Abstract
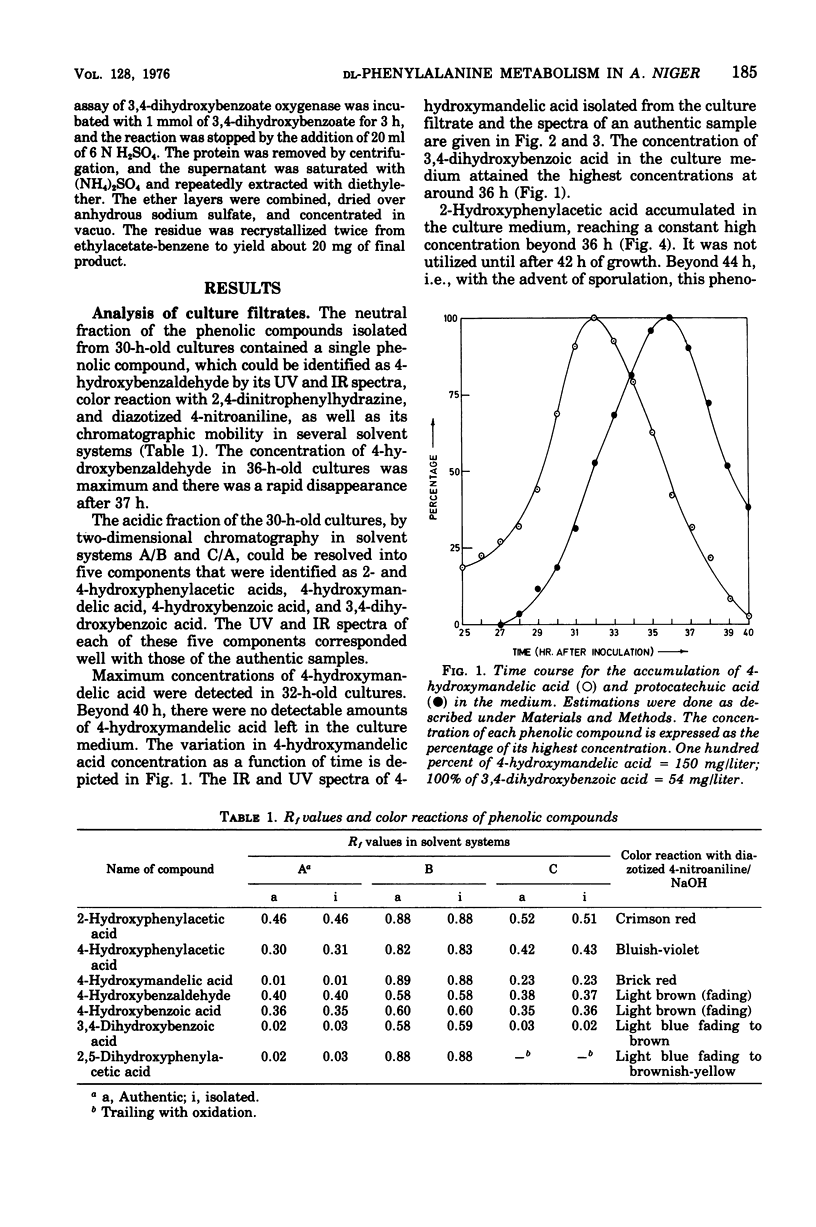
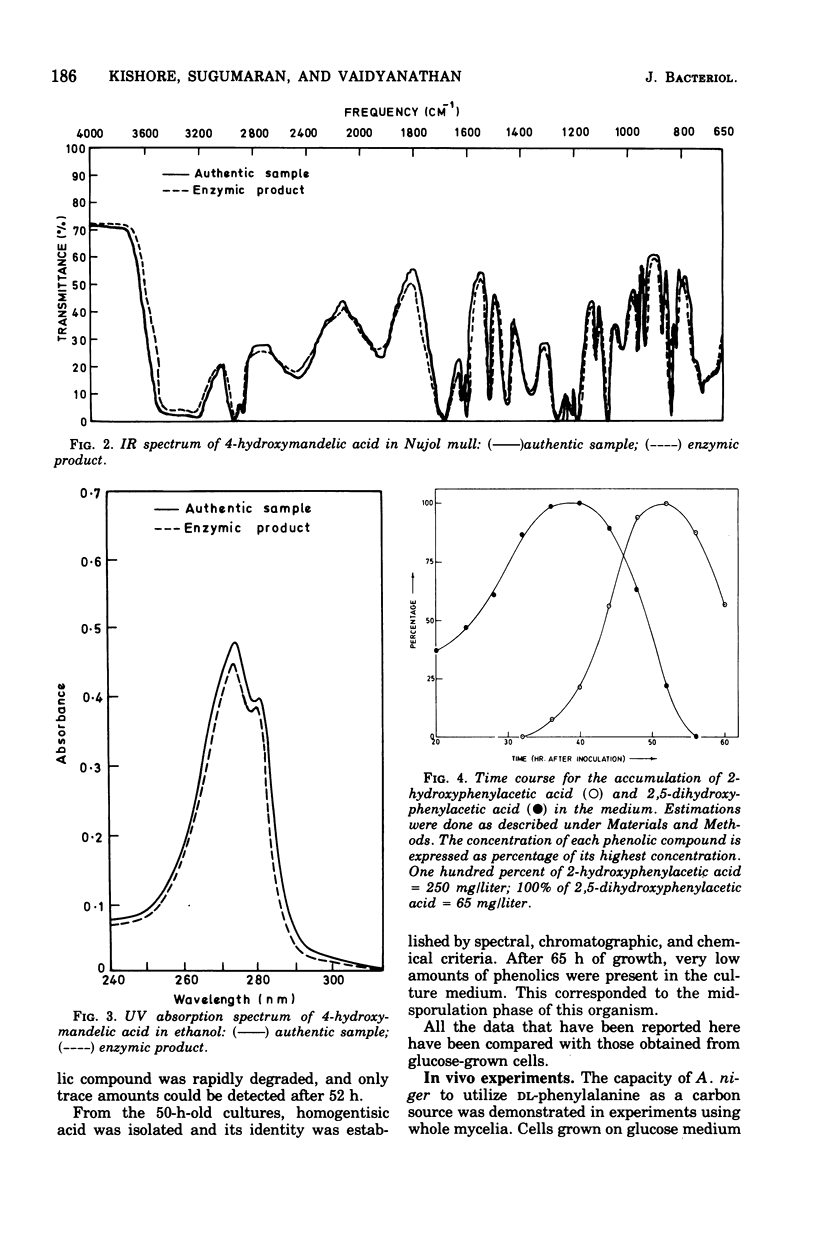
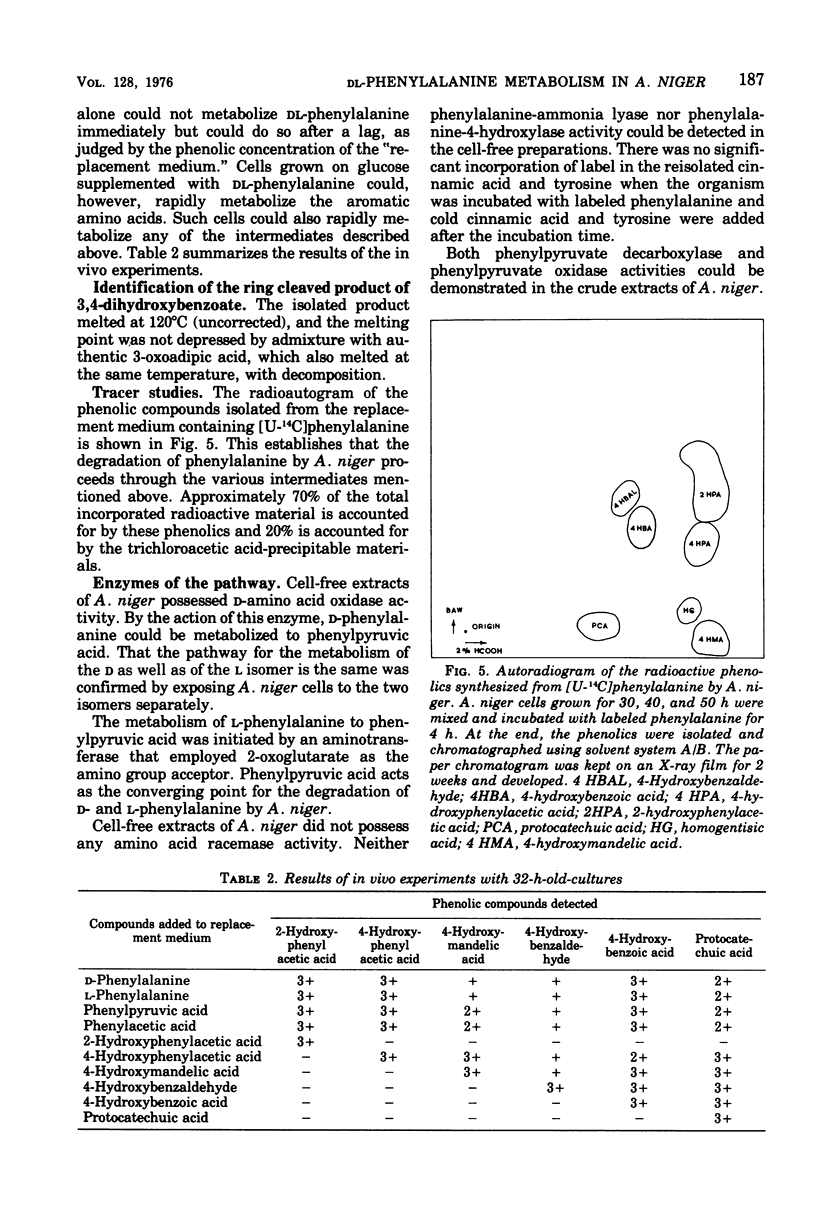
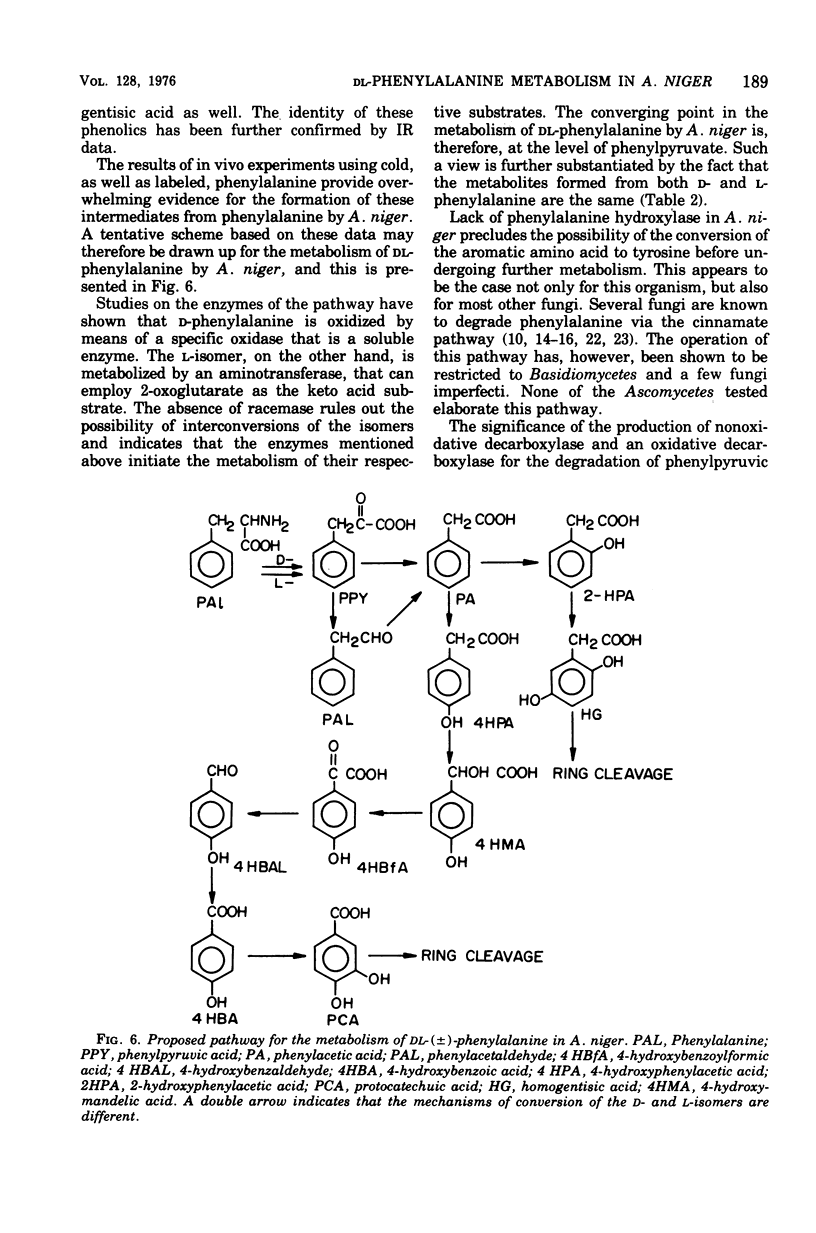
A fungus capable of degrading DL-phenylalanine was isolated from the soil and identified as Aspergillus niger. It was found to metabolize DL-phenylalanine by a new pathway involving 4-hydroxymandelic acid. D-Amino acid oxidase and L-phenylalanine: 2-oxoglutaric acid aminotransferase initiated the degradation of D- and L-phenylalanine, respectively. Both phenylpyruvate oxidase and phenylpyruvate decarboxylase activities could be demonstrated in the cell-free system. Phenylacetate hydroxylase, which required reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, converted phenylacetic acid to 2- and 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid. Although 4-hydroxyphenylacetate was converted to 4-hydroxymandelate, 2-hydroxyphenylacetate was not utilized until the onset of sporulation. During sporulation, it was converted rapidly into homogentisate and oxidized to ring-cleaved products. 4-Hydroxymandelate was degraded to protocatechuate via 4-hydroxybenzoylformate, 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde, and 4-hydroxybenzoate.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BYRDE R. J., HARRIS J. F., WOODCOCK D. Fungal detoxication, the metabolism of -(2-naphthyloxy)-n-alkylcarboxylic acids by Aspergillus niger. Biochem J. 1956 Sep;64(1):154–160. doi: 10.1042/bj0640154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cain R. B., Bilton R. F., Darrah J. A. The metabolism of aromatic acids by micro-organisms. Metabolic pathways in the fungi. Biochem J. 1968 Aug;108(5):797–828. doi: 10.1042/bj1080797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowden R. K. Biosynthesis of the polyphenolic acid metabolites of Polyporus tumulosus Cooke. Can J Microbiol. 1967 Feb;13(2):181–197. doi: 10.1139/m67-025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellman J. H., Fujita T. S., Roth E. S. Assay, properties and tissue distribution of p-hydroxyphenylpyruvate hydroxylase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 19;284(1):90–100. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90048-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUNSALUS I. C., GUNSALUS C. F., STANIER R. Y. The enzymatic conversion of mandelic acid to benzoic acid. I. Gross fractionation of the system into soluble and particulate components. J Bacteriol. 1953 Nov;66(5):538–542. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.5.538-542.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson D. T. Microbial degradation of aromatic compounds. Science. 1967 Sep 13;161(3846):1093–1097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamaluddin M., Rao P. V., Vaidyanathan C. S. Involvement of the protocatechuate pathway in the metabolism of mandelic acid by Aspergillus niger. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):786–793. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.786-793.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRSHNER N. Pathway of noradrenaline formation from DOPA. J Biol Chem. 1957 Jun;226(2):821–825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalghatgi K. K., Nambudiri A. M., Bhat J. V., Subba Rao P. V. Degradation of L-penylalanine by Rhizoctonia solani. Indian J Biochem Biophys. 1974 Jun;11(2):116–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishore G., Sugumaran M., Vaidyanathan C. S. p-Hydroxymandelic acid--a key intermediate in the metabolism of DL (plus or minus)-phenylalanine by Aspergillus niger. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Feb 27;56(4):851–859. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80266-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore K., Rao P. V., Towers G. H. Degradation of phenylalanine and tyrosine by Sporobolomyces roseus. Biochem J. 1968 Jan;106(2):507–514. doi: 10.1042/bj1060507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore K., Rao P. V., Towers G. H. Degradion of phenylalanine and tyrosine by Basidiomycetes. Life Sci. 1967 Dec 15;6(24):2629–2633. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(67)90113-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore K., Towers G. H. Degradation of aromatic amino acids by fungi. I. Fate of L-phenylalanine in Schizophyllum commune. Can J Biochem. 1967 Nov;45(11):1659–1665. doi: 10.1139/o67-196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAIR P. M., VAIDYANATHAN C. S. A COLORIMETRIC METHOD FOR DETERMINATION OF PYROCATECHOL AND RELATED SUBSTANCES. Anal Biochem. 1964 Mar;7:315–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J. A., Coon M. J. Enzymatic omega-oxidation. 3. Purification and properties of rubredoxin, a component of the omega-hydroxylation system of Pseudomonas oleovorans. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jan 25;243(2):329–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramanarayanan M., Vaidyanathan C. S. Mandelate oxidase of Aspergillus niger. I. Properties of particulate D(-)-mandelate oxidase. Indian J Biochem Biophys. 1973 Dec;10(4):254–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stachow C. S., Stevenson I. L., Day D. Purification and properties of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-specific benzaldehyde dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas. J Biol Chem. 1967 Nov 25;242(22):5294–5300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


