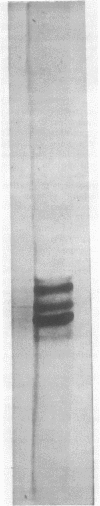
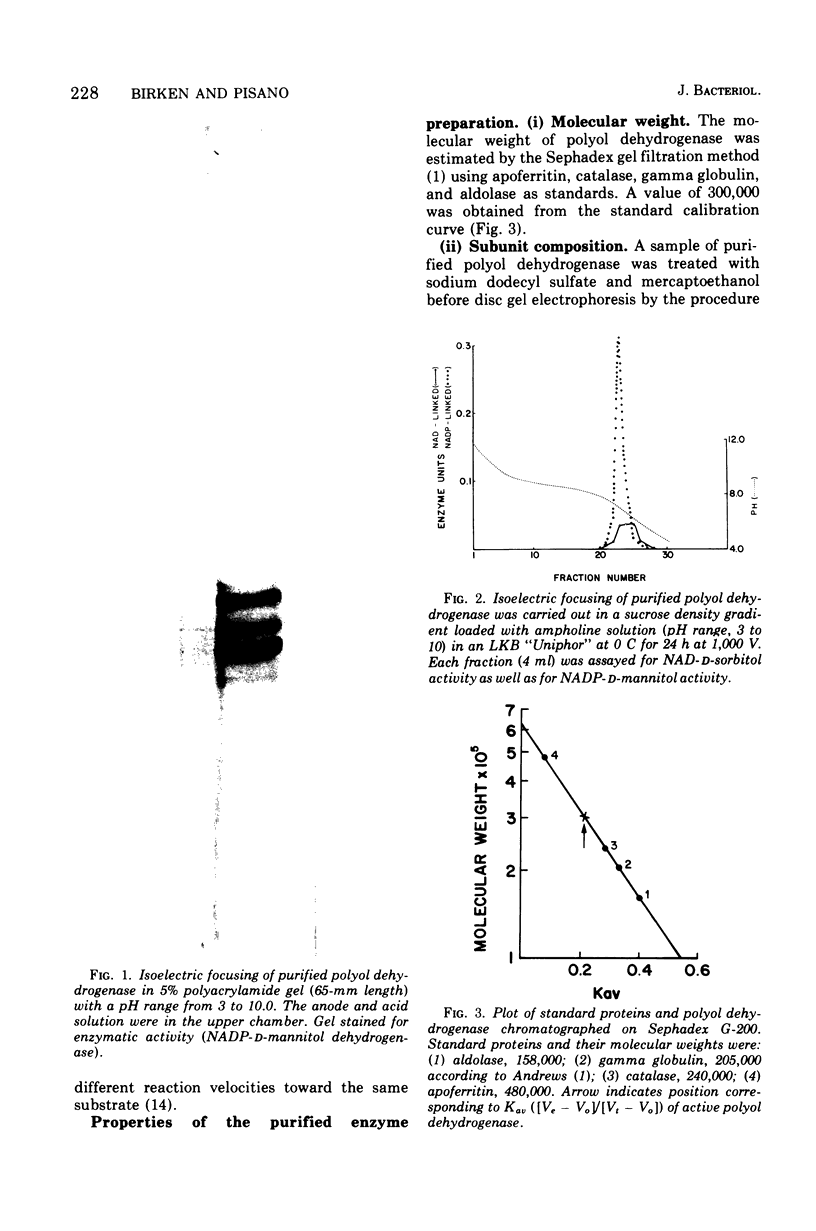
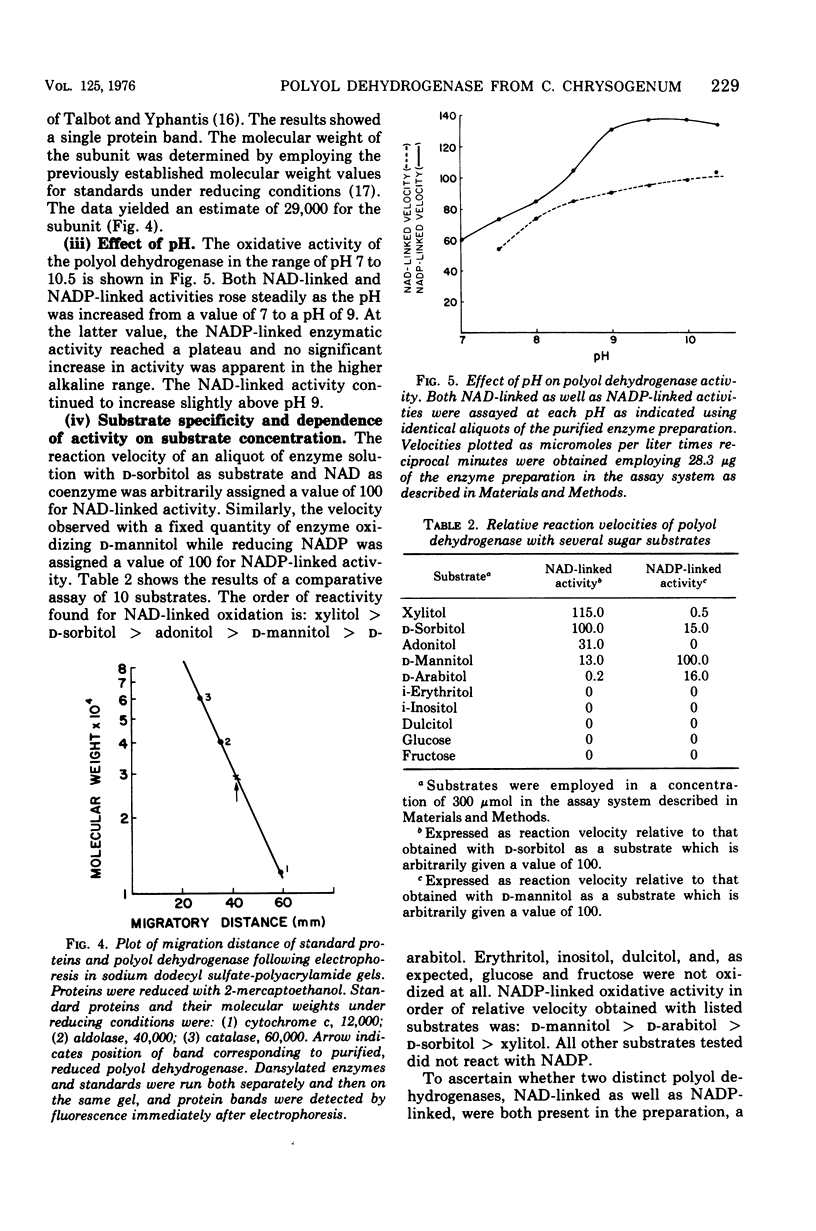
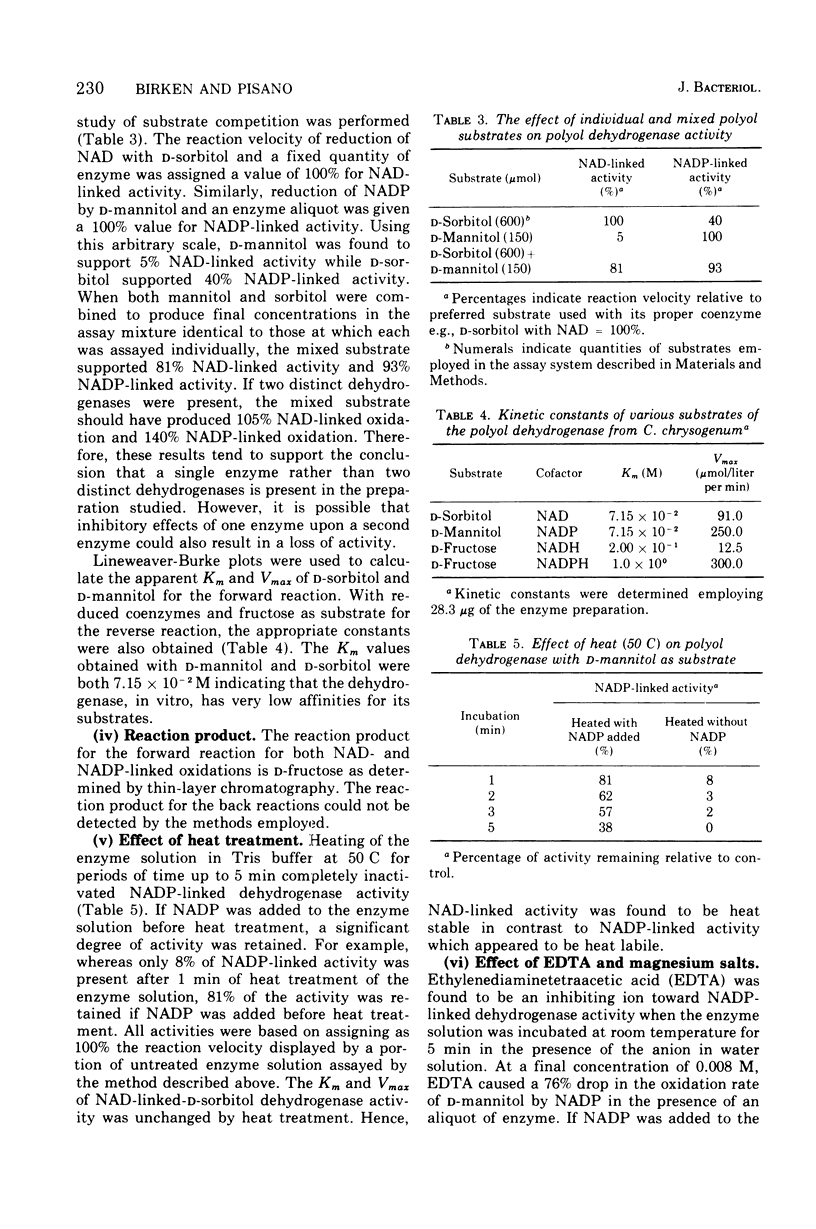
Abstract
A polyol dehydrogenase of broad specificity was purified 178-fold from extracts of the filamentous fungus Cephalosporium chrysogenum. The enzyme was found to act as an oxido-reductase in two substrate-coenzyme systems: D-sorbitol (or xylitol)-nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and D-mannitol-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP). The dehydrogenase was composed of five isozymes, which, as a mixture, exhibited these properties: Km to D-sorbitol and D-mannitol, 7.15 to 10(-2) M; PH optimum, 9 to 10; molecular weight, 300,000 subunit weight, 29,000; PI, 5.8 to 7.5. The NADP-linked activity was labile to treatment with heat or ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid. Mixed substrate assays support the hypothesis that both NAD-, and NADP-linked activities are associated with isozymes of a single dehydrogenase.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. Estimation of molecular size and molecular weights of biological compounds by gel filtration. Methods Biochem Anal. 1970;18:1–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAKRAVORTY M., VEIGA L. A., BACILA M., HORECKER B. L. Pentose metabolism in Candida. II. The diphosphopyridine nucleotide-specific polyol dehydrogenase of Candida utilis. J Biol Chem. 1962 Apr;237:1014–1020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHIANG C., KNIGHT S. G. Metabolism of d-xylose by moulds. Nature. 1960 Oct 1;188:79–81. doi: 10.1038/188079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desai B. M., Modi V. V., Shah V. K. Studies on polyol metabolism in Aspergillus niger. 3. Purification and properties of sorbitol dehydrogenase. Arch Mikrobiol. 1969;67(1):16–20. doi: 10.1007/BF00413677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERS H. G. [The mechanism of the formation of seminal fructose and fetal fructose]. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Jan 1;37:127–138. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90086-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORECKER B. L. PATHWAYS OF CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM AND THEIR PHYSIOLOGICAL SIGNIFICANCE. J Chem Educ. 1965 May;42:244–253. doi: 10.1021/ed042p244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORWITZ S. B., KAPLAN N. O. HEXITOL DEHYDROGENASES OF BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Mar;239:830–838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haglund H. Isoelectric focusing in pH gradients--a technique for fractionation and characterization of ampholytes. Methods Biochem Anal. 1971;19:1–104. doi: 10.1002/9780470110386.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markert C. L., Møller F. MULTIPLE FORMS OF ENZYMES: TISSUE, ONTOGENETIC, AND SPECIES SPECIFIC PATTERNS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1959 May;45(5):753–763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.45.5.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot D. N., Yphantis D. A. Fluorescent monitoring of SDS gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1971 Nov;44(1):246–253. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90367-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]