Abstract
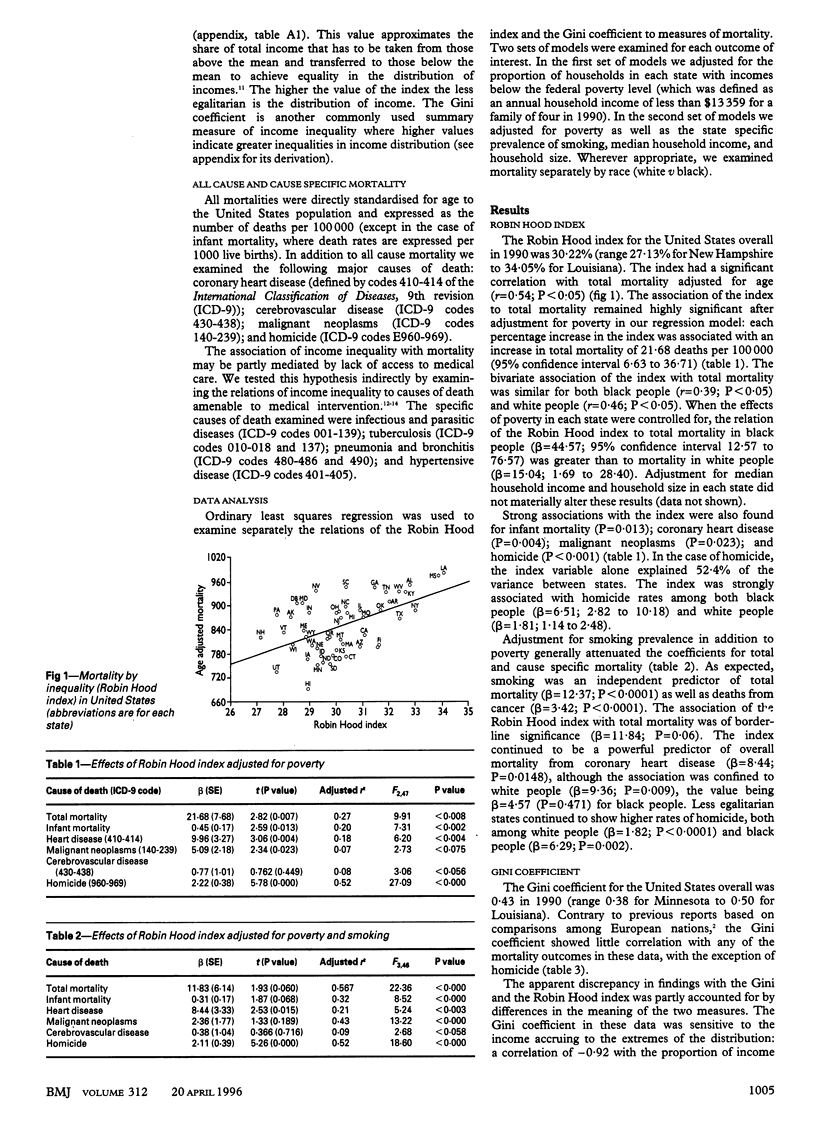
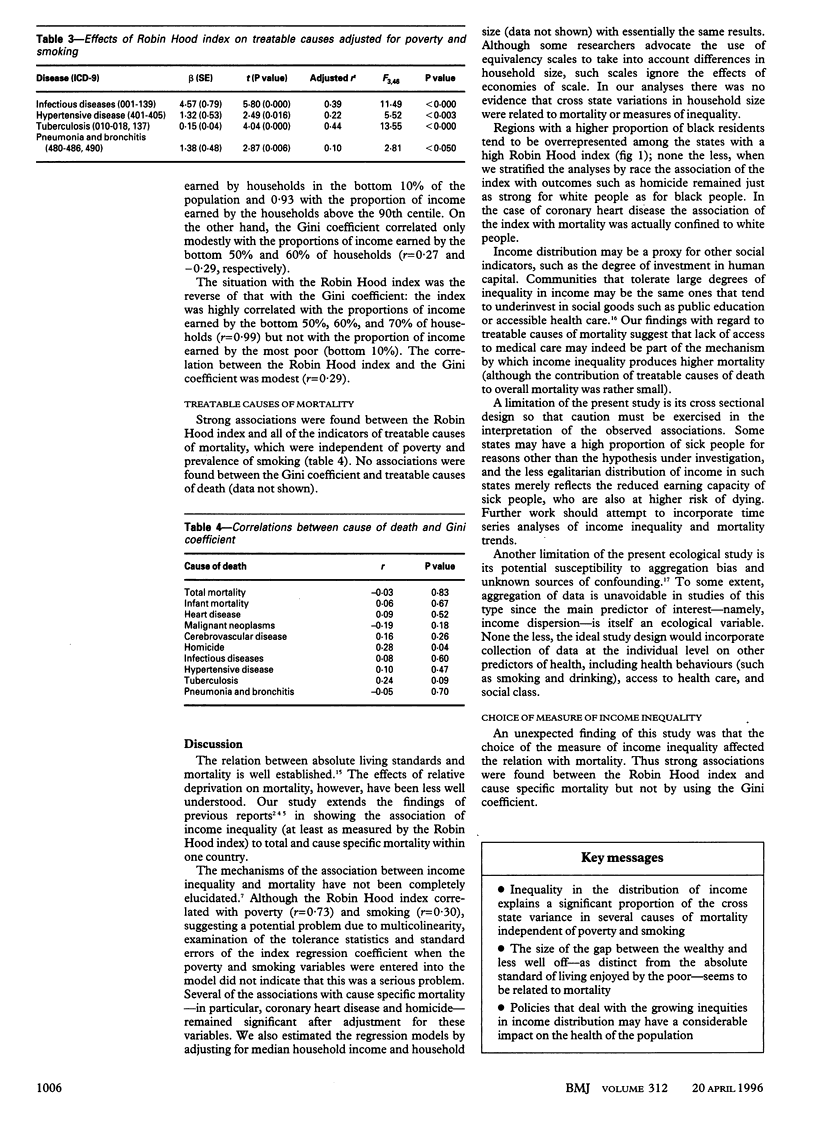
OBJECTIVE--To determine the effect of income inequality as measured by the Robin Hood index and the Gini coefficient on all cause and cause specific mortality in the United States. DESIGN--Cross sectional ecological study. SETTING--Households in the United States. MAIN OUTCOME MEASURES--Disease specific mortality, income, household size, poverty, and smoking rates for each state. RESULTS--The Robin Hood index was positively correlated with total mortality adjusted for age (r = 0.54; P < 0.05). This association remained after adjustment for poverty (P < 0.007), where each percentage increase in the index was associated with' an increase in the total mortality of 21.68 deaths per 100,000. Effects of the index were also found for infant mortality (P = 0.013); coronary heart disease (P = 0.004); malignant neoplasms (P = 0.023); and homicide (P < 0.001). Strong associations were also found between the index and causes of death amenable to medical intervention. The Gini coefficient showed very little correlation with any of the causes of death. CONCLUSION--Variations between states in the inequality of income were associated with increased mortality from several causes. The size of the gap between the wealthy and less well off--as distinct from the absolute standard of living enjoyed by the poor--seems to matter in its own right. The findings suggest that policies that deal with the growing inequities in income distribution may have an important impact on the health of the population.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Charlton J. R., Velez R. Some international comparisons of mortality amenable to medical intervention. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Feb 1;292(6516):295–301. doi: 10.1136/bmj.292.6516.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flegg A. T. Inequality of income, illiteracy and medical care as determinants of infant mortality in underdeveloped countries. Popul Stud (Camb) 1982 Nov;36(3):441–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friede A., Reid J. A., Ory H. W. CDC WONDER: a comprehensive on-line public health information system of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Am J Public Health. 1993 Sep;83(9):1289–1294. doi: 10.2105/ajph.83.9.1289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Judge K. Income distribution and life expectancy: a critical appraisal. BMJ. 1995 Nov 11;311(7015):1282–1287. doi: 10.1136/bmj.311.7015.1282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgenstern H. Uses of ecologic analysis in epidemiologic research. Am J Public Health. 1982 Dec;72(12):1336–1344. doi: 10.2105/ajph.72.12.1336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson R. G. Income distribution and life expectancy. BMJ. 1992 Jan 18;304(6820):165–168. doi: 10.1136/bmj.304.6820.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson R. G. The epidemiological transition: from material scarcity to social disadvantage? Daedalus. 1994 Fall;123(4):61–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


