Abstract
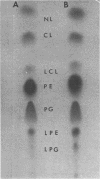
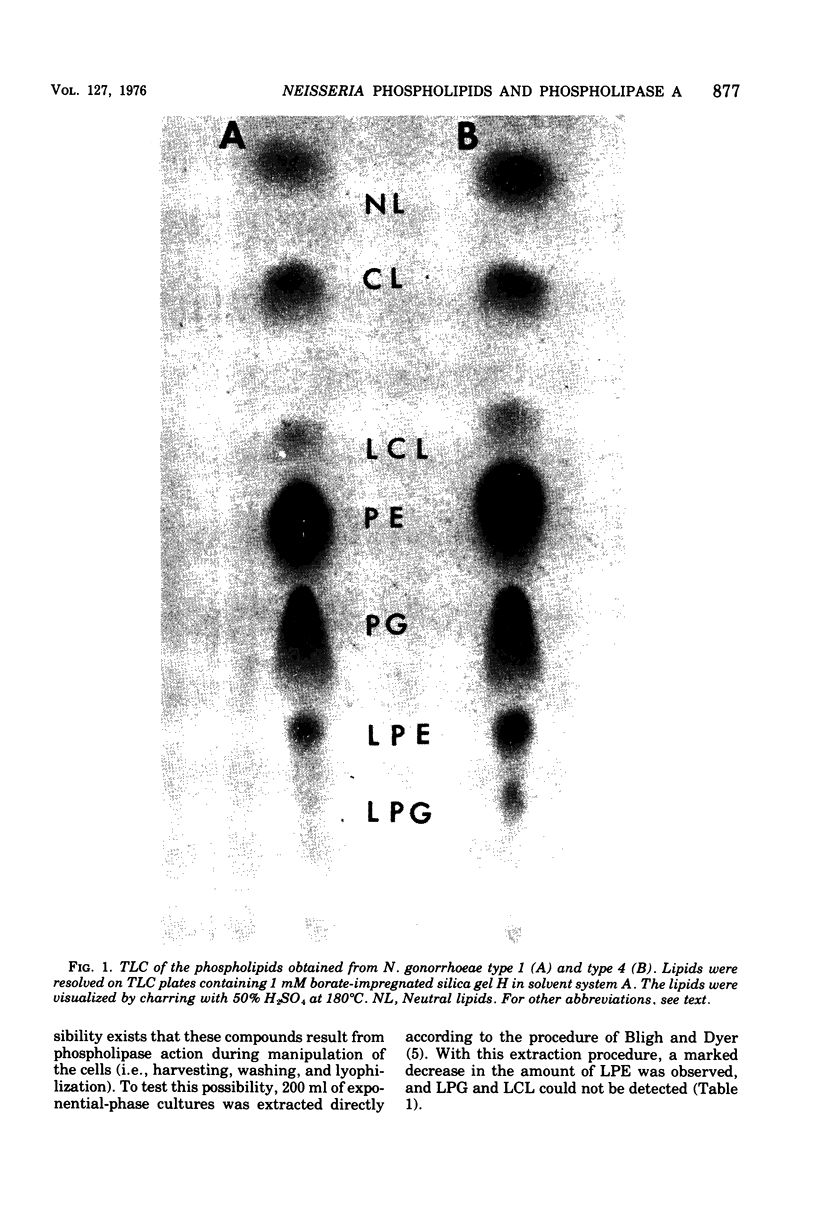
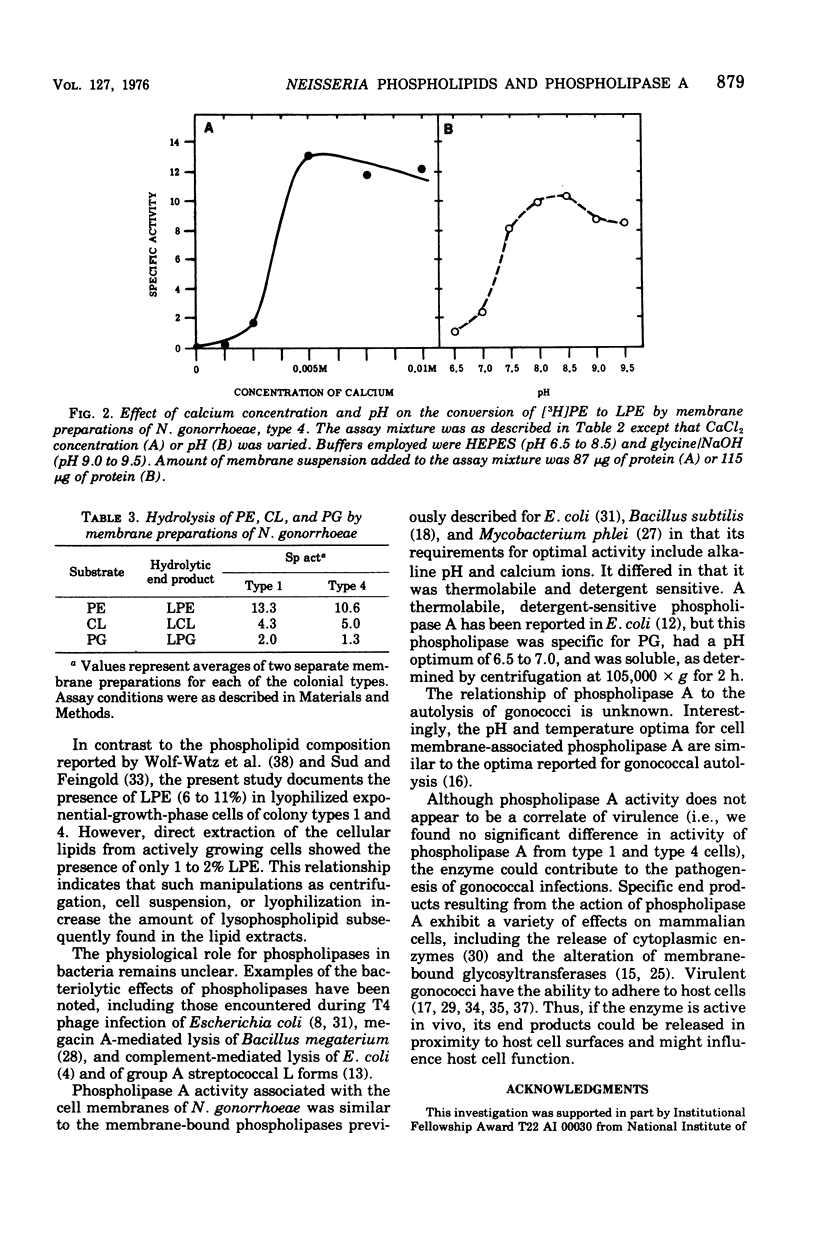
Exponential-phase cells of Neisseria gonorrhaeae 2686 were examined for phospholipid composition and for membrane-associated phospholipase A activity. When cells were harvested by centrifugation, washed, and lyophilized before extraction, approximately 74% of the total phospholipid was phosphatidylethanolamine, 18% was phosphatidylglycerol, 2% was cardiolipin, and 10% was lysophosphatidylethanolamine. However, when cells still suspended in growth medium were extracted, the amount of lysophosphatidylethanolamine decreased to approximately 1% of the phospholipid composition. This suggests that a gonococcal phospholipase A may be activated by conditions encountered during centrifugation and/or lyophilization of cells preceding extraction. Phospholipase A activity associated with cell membranes was assayed by measuring the conversion of tritiated phosphatidylethanolamine to lysophosphatidylethanolamine. Optimal activity was demonstrated in 10% methanol at pH 8.0 to 8.5, in the presence of calcium ions. The activity was both detergent sensitive and thermolabile. Comparisons of gonococcal colony types 1 and 4 showed no significant differences between the two types with respect to either phospholipid content or phospholipase A activity.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albright F. R., White D. A., Lennarz W. J. Studies on enzymes involved in the catabolism of phospholipids in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3968–3977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Audet A., Nantel G., Proulx P. Phospholipase A activity in growing Escherichia coli cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jun 26;348(3):334–343. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(74)90213-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbu E., Lux M. Transformation des phospholipides bactériens conséctive à l'action du complément. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1969 Jan 13;268(2):449–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brookes R., Hedén C. G. Dense cultures of Neisseria gonorrhoeae in liquid medium. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Mar;15(2):219–223. doi: 10.1128/am.15.2.219-223.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks J. B., Kellogg D. S., Thacker L., Turner E. M. Analysis by gas chromatography of fatty acids found in whole cultural extracts of Neisseria species. Can J Microbiol. 1971 Apr;17(4):531–543. doi: 10.1139/m71-088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DITTMER J. C., LESTER R. L. A SIMPLE, SPECIFIC SPRAY FOR THE DETECTION OF PHOSPHOLIPIDS ON THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAMS. J Lipid Res. 1964 Jan;5:126–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doi O., Oki M., Nojima S. Two kinds of phospholipase A and lysophospholipase in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 21;260(2):244–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drach G., Cavard D., Barbu E. Transformation des phospholipides des formes L du streptocoque du groupe A sous l'action du complément du sérum humain. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1973 Nov 12;277(19):2085–2088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfine H. Comparative aspects of bacterial lipids. Adv Microb Physiol. 1972;8:1–58. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60187-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham A. B., Wood G. C. On the activation of microsomal UDPglucuronyltransferase by phospholipase A. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Dec 29;370(2):431–440. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90104-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebeler B. H., Young F. E. Autolysis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1975 May;122(2):385–392. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.2.385-392.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James-Holmquest A. N., Swanson J., Buchanan T. M., Wende R. D., Williams R. P. Differential attachment by piliated and nonpiliated Neisseria gonorrhoeae to human sperm. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):897–902. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.897-902.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent C., Lennarz W. J. An osmotically fragile mutant of Bacillus subtilis with an active membrane-associated phospholipase A 1 . Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2793–2797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krag S. S., Lennarz W. J. Purification and characterization of an inhibitor of phospholipase A1 in Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 25;250(8):2813–2822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ley H. L., Jr, Mueller J. H. On the Isolation from Agar of an Inhibitor for Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1946 Oct;52(4):453–460. doi: 10.1128/jb.52.4.453-460.1946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makula R. A., Finnerty W. R. Microbial assimilation of hydrocarbons: phospholipid metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1971 Sep;107(3):806–814. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.3.806-814.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makula R. A., Finnerty W. R. Phospholipid composition of Desulfovibrio species. J Bacteriol. 1974 Dec;120(3):1279–1283. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.3.1279-1283.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer L. W., Holmes K. K., Falkow S. Characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid from Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1974 Oct;10(4):712–717. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.4.712-717.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mookerjea S., Yung J. W. A study on the effect of lysolecithin and phospholipase A on membrane-bound galactosyltransferase. Can J Biochem. 1974 Nov;52(11):1053–1066. doi: 10.1139/o74-147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse S. A., Bartenstein L. Factors affecting autolysis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Apr;145(4):1418–1421. doi: 10.3181/00379727-145-38025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Nojima S. Phospholipases of the membrane fraction of Mycobacterium phlei. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jan 21;176(1):111–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Punsalang A. P., Jr, Sawyer W. D. Role of pili in the virulence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):255–263. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.255-263.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. M., Wilkinson J. H. The effect of phospholipases on the release of enzymes from intact cells. Clin Chim Acta. 1973 Sep 14;47(3):347–356. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(73)90266-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SNYDER F., STEPHENS N. A simplified spectrophotometric determination of ester groups in lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Jul;34:244–245. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90255-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scandella C. J., Kornberg A. A membrane-bound phospholipase A1 purified from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1971 Nov 23;10(24):4447–4456. doi: 10.1021/bi00800a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sud I. J., Feingold D. S. Phospholipids and fatty acids of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):713–717. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.713-717.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. IV. Pili: their role in attachment of gonococci to tissue culture cells. J Exp Med. 1973 Mar 1;137(3):571–589. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.3.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thongthai C., Sawyer W. D. Studies on the virulence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. I. Relation of colonial morphology and resistance to phagocytosis by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):373–379. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.373-379.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walstad D. L., Reitz R. C., Sparling P. F. Growth inhibition among strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae due to production of inhibitory free fatty acids and lysophosphatidylethanolamine: absence of bacteriocins. Infect Immun. 1974 Sep;10(3):481–488. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.3.481-488.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward M. E., Watt P. J., Robertson J. N. The human fallopian tube: a laboratory model for gonococcal infection. J Infect Dis. 1974 Jun;129(6):650–659. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.6.650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf-Watz H., Elmros T., Normark S., Bloom G. D. Cell envelope of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: outer membrane and peptidoglycan composition of penicillin-sensitive and-resistant strains. Infect Immun. 1975 Jun;11(6):1332–1341. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.6.1332-1341.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Haas G. H., Sarda L., Roger J. Positional specific hydrolysis of phospholipids by pancreatic lipase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Dec 2;106(3):638–640. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(65)90082-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]