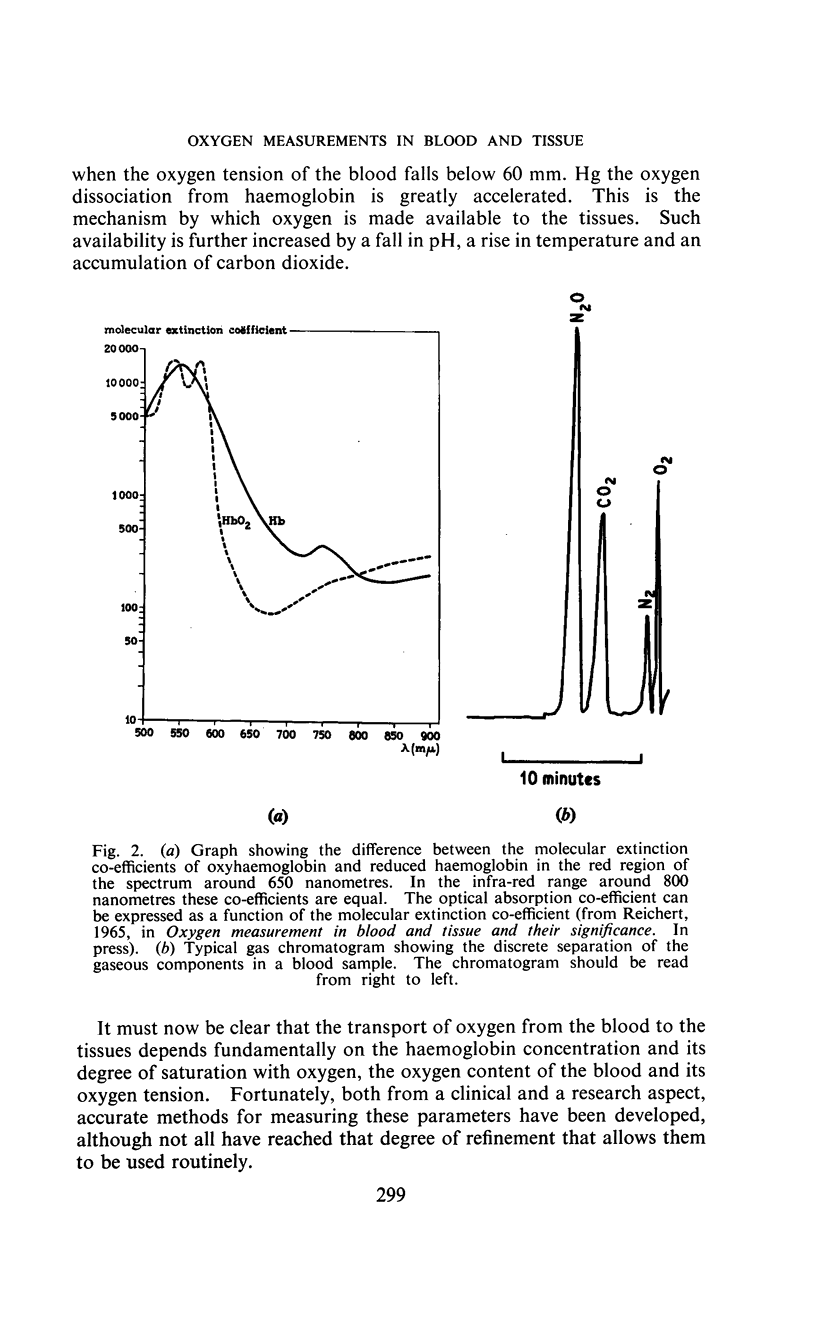
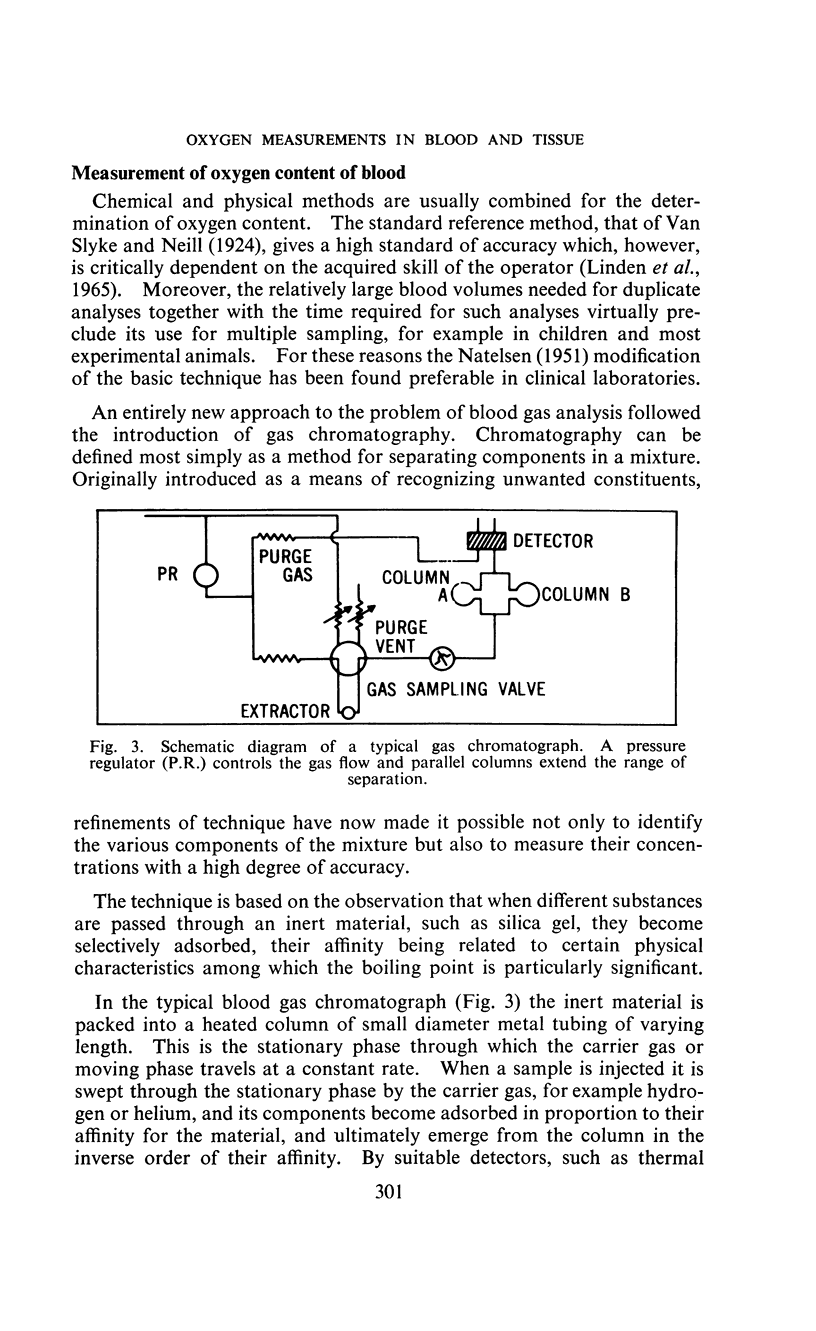
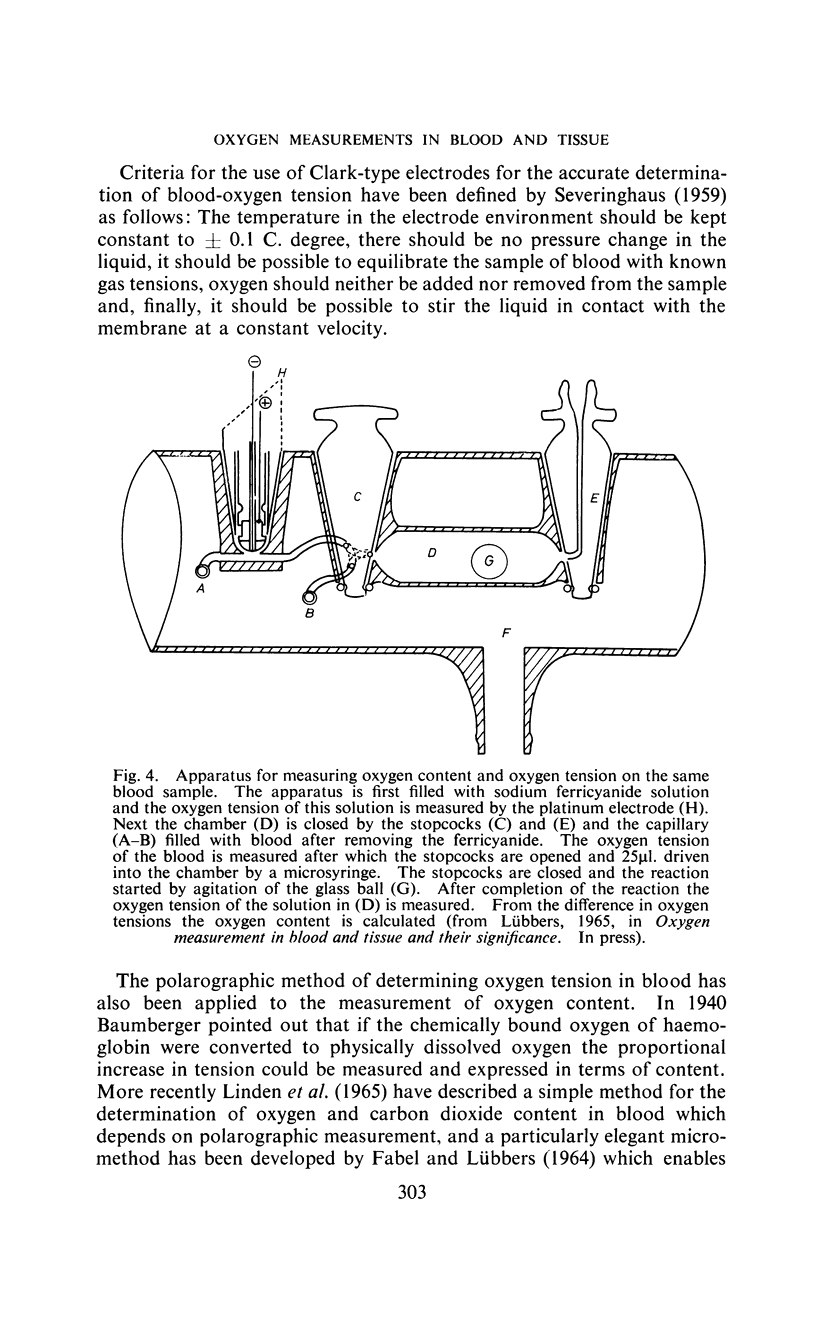
Full text
PDF


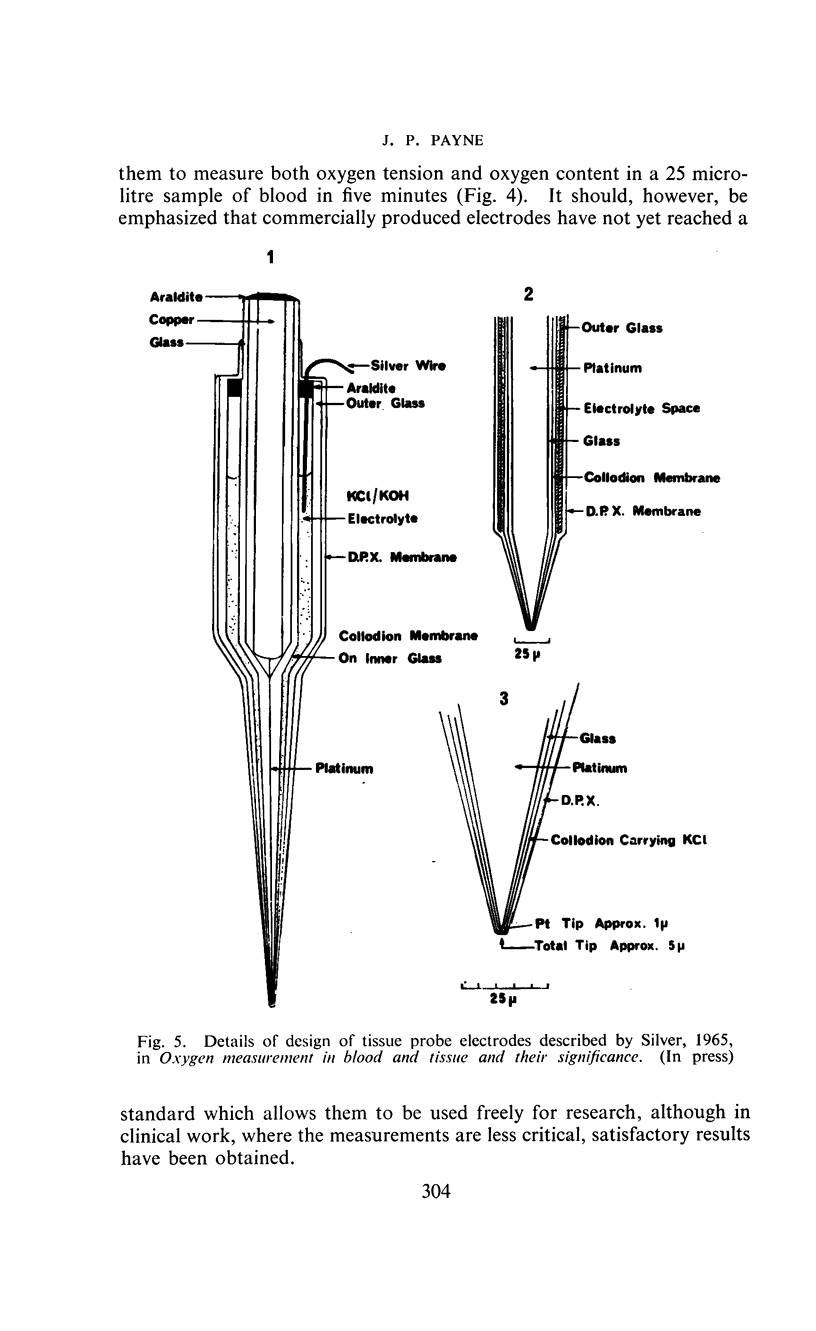
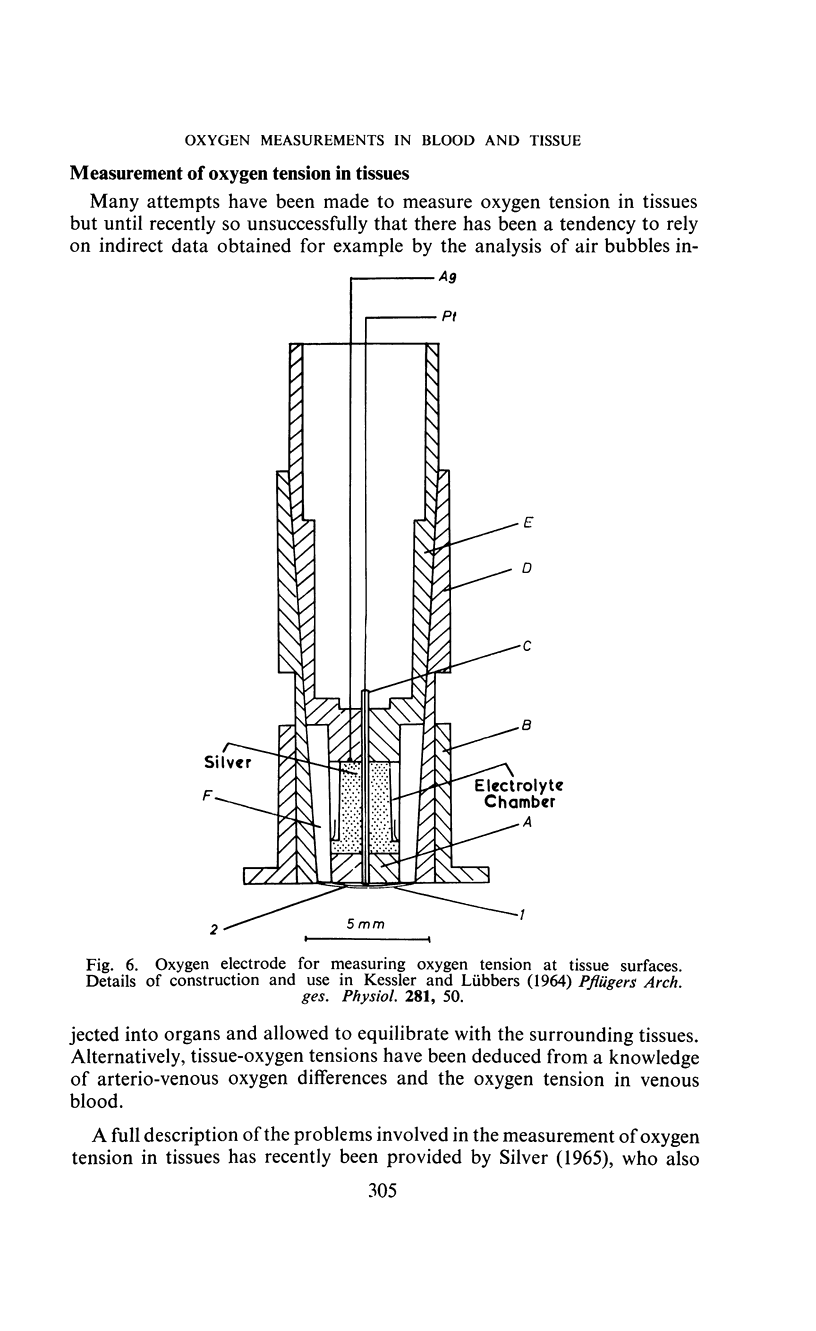



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRINKMAN R., ZYLSTRA W. G. Determination and continuous registration of the percentage oxygen saturation in clinical conditions. Arch Chir Neerl. 1949;1(3):177–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
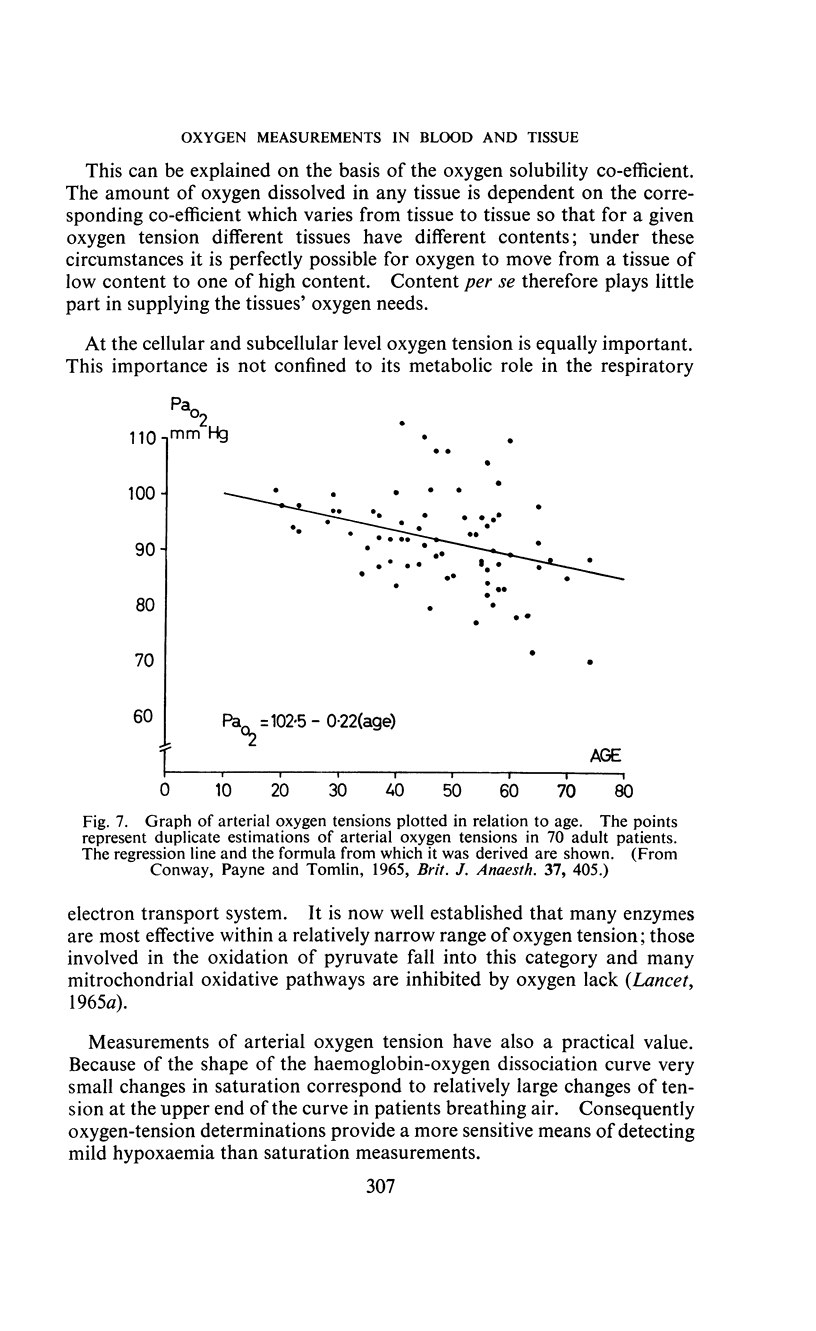
- CONWAY C. M., PAYNE J. P., TOMLIN P. J. ARTERIAL OXYGEN TENSIONS OF PATIENTS AWAITING SURGERY. Br J Anaesth. 1965 Jun;37:405–408. doi: 10.1093/bja/37.6.405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONWAY C. M., PAYNE J. P., TOMLIN P. J. ARTERIAL OXYGEN TENSIONS OF PATIENTS AWAITING SURGERY. Br J Anaesth. 1965 Jun;37:405–408. doi: 10.1093/bja/37.6.405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NATELSON S. Routine use of ultramicro methods in the clinical laboratory; estimation of sodium, potassium, chloride, protein, hematocrit value, sugar, urea and nonprotein nitrogen in fingertip blood; construction of ultramicro pipets; a practical microgasometer for estimation of carbon dioxide. Am J Clin Pathol. 1951 Dec;21(12):1153–1172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NUNN J. F., PAYNE J. P. Hypoxaemia after general anaesthesia. Lancet. 1962 Sep 29;2(7257):631–632. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(62)92541-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAINE J. M., BISHOP J. M. A-a difference in O2 tension and physiological dead space in normal man. J Appl Physiol. 1963 Mar;18:284–288. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1963.18.2.284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEPHEN C. R., TALTON I. IMMEDIATE POSTOPERATIVE CARE, WITH PARTICULAR REFERENCE TO BLOOD-GAS STUDIES. Can Anaesth Soc J. 1964 Nov;11:586–597. doi: 10.1007/BF03004103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YEE H. Y. CALIBRATION FOR BLOOD GAS DETERMINATION BY GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY. Anal Chem. 1965 Jun;37:924–925. doi: 10.1021/ac60226a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


