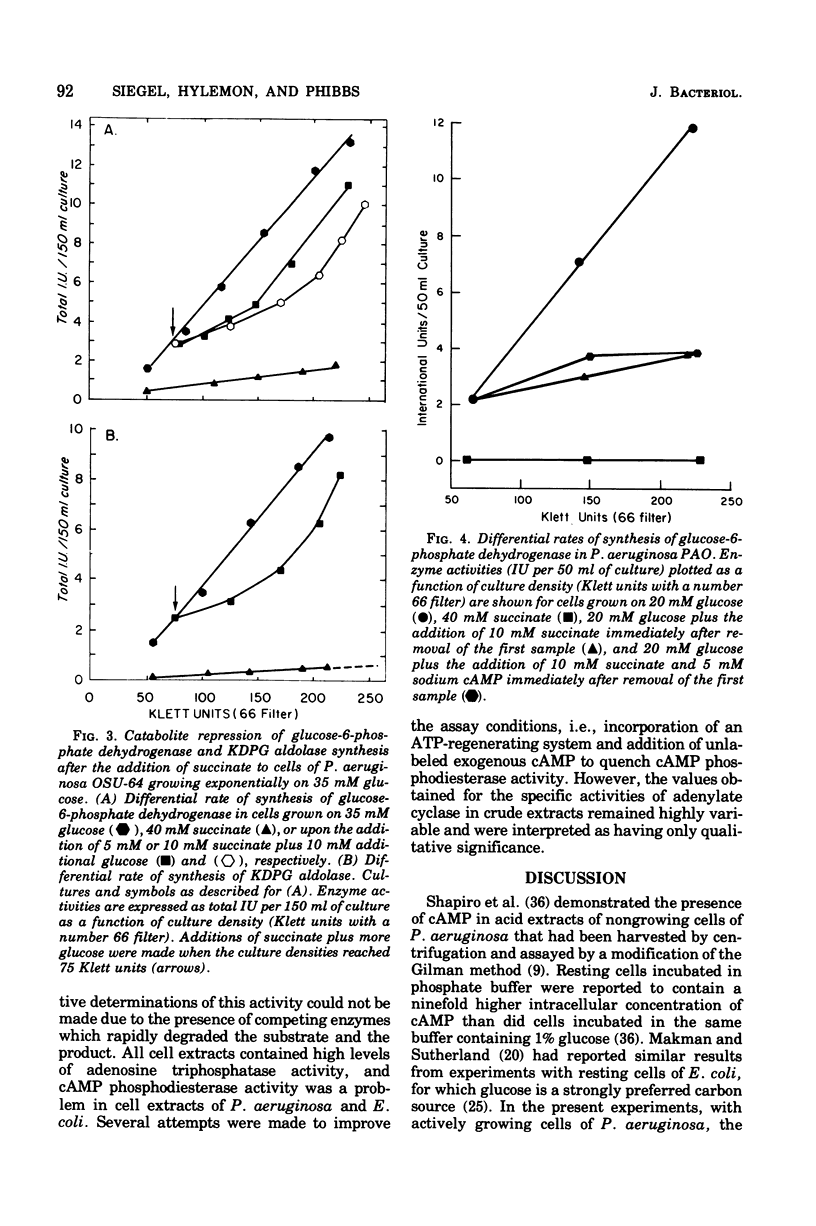
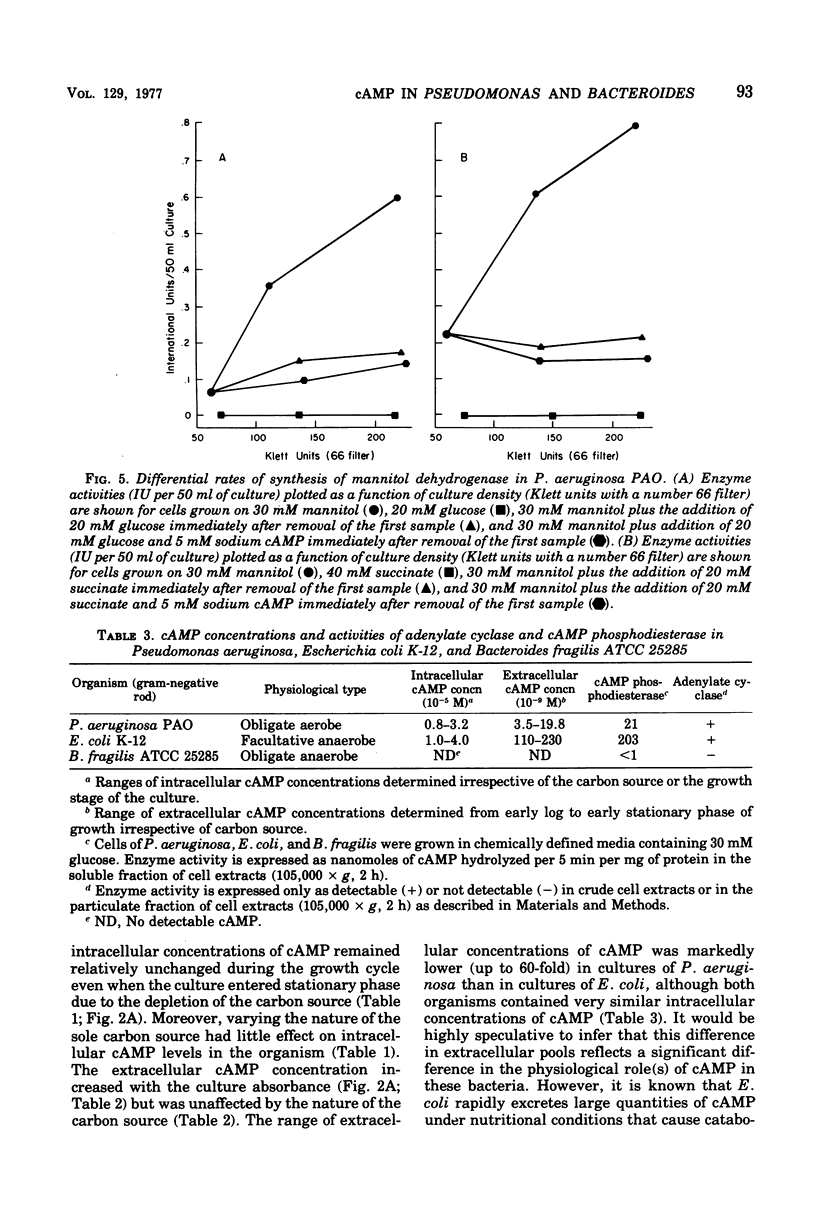
Abstract
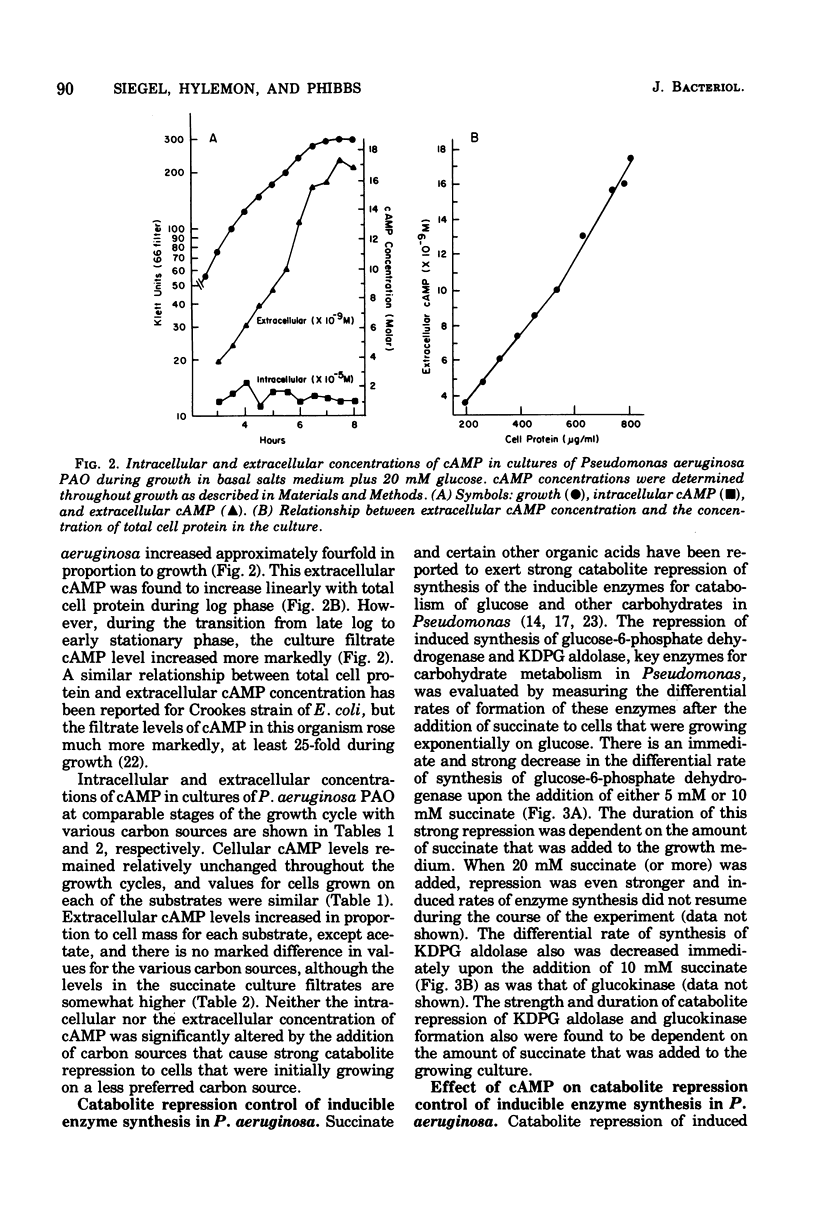
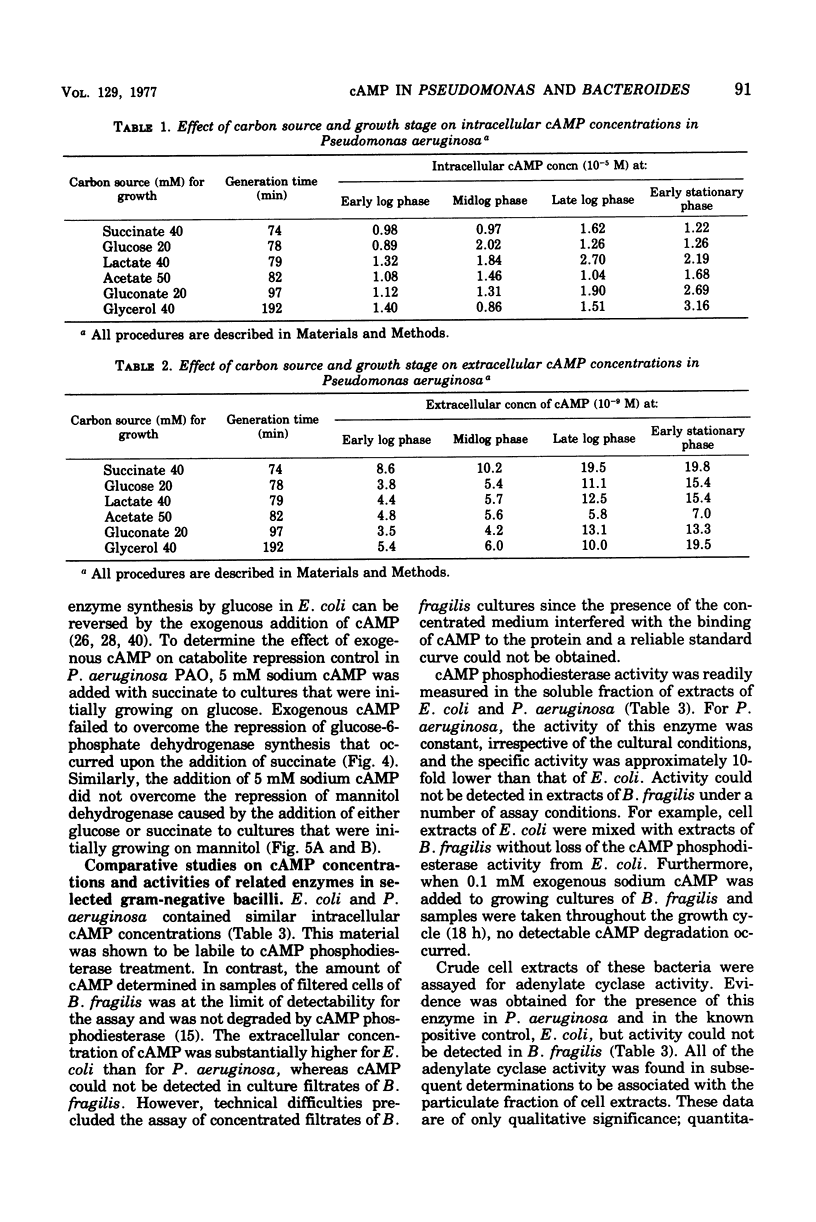
A modified Gilman assay was used to determine the concentrations of cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate (cAMP) in rapidly filtered cells and in the culture filtrates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli K-12, and Bacteroides fragilis. In P. aeruginosa cultures, levels of cAMP in the filtrate increased with the culture absorbance (3.5 to 19.8 X 10(-9) M) but did not vary significantly with the carbon source used to support growth. Intracellular concentrations (0.8 to 3.2 X 10(-5) M) were substantially higher and did not vary appreciably during growth or with carbon source. Sodium cAMP (5 mM) failed to reverse the catabolite repression of inducible glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.49) synthesis caused by the addition of 10 mM succinate. Exogenous cAMP also had no discernible effect on the catabolite repression control of inducible mannitol dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.67). P. aeruginosa was found to contain both soluble cAMP phosphodiesterase (EC 3.1.4.17) and membrane-associated adenylate cyclase (EC 4.6.1.1) activity, and these were compared to the activities detected in crude extracts of E. coli. B. fragilis crude cell extracts contain neither of these enzyme activities, and little or no cAMP was detected in cells or culture filtrates of this anaerobic bacterium.
Full text
PDF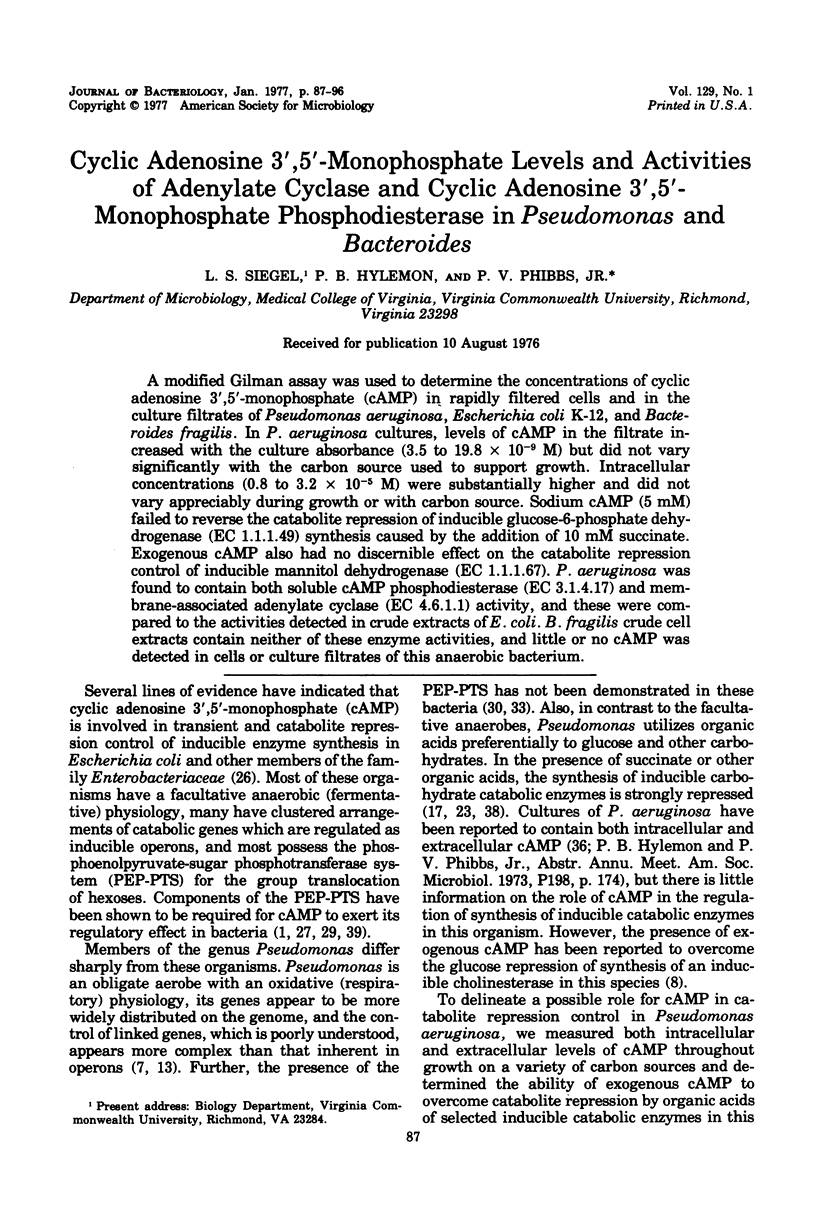




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abou-Sabé M., Mento S. On the regulation of cyclic AMP level in bacteria. II. In vitro regulation of adenylate cyclase activity. Solubilization and reconstitution of a functional membrane-bound adenylate cyclase system responsive to regulation by glucose. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 7;385(2):294–304. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90357-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernlohr R. W., Haddox M. K., Goldberg N. D. Cyclic guanosine 3':5'-monophosphate in Escherichia coli and Bacillus lichenformis. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4329–4331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buettner M. J., Spitz E., Rickenberg H. V. Cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):1068–1073. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.1068-1073.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung W. Y. Cyclic 3'.5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Effect of binding protein on the hydrolysis of cyclic AMP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jan 14;46(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90635-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss R., 3rd, Charamella L. J., Berg C. M., Harris P. E. Kinetic and genetic analyses of D-cycloserine inhibition and resistance in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1965 Nov;90(5):1238–1250. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.5.1238-1250.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond G. I., Duncan L. Adenyl cyclase in cardiac tissue. J Biol Chem. 1970 Mar 10;245(5):976–983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARGIE B., HOLLOWAY B. W. ABSENCE OF CLUSTERING OF FUNCTIONALLY RELATED GENES IN PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA. Genet Res. 1965 Jul;6:284–299. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300004158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilboa-Garber N., Zakut V., Mizrahi L. Production of cholinesterase by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, its regulation by glucose and cyclic AMP and inhibition by antiserum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 24;297(1):120–124. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90055-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. A protein binding assay for adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):305–312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guymon L. F., Eagon R. G. Transport of glucose, gluconate, and methyl alpha-D-glucoside by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1974 Mar;117(3):1261–1269. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.3.1261-1269.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haggerty D. M., Schleif R. F. Kinetics of the onset of catabolite repression in Escherichia coli as determined by lac messenger ribonucleic acid initiations and intracellular cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate levels. J Bacteriol. 1975 Sep;123(3):946–953. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.3.946-953.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway B. W. Genetics of Pseudomonas. Bacteriol Rev. 1969 Sep;33(3):419–443. doi: 10.1128/br.33.3.419-443.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hylemon P. B., Phibbs P. V., Jr Evidence against the presence of cyclic AMP and related enzymes in selected strains of Bacteroides fragilis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Sep 9;60(1):88–95. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90176-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hylemon P. B., Phibbs P. V., Jr Independent regulation of hexose catabolizing enzymes and glucose transport activity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Sep 5;48(5):1041–1048. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90813-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khandelwal R. L., Hamilton I. R. Purification and properties of adenyl cyclase from Streptococcus salivarius. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 25;246(10):3297–3304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lessie T. G., Wyk J. C. Multiple forms of Pseudomonas multivorans glucose-6-phosphate and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenases: differences in size, pyridine nucleotide specificity, and susceptibility to inhibition by adenosine 5'-triphosphate. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jun;110(3):1107–1117. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.3.1107-1117.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lessie T., Neidhardt F. C. Adenosine triphosphate-linked control of Pseudomonas aeruginosa glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. J Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(4):1337–1345. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.4.1337-1345.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAKMAN R. S., SUTHERLAND E. W. ADENOSINE 3',5'-PHOSPHATE IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Biol Chem. 1965 Mar;240:1309–1314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MELOCHE H. P., WOOD W. A. THE MECHANISM OF 2-KETO-3-DEOXY-6-PHOSPHOGLUCONIC ALDOLASE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Oct;239:3511–3514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng F. M., Dawes E. A. Chemostat studies on the regulation of glucose metabolism in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by citrate. Biochem J. 1973 Feb;132(2):129–140. doi: 10.1042/bj1320129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen L. D., Monard D., Rickenberg H. V. Cyclic 3',5'-adenosine monophosphate phosphodiesterase of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):857–866. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.857-866.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Náprstek J., Janecek J., Spizek J., Dobrová Z. Culic 3', 5', -adenosine monophosphate and catabolic repression in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jan 2;64(3):845–850. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90124-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., Perlman R. L. Repression of beta-galactosidase synthesis by glucose in phosphotransferase mutants of Escherichia coli. Repression in the absence of glucose phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 10;244(21):5836–5842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., Perlman R. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate in bacteria. Science. 1970 Jul 24;169(3943):339–344. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3943.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterkofsky A., Gazdar C. Interaction of enzyme I of the phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system with adenylate cyclase of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):2920–2924. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.2920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phibbs P. V., Jr, Eagon R. G. Transport and phosphorylation of glucose, fructose, and mannitol by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Jun;138(2):470–482. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90371-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phibbs P. V., Jr, Feary T. W., Blevins W. T. Pyruvate carboxylase deficiency in pleiotropic carbohydrate-negative mutant strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jun;118(3):999–1009. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.3.999-1009.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickenberg H. V. Cyclic AMP in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1974;28(0):353–369. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.28.100174.002033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romano A. H., Eberhard S. J., Dingle S. L., McDowell T. D. Distribution of the phosphoenolpyruvate: glucose phosphotransferase system in bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):808–813. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.808-813.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Feucht B. U., McCaman M. T. Regulation of intracellular adenosine cyclic 3':5'-monophosphate levels in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. Evidence for energy-dependent excretion of the cyclic nucleotide. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 10;250(19):7593–7601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow P. Inability of detect cyclic AMP in vegetative or sporulating cells or dormant spores of Bacillus megaterium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 May 15;52(2):365–372. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90720-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro L., Agabian-Keshishian N., Hirsch A., Rosen O. M. Effect of dibutyryladenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate on growth and differentiation in Caulobacter crescentus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 May;69(5):1225–1229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.5.1225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson W. J., Appleman M. M. Multiple cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase activities from rat brain. Biochemistry. 1971 Jan 19;10(2):311–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari N. P., Campbell J. J. Enzymatic control of the metabolic activity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa grown in glucose or succinate media. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Dec 30;192(3):395–401. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(69)90388-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler B., Magasanik B. Physiological basis of transient repression of catabolic enzymes in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1970 May;102(2):411–422. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.2.411-422.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullmann A., Monod J. Cyclic AMP as an antagonist of catabolite repression in Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1968 Nov;2(1):57–60. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(68)80100-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


