Abstract
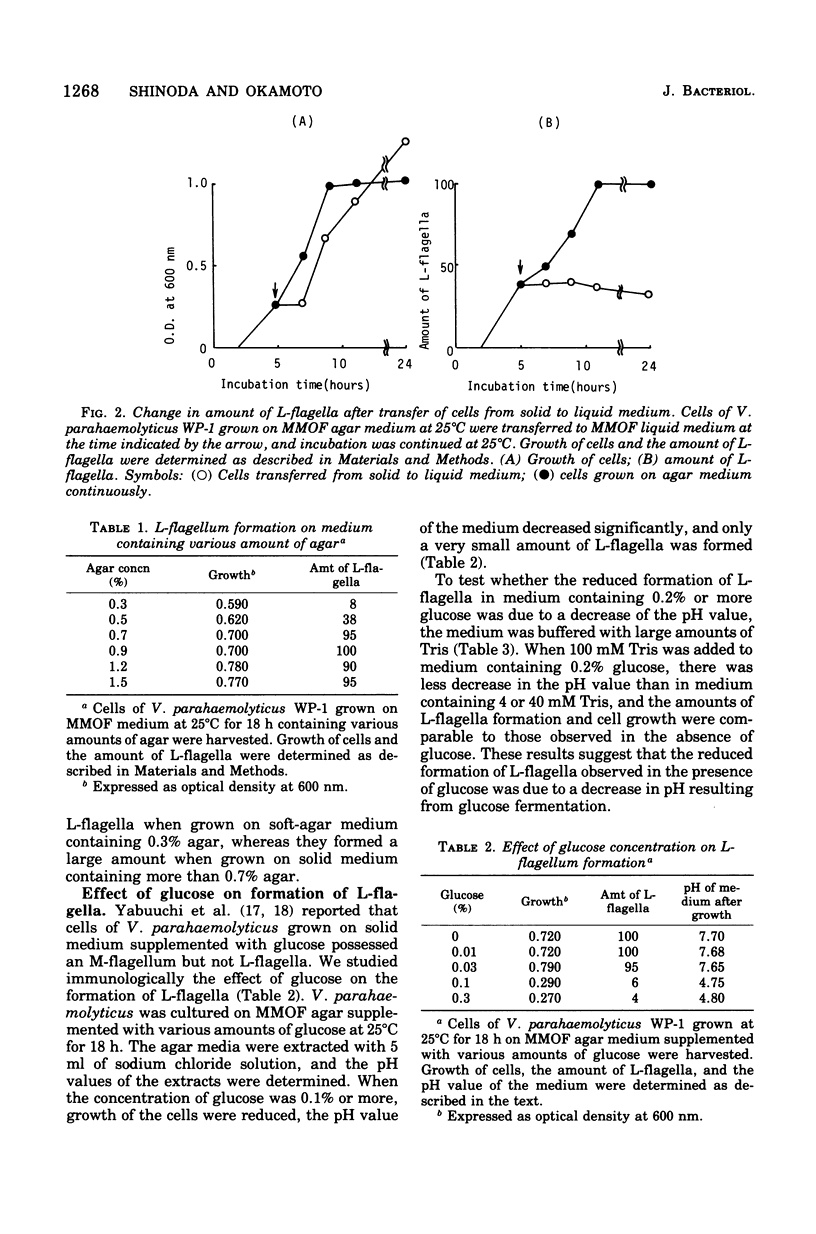
Formation of the lateral flagella (L-flagella) of Vibrio parahaemolyticus was studied immunologically, using specific antiserum against L-flagella. On solid medium, L-flagella were formed at both high (37 degrees C) and low (25 degrees C) temperatures, although at high temperatures they became dissociated from the cells and decomposed in the medium. L-flagella were not formed in liquid or soft-agar medium. Formation of L-flagella was decreased by lowering the pH of the medium and repressed by transferring the cells from solid medium to liquid medium. Mutants possessing L-flagella but not a polar monotrichous flagellum (M-flagellum) swarmed on solid medium, whereas mutants were grown on solid medium and then transfered to liquid medium, the cells oscillated until they lost L-flagella. It is postulated that L-flagella are locomotive organelles on solid medium and in some cases also in liquid medium, whereas M-flagella are locomotive organelles only in liquid medium.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. D., Baumann P. Structure and arrangement of flagella in species of the genus Beneckea and Photobacterium fischeri. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jul;107(1):295–302. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.1.295-302.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann P., Baumann L., Mandel M. Taxonomy of marine bacteria: the genus Beneckea. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jul;107(1):268–294. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.1.268-294.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann P., Baumann L., Reichelt J. L. Taxonomy of marine bacteria: Beneckea parahaemolytica and Beneckea alginolytica. J Bacteriol. 1973 Mar;113(3):1144–1155. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.3.1144-1155.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Boer S. E., Golten C., Scheffers W. A. Effects of some chemical factors on flagellation and swarming of Vibrio alginolyticus. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1975;41(4):385–403. doi: 10.1007/BF02565083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEIFSON E. Staining, shape and arrangement of bacterial flagella. J Bacteriol. 1951 Oct;62(4):377–389. doi: 10.1128/jb.62.4.377-389.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miwatani T., Shinoda S., Fujino T. Purification of monotrichous flagella of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Biken J. 1970 Sep;13(3):149–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinoda S., Honda T., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Antigenic difference between polar montrichous and peritrichous flagella of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J Bacteriol. 1974 Nov;120(2):923–928. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.2.923-928.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinoda S., Miwatani T., Fujino T. Antigens of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. II. Existence of two different subunits in the flagella of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and their characterization. Biken J. 1970 Dec;13(4):241–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulitzer S. The mechanism of swarming of Vibrio alginolyticus. Arch Microbiol. 1975 Jun 20;104(1):67–71. doi: 10.1007/BF00447301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulitzur S. Induction of swarming in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Arch Microbiol. 1974;101(4):357–363. doi: 10.1007/BF00455952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yabuuchi E., Miwatani T., Takeda Y., Arita M. Flagellar morphology of Vibrio parahaemolyticus (Fujino et al) Sakazaki, Iwanami and Fukumi 1963. Jpn J Microbiol. 1974 Jul;18(4):295–305. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1974.tb00813.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


