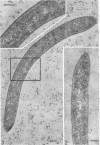
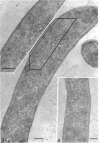
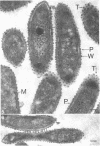
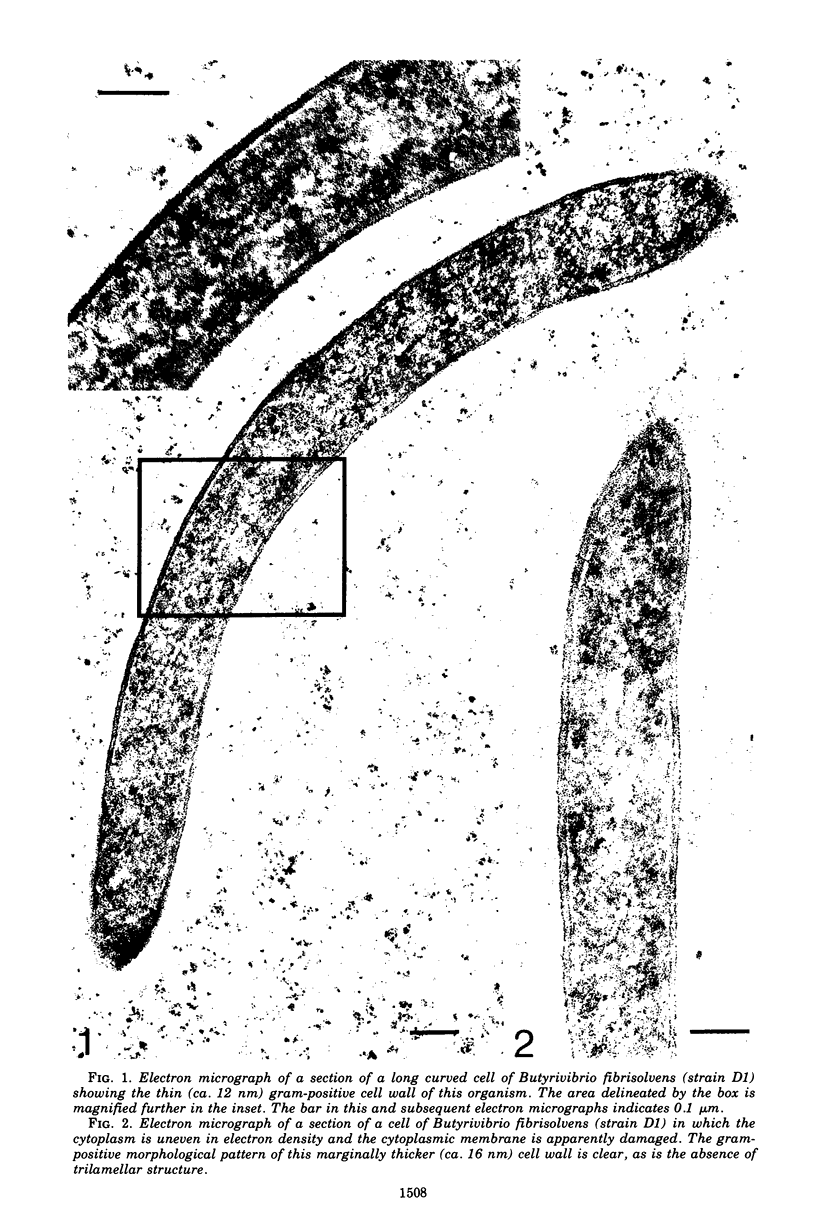
Abstract
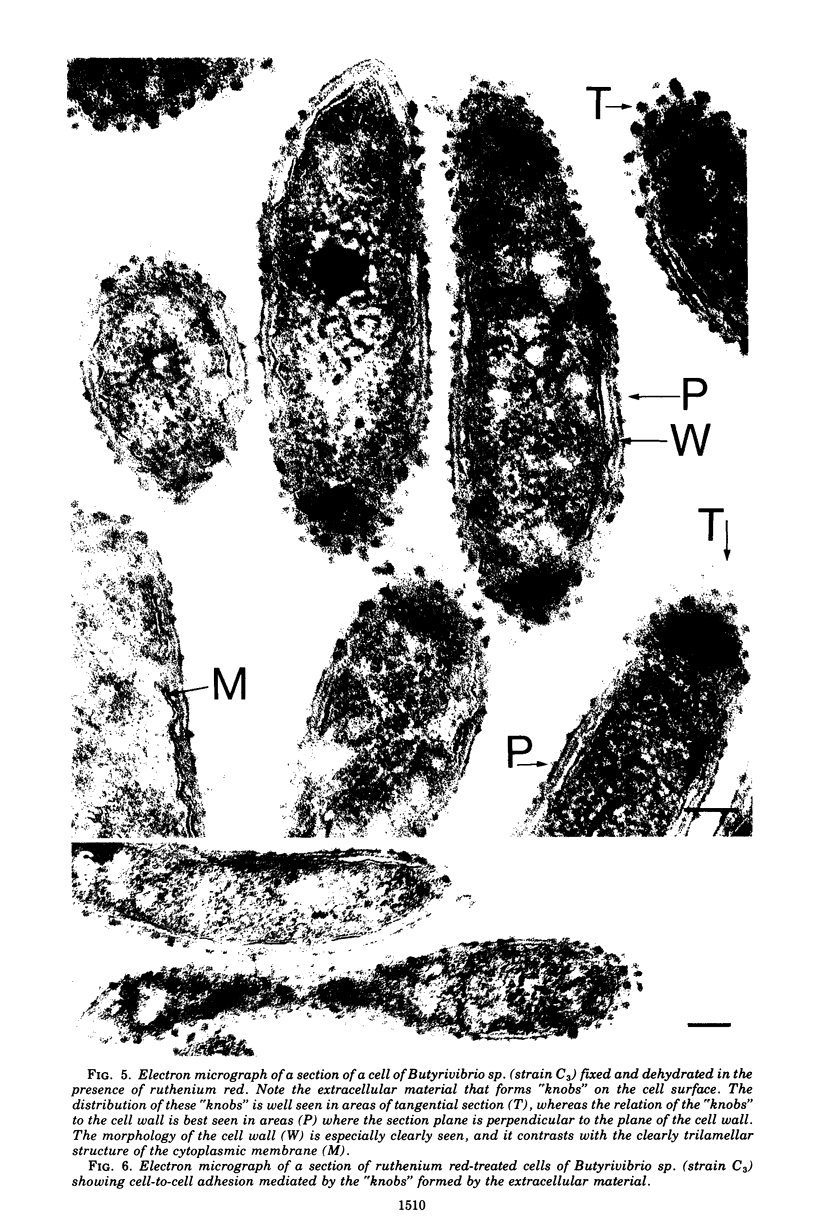
The cells of bacteria of the genus Butyrivibrio are universally described as being gram negative, and they produce an unequivocal gram-negative reaction in the standard staining procedure. However, their cell walls contain derivatives of teichoic acid, which are characteristic of gram-positive cells. In this study, the cell walls of two representative strains of Butyrivibrio were of the gram-positive morphological type, as seen by electron microscopy, but they were very thin (12 to 18 nm). The thinness of these cell walls may account for the tendency of these cells to stain gram negatively in the standard staining procedure. Ruthenium red staining revealed an extracellular structure surrounding cells of Butyrivibio sp. (strain C3). This structure was composed of individual "knobs" that sometimes mediated cell-to-cell adhesion in the culture.
Full text
PDF

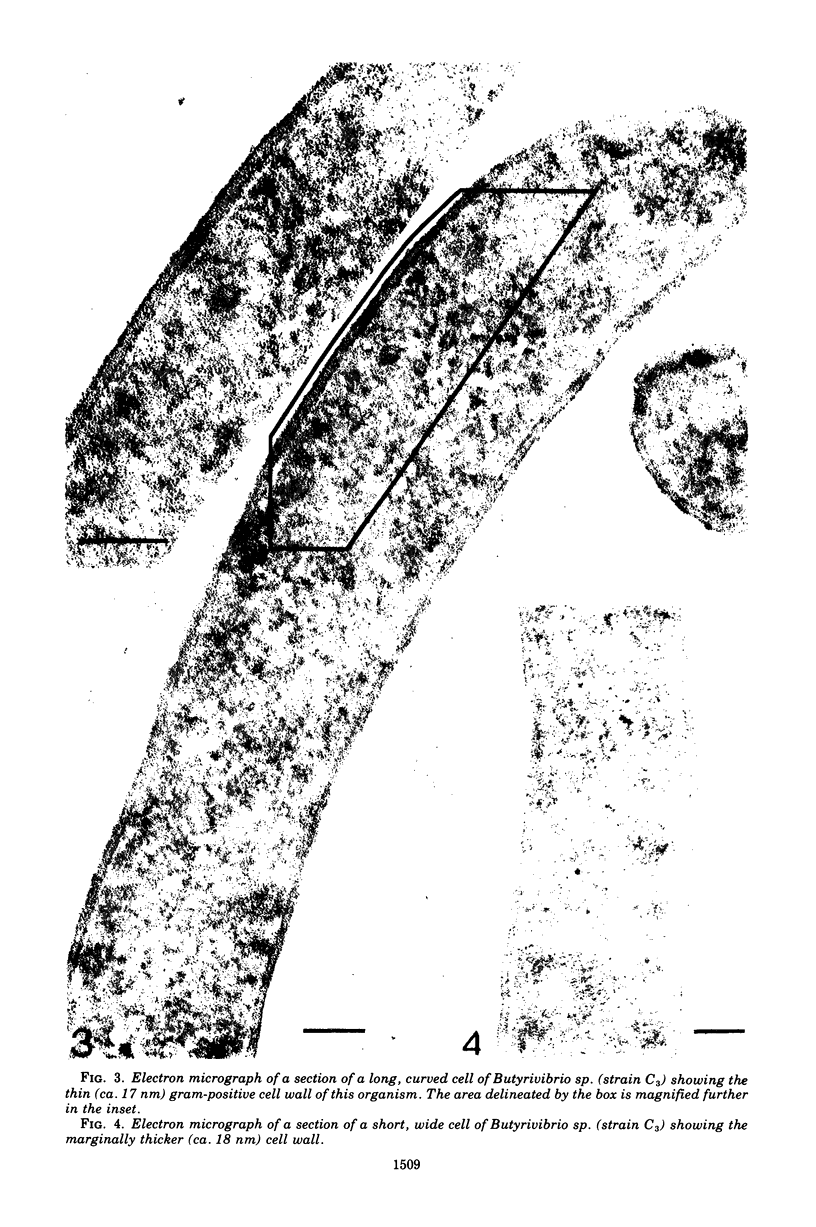


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akin D. E. Ultrastructure of rumen bacterial attachment to forage cell walls. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Apr;31(4):562–568. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.4.562-568.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRYANT M. P. Bacterial species of the rumen. Bacteriol Rev. 1959 Sep;23(3):125–153. doi: 10.1128/br.23.3.125-153.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRYANT M. P., SMALL N. The anaerobic monotrichous butyric acid-producing curved rod-shaped bacteria of the rumen. J Bacteriol. 1956 Jul;72(1):16–21. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.1.16-21.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng K. J., Costerton J. W. Localization of alkaline phosphatase in three gram-negative rumen bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1973 Oct;116(1):424–440. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.1.424-440.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng K. J., Costerton J. W. Ultrastructure of cell envelopes of bacteria of the bovine rumen. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Jun;29(6):841–849. doi: 10.1128/am.29.6.841-849.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng K. J., Hironaka R., Jones G. A., Nicas T., Costerton J. W. Frothy feedlot bloat in cattle: production of extracellular polysaccharides and development of viscosity in cultures of Streptococcus bovis. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Apr;22(4):450–459. doi: 10.1139/m76-071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng K. J., Jones G. A., Simpson F. J., Bryant M. P. Isolation and identification of rumen bacteria capable of anaerobic rutin degradation. Can J Microbiol. 1969 Dec;15(12):1365–1371. doi: 10.1139/m69-247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Cheng K. J. The role of the bacterial cell envelope in antibiotic resistance. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1975 Dec;1(4):363–377. doi: 10.1093/jac/1.4.363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Damgaard H. N., Cheng K. J. Cell envelope morphology of rumen bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jun;118(3):1132–1143. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.3.1132-1143.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Ingram J. M., Cheng K. J. Structure and function of the cell envelope of gram-negative bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Mar;38(1):87–110. doi: 10.1128/br.38.1.87-110.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W. The structure and function of the cell envelope of gram-negative bacteria. Rev Can Biol. 1970 Sep;29(3):299–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNGATE R. E. The anaerobic mesophilic cellulolytic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1950 Mar;14(1):1–49. doi: 10.1128/br.14.1.1-49.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewett M. J., Wicken A. J., Knox K. W., Sharpe M. E. Isolation of lipoteichoic acids from Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 May;94(1):126–130. doi: 10.1099/00221287-94-1-126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins M. L., Shockman G. D. Model for cell wall growth of Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1970 Feb;101(2):643–648. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.2.643-648.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft J. H. Ruthenium red and violet. I. Chemistry, purification, methods of use for electron microscopy and mechanism of action. Anat Rec. 1971 Nov;171(3):347–368. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091710302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURRAY R. G., STEED P., ELSON H. E. THE LOCATION OF THE MUCOPEPTIDE IN SECTIONS OF THE CELL WALL OF ESCHERICHIA COLI AND OTHER GRAM-NEGATIVE BACTERIA. Can J Microbiol. 1965 Jun;11:547–560. doi: 10.1139/m65-072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCready R. G., Costerton J. W., Laishley E. J. Morphological modifications of cells of Clostridium pasteurianum caused by growth on sulfite. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Feb;22(2):269–275. doi: 10.1139/m76-036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson H., Irvin R., Costerton J. W., Cheng K. J. Ultrastructure and adhesion properties of Ruminococcus albus. J Bacteriol. 1975 Apr;122(1):278–287. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.1.278-287.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCOTT H. W., DEHORITY B. A. VITAMIN REQUIREMENTS OF SEVERAL CELLULOLYTIC RUMEN BACTERIA. J Bacteriol. 1965 May;89:1169–1175. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.5.1169-1175.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe M. E., Brock J. H., Phillips B. A. Glycerol teichoic acid as an antigenic determinant in a Gram-negative bacterium Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Jun;88(2):355–363. doi: 10.1099/00221287-88-2-355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicken A. J., Knox K. W. Lipoteichoic acids: a new class of bacterial antigen. Science. 1975 Mar 28;187(4182):1161–1167. doi: 10.1126/science.46620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]