Abstract
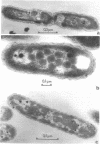
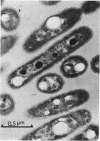
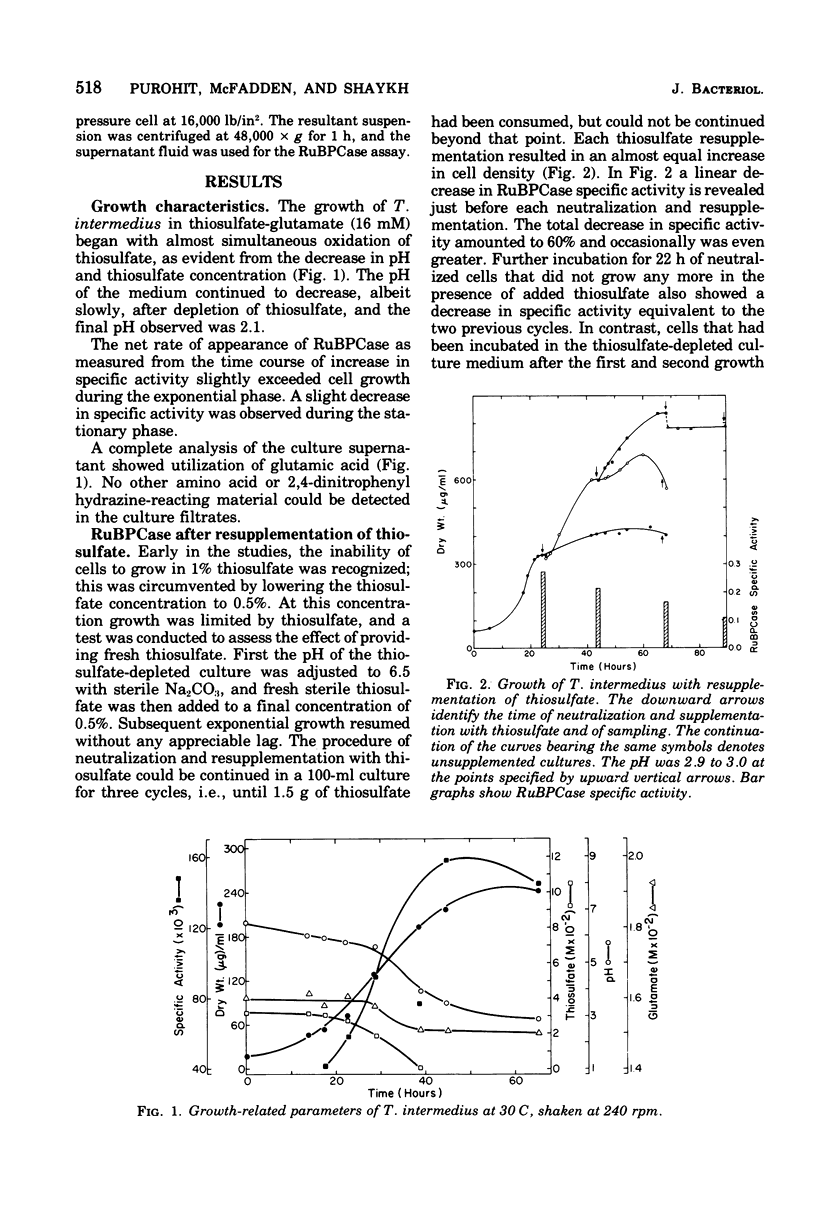
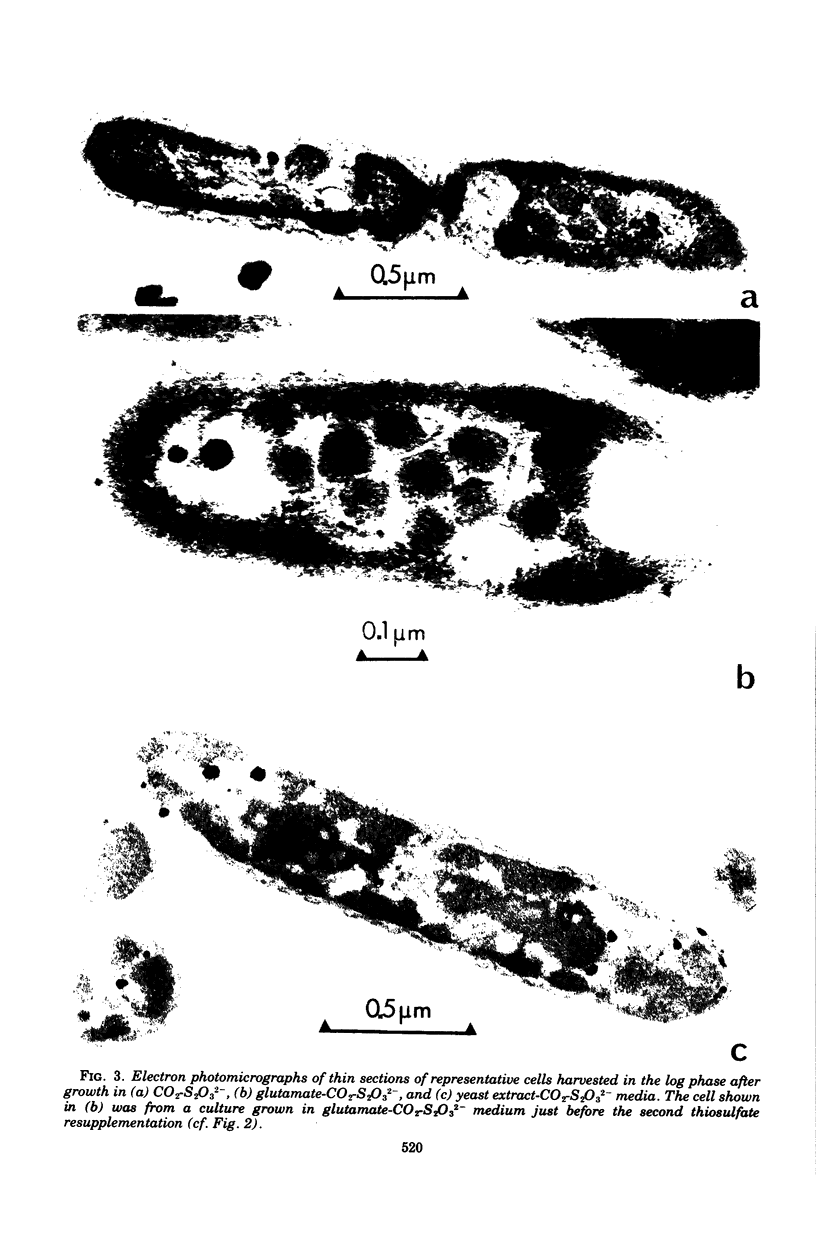
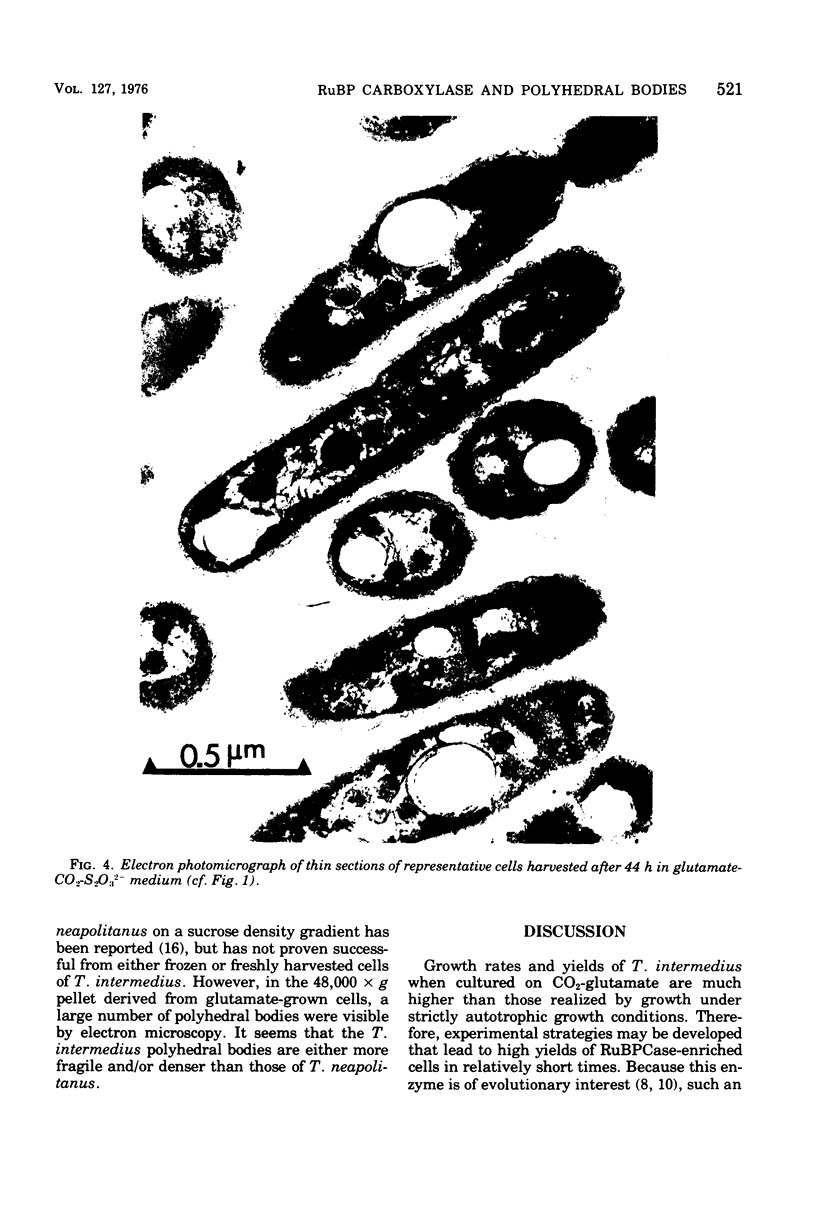
The growth-related parameters of Thiobacillus intermedius, cultured in glutamate-CO2-S2O32- medium, have been determined. After centrifugation at 48,000 X g for 1 h, 24% of the D-ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase (RuBPCase) activity of the disrupted-cell suspensions obtained from CO2-S2O32--and glutamate-CO2-S2O3(3)- grown cells could be sedimented, and the specific activities of this enzyme in the supernatant fractions were almost equivalent. The enzyme was stable in T. intermedius starved of thiosulfate in the presence and absence of glutamate, but a progressive decrease was evident in several growth cycles, each cycle supported by resupplementation of cells with thiosulfate. Polyhedral inclusion bodies were present in CO2-S2O3(2)- and glutamate-CO2S2O3(2)- grown cells. The number of polyhedral bodies per cell increased during mixotrophic growth approximately in proportion to the observed increase in the specific activity of RuBPCase. RuBPCase could not be detected in T. intermedius grown heterotrophically on yeast extract, nor could polyhedral bodies be found.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Kuehn G. D., McFadden B. A. Factors affecting the synthesis and degradation of ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase in Hydrogenomonas facilis and Hydrogenomonas eutropha. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):937–946. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.937-946.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- London J., Rittenberg S. C. Effects of organic matter on the growth of Thiobacillus intermedius. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1062–1069. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1062-1069.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden B. A. Autotrophic CO2 assimilation and the evolution of ribulose diphosphate carboxylase. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Sep;37(3):289–319. doi: 10.1128/br.37.3.289-319.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden B. A., Denend A. R. Ribulose diphosphate carboxylase from autotrophic microorganisms. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):633–642. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.633-642.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden B. A., Tabita F. R. D-ribulose-1, 5-diphosphate carboxylase and the evolution of autotrophy. Biosystems. 1974 Oct;6(2):93–112. doi: 10.1016/0303-2647(74)90002-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden B. A., Tabita F. R., Kuehn G. D. Ribulose-diphosphate carboxylase from the hydrogen bacteria and Rhodospirillum rubrum. Methods Enzymol. 1975;42:461–472. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)42152-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. R., Girard A. E., Tilton R. C. Ultrastructure of a marine Thiobacillus. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Nov;85(1):130–138. doi: 10.1099/00221287-85-1-130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purohit K., McFadden B. A., Cohen A. L. Purification, quaternary structure, composition, and properties of D-ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from Thiobacillus intermedius. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jul;127(1):505–515. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.1.505-515.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shively J. M., Ball F. L., Kline B. W. Electron microscopy of the carboxysomes (polyhedral bodies) of Thiobacillus neapolitanus. J Bacteriol. 1973 Dec;116(3):1405–1411. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.3.1405-1411.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shively J. M., Ball F., Brown D. H., Saunders R. E. Functional organelles in prokaryotes: polyhedral inclusions (carboxysomes) of Thiobacillus neapolitanus. Science. 1973 Nov 9;182(4112):584–586. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4112.584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shively J. M., Decker G. L., Greenawalt J. W. Comparative ultrastructure of the thiobacilli. J Bacteriol. 1970 Feb;101(2):618–627. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.2.618-627.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. W., Rittenberg S. C. On the sulfur-source requirement for growth of Thiobacillus intermedius. Arch Microbiol. 1974;100(1):65–71. doi: 10.1007/BF00446307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki I. Mechanisms of inorganic oxidation and energy coupling. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1974;28(0):85–101. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.28.100174.000505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]