Abstract
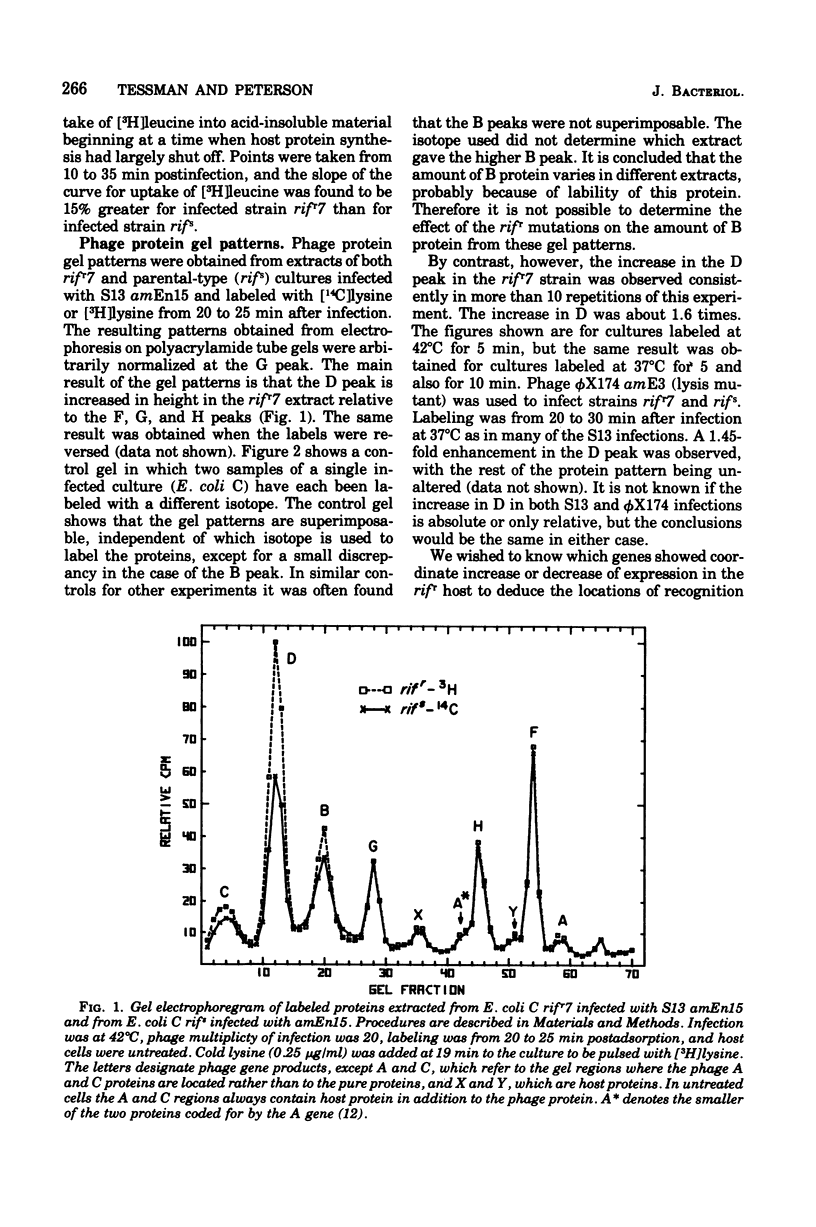
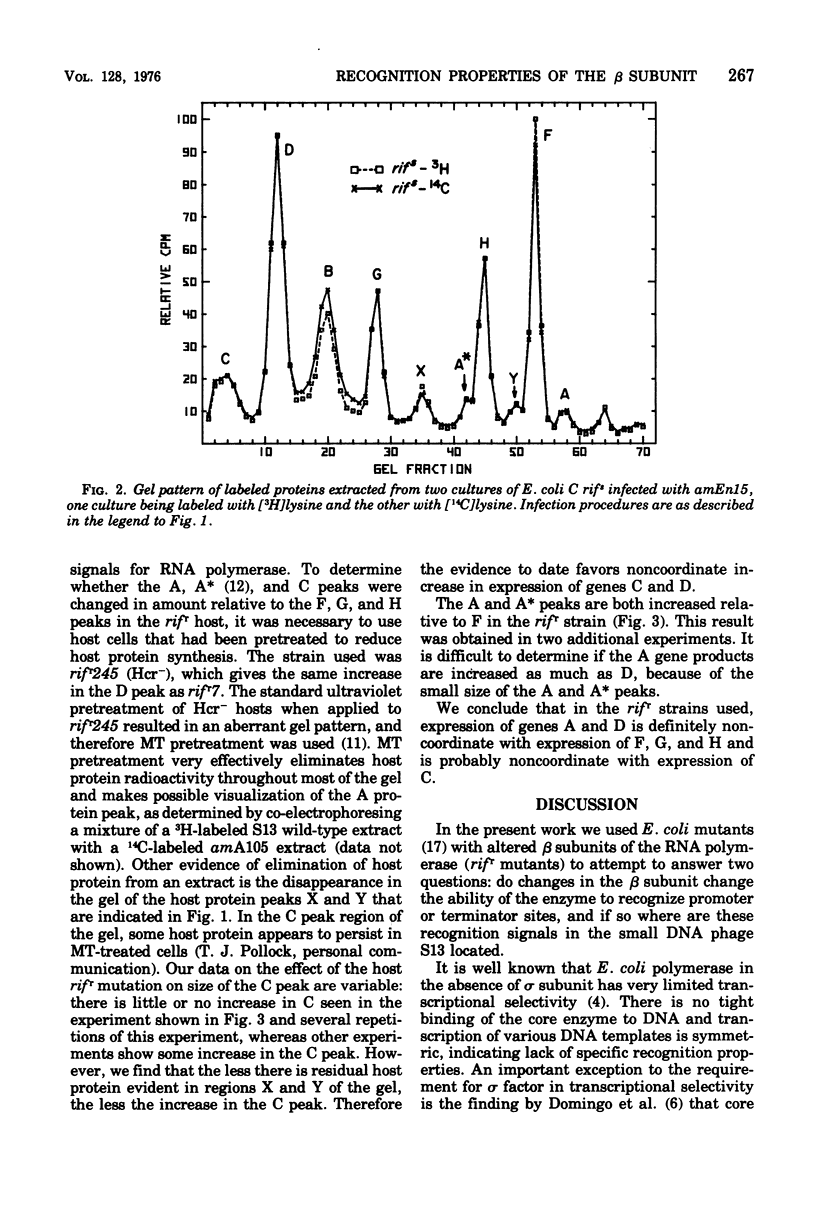
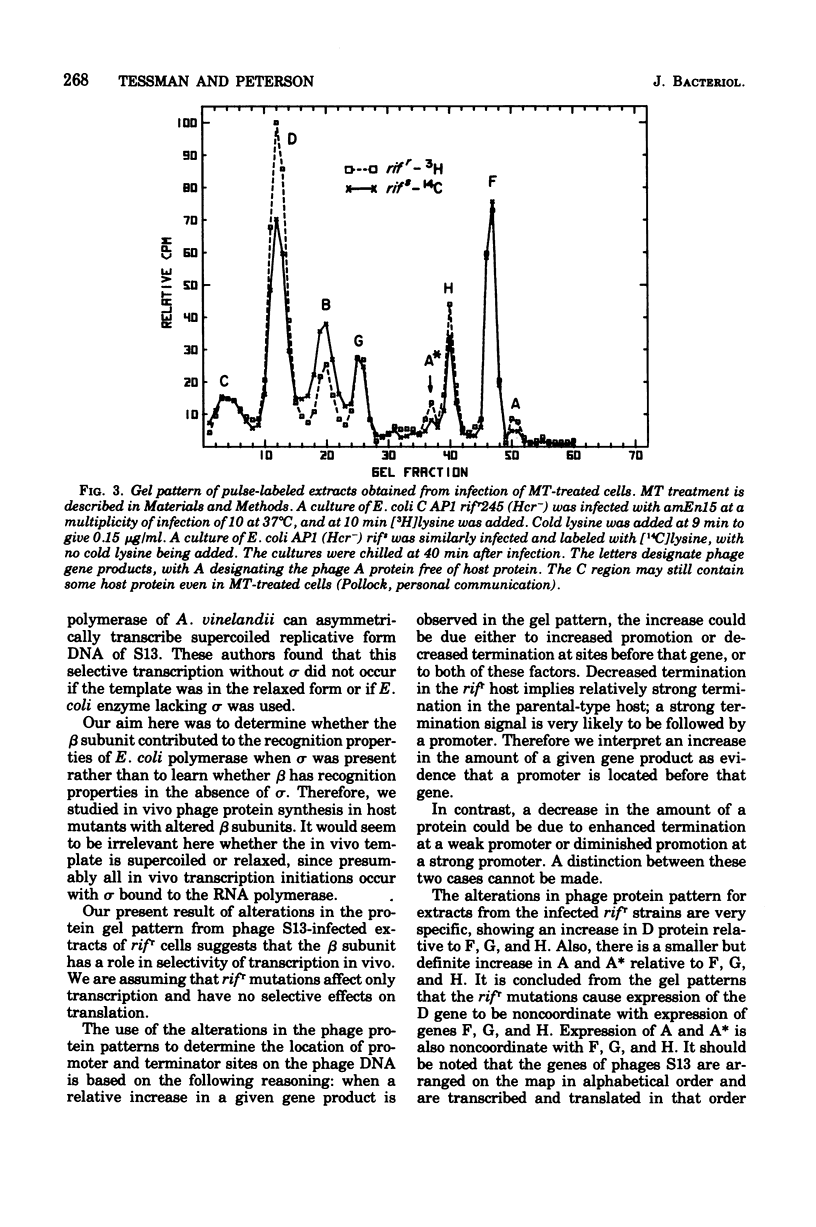
Changes in the phage protein patterns obtained by gel electrophoresis of extracts from phage S13 and phiX174 infection of rifampin-resistant hosts suggest that the beta subunit of ribonucleic acid polymerase of Escherichia coli has a function in the recognition of promoter or terminator sites or both. The altered protein patterns also provide information on the location of some ribonucleic acid polymerase recognition signals in S13 deoxyribonucleic acid. There is a promoter site before gene A, which lies either in gene H or between H and A. There is evidence for a promotor between genes C and D or in gene C. There is either a terminator or a promoter somewhere between the end of gene D and the beginning of gene F.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bautz E. K., Bautz F. A., Beck E. Specificity of sigma-dependent binding of RNA polymerase to DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;118(3):199–207. doi: 10.1007/BF00333456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bautz E. K., Bautz F. A., Dunn J. J. E. coli sigma factor: a positive control element in phage T4 development. Nature. 1969 Sep 6;223(5210):1022–1024. doi: 10.1038/2231022a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrás M. T., Vanderbilt A. S., Tessman E. S. Identification of the acrylamide gel protein peak for gene C of phages S13 and phy X174. Virology. 1971 Sep;45(3):802–803. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90199-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlin M. J. The selectivity of transcription. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):721–775. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.003445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. Y., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Edgell M. H. Isolation and genetic localization of three phi-X174 promoter regions. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jun 20;243(129):233–236. doi: 10.1038/newbio243233a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domingo E., Escarmis C., Warner R. C. Transcription of bacteriophage deoxyribonucleic acid. Comparison of Escherichia coli and Azotobacter vinelandii sigma subunits. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 25;250(8):2866–2871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand D. H., Hayashi M. Electrophoretic characterization of phiX174-specific proteins. J Mol Biol. 1969 Sep 28;44(3):501–516. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90376-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg R. B., Bender R. A., Streicher S. L. Direct selection for P1-sensitive mutants of enteric bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jun;118(3):810–814. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.3.810-814.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinkle D. C., Chamberlin M. J. Studies of the binding of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase to DNA. I. The role of sigma subunit in site selection. J Mol Biol. 1972 Sep 28;70(2):157–185. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90531-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linney E. A., Hayashi M. N., Hayashi M. Gene A of X174. 1. Isolation and identification of its products. Virology. 1972 Nov;50(2):381–387. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90389-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linney E., Hayashi M. Intragenic regulation of the synthesis of phi chi 174 gene A proteins. Nature. 1974 May 24;249(455):345–348. doi: 10.1038/249345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mailhammer R., Yang H. L., Reiness G., Zubay G. Effects of bacteriophage T4-induced modification of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase on gene expression in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4928–4932. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller K. The function of the -factor of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase in template site selection. Mol Gen Genet. 1971;111(3):273–296. doi: 10.1007/BF00433112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puga A., Tessman I. Mechanism of transcription of bacteriophage S13. II. Inhibition of phage-specific transcription by nalidixic acid. J Mol Biol. 1973 Mar 25;75(1):99–108. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90531-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabussay D., Zillig W. A rifampicin resistent rna-polymerase from E. coli altered in the beta-subunit. FEBS Lett. 1969 Oct 21;5(2):104–106. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80305-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosner J. L. Formation, induction, and curing of bacteriophage P1 lysogens. Virology. 1972 Jun;48(3):679–689. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90152-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tessman I., Tessman E. S., Pollock T. H., Borrás M. T., Puga A., Baker R. Reinitiation mutants of gene B of bacteriophage S13 that mimic gene A mutants in blocking replicative form DNA synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1976 May 25;103(3):583–598. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90218-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderbilt A. S., Borrás M. T., Germeraad S., Tessman I., Tessman E. S. A promoter site and polarity gradients in phage S13. Virology. 1972 Oct;50(1):171–179. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90357-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderbilt A. S., Borrás M. T., Tessman E. S. Direction of translation in phage S13 as determined from the sizes of polypeptide fragments of nonsense mutants. Virology. 1971 Feb;43(2):352–355. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90307-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderbilt A. S., Tessman I. Mutagenic methods for determining which DNA strand is transcribed for individual viral genes. Nature. 1970 Oct 3;228(5266):54–56. doi: 10.1038/228054a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


