Abstract
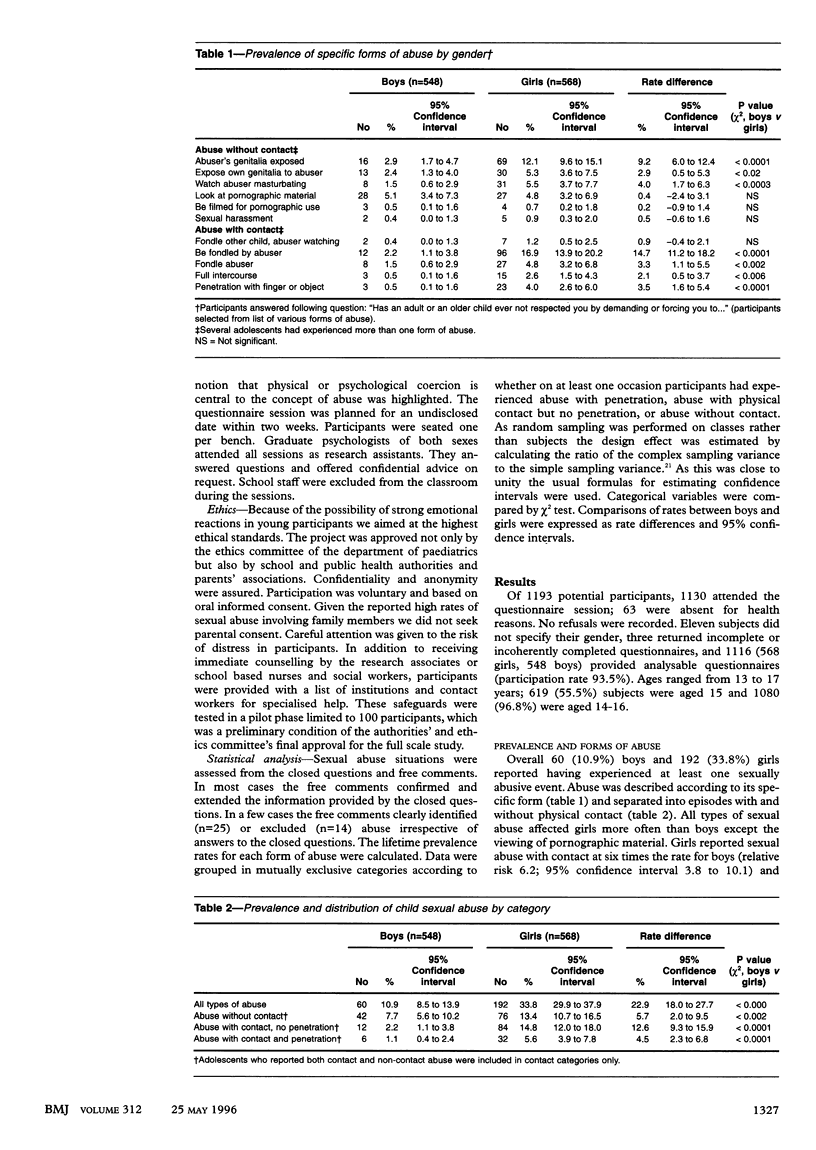
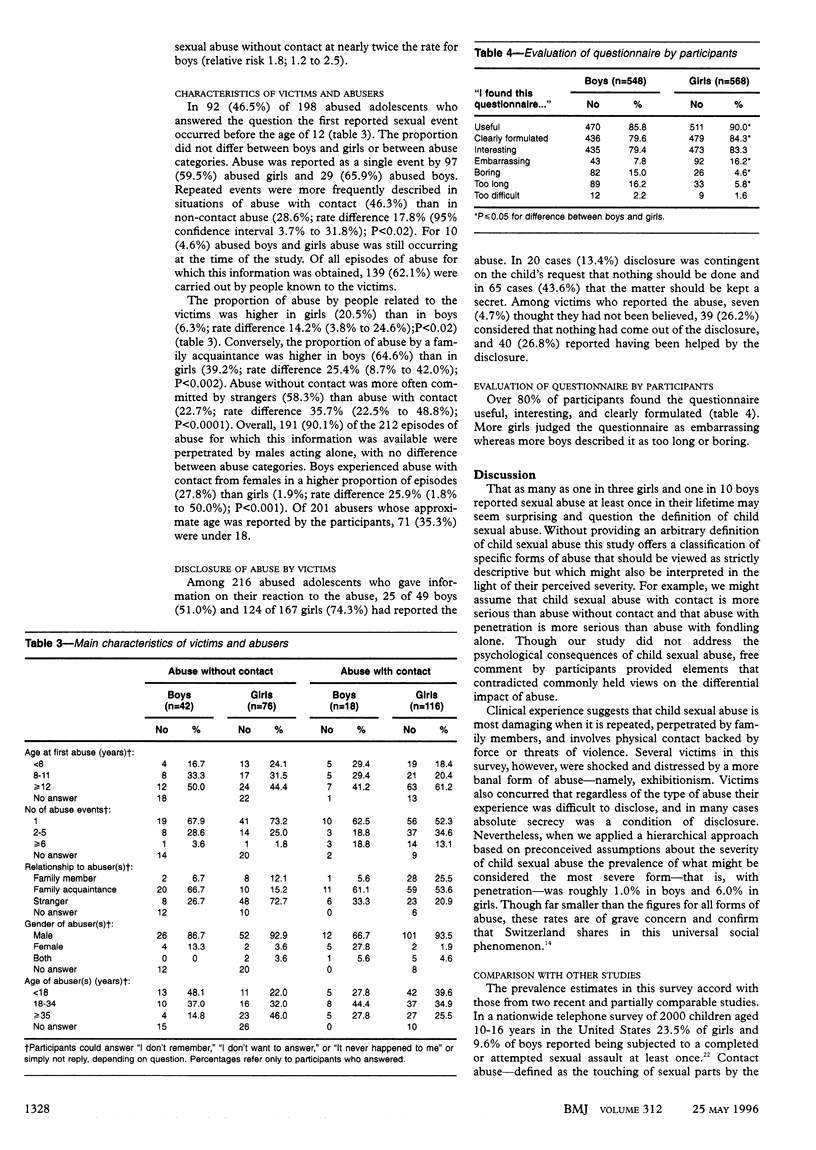
OBJECTIVE--To measure the cumulative prevalence of child sexual abuse in a representative sample of the adolescent population of Geneva. DESIGN--Cross sectional survey with an anonymous self administered questionnaire centred on a factual description of sexual activities. SETTING--68 classes (17 schools) randomly selected from the 201 ninth grade classes of the public school system in Geneva. SUBJECTS--1193 adolescents aged 13-17 years, of whom 1116 (93.5%; 568 girls, 548 boys) consented to the study and returned completed questionnaires. RESULTS--192 (33.8%) girls and 60 (10.9%) boys reported having experienced at least one sexually abusive event. The prevalence of abuse involving physical contact was 20.4% (116 cases) among girls and 3.3% (18) among boys. The prevalence of abuse involving some form of penetration was 5.6% (32 cases) among girls and 1.1% (six) among boys. One third of the abused adolescents had experienced more than one abusive event and 46.5% (92/198) had experienced the first event before age 12. Abuse by a family member was reported by 20.5% (36/176) of abused girls and 6.3% (3/48) of abused boys. Abusers were known to victims in two thirds of cases. Ninety per cent of abusers were male and 35.3% (71/201) came from the victim's peer group. Over 80% of participants found the questionnaire interesting, clearly formulated, and useful. CONCLUSIONS--Child sexual abuse is a universal social phenomenon. Adolescents themselves can contribute to research and so help in the search for more efficient prevention and intervention strategies.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Browne A., Finkelhor D. Impact of child sexual abuse: a review of the research. Psychol Bull. 1986 Jan;99(1):66–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst C., Angst J., Földényi M. The Zurich Study. XVII. Sexual abuse in childhood. Frequency and relevance for adult morbidity data of a longitudinal epidemiological study. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 1993;242(5):293–300. doi: 10.1007/BF02190389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelhor D., Dziuba-Leatherman J. Children as victims of violence: a national survey. Pediatrics. 1994 Oct;94(4 Pt 1):413–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelhor D. The international epidemiology of child sexual abuse. Child Abuse Negl. 1994 May;18(5):409–417. doi: 10.1016/0145-2134(94)90026-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haugaard J. J., Emery R. E. Methodological issues in child sexual abuse research. Child Abuse Negl. 1989;13(1):89–100. doi: 10.1016/0145-2134(89)90032-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall-Tackett K. A., Williams L. M., Finkelhor D. Impact of sexual abuse on children: a review and synthesis of recent empirical studies. Psychol Bull. 1993 Jan;113(1):164–180. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.113.1.164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narring F., Michaud P. A. Methodological issues in adolescent health surveys: the case of the Swiss Multicenter-adolescent Survey on Health. Soz Praventivmed. 1995;40(3):172–182. doi: 10.1007/BF01318638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plunkett A., Oates R. K. Methodological considerations in research on child sexual abuse. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 1990 Jul;4(3):351–360. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3016.1990.tb00657.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sariola H., Uutela A. The prevalence of child sexual abuse in Finland. Child Abuse Negl. 1994 Oct;18(10):827–835. doi: 10.1016/0145-2134(94)90062-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott K. D. Childhood sexual abuse: impact on a community's mental health status. Child Abuse Negl. 1992;16(2):285–295. doi: 10.1016/0145-2134(92)90035-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widom C. S. Child abuse, neglect, and adult behavior: research design and findings on criminality, violence, and child abuse. Am J Orthopsychiatry. 1989 Jul;59(3):355–367. doi: 10.1111/j.1939-0025.1989.tb01671.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt G. E., Peters S. D. Methodological considerations in research on the prevalence of child sexual abuse. Child Abuse Negl. 1986;10(2):241–251. doi: 10.1016/0145-2134(86)90085-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


