Abstract
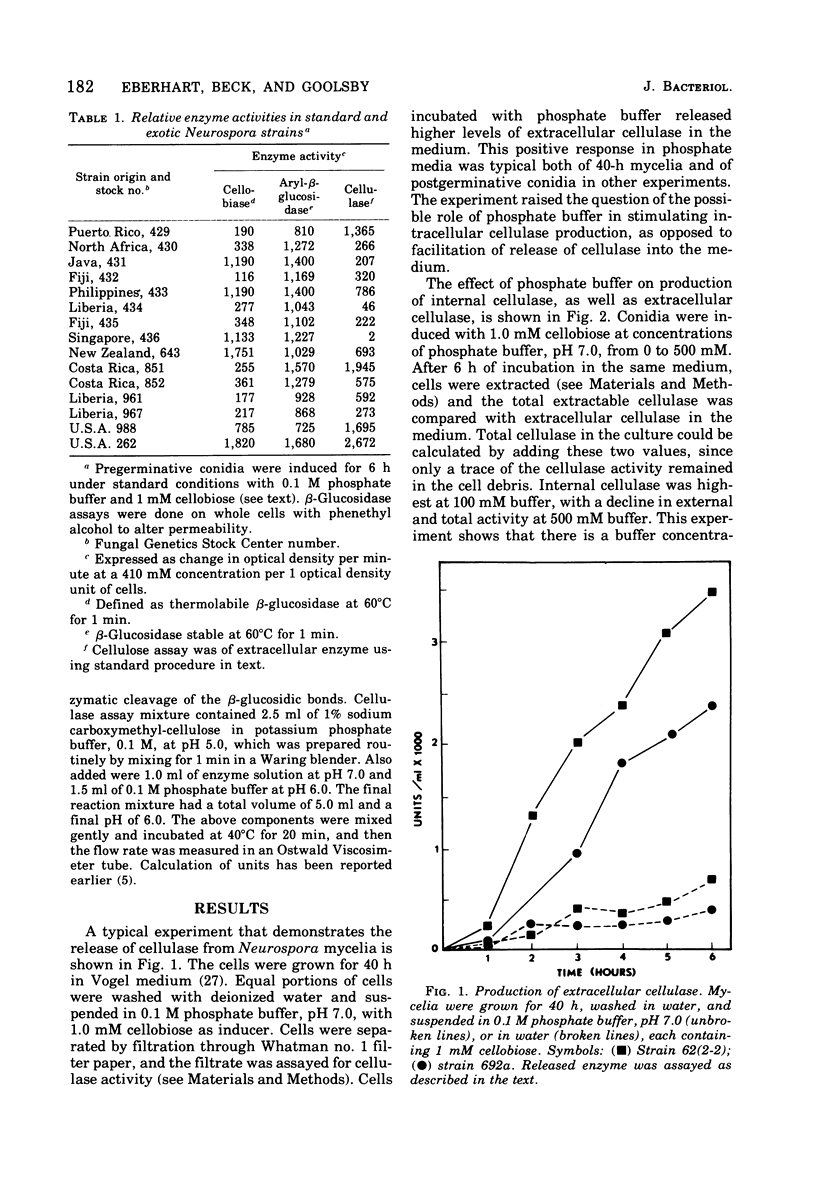
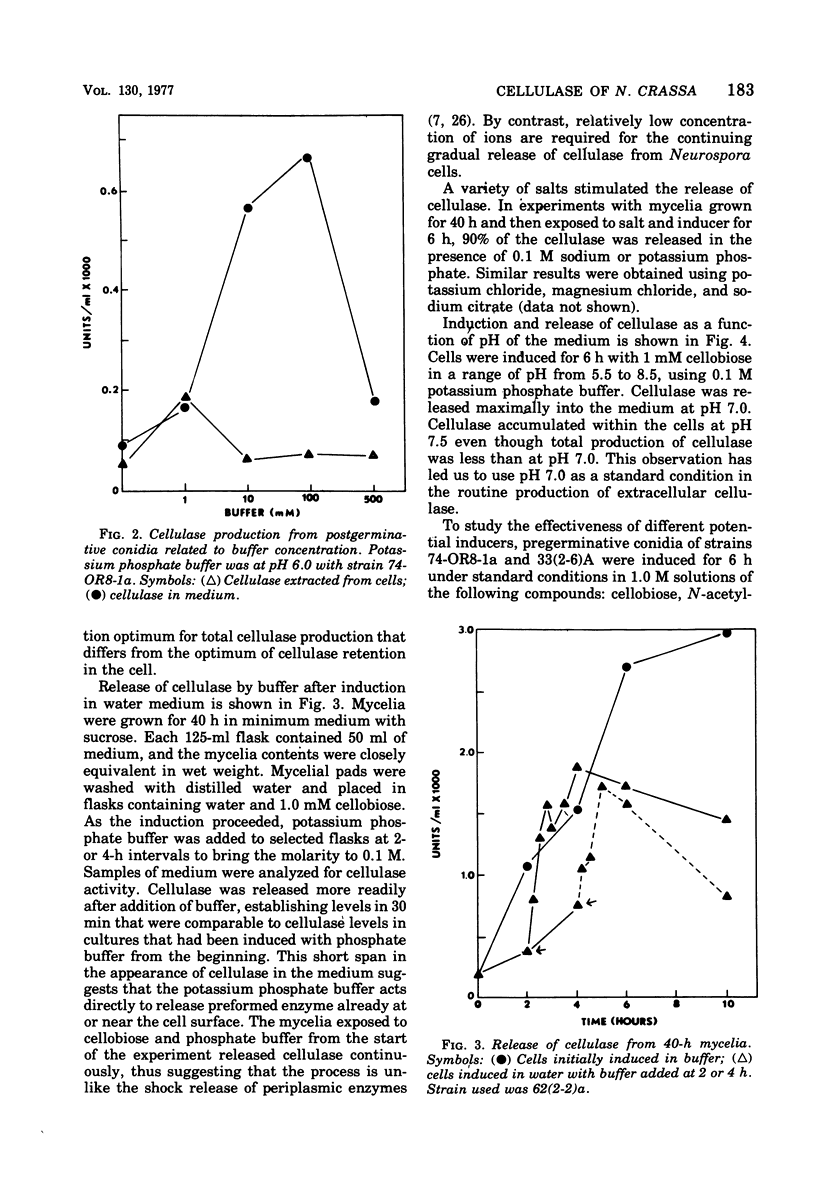
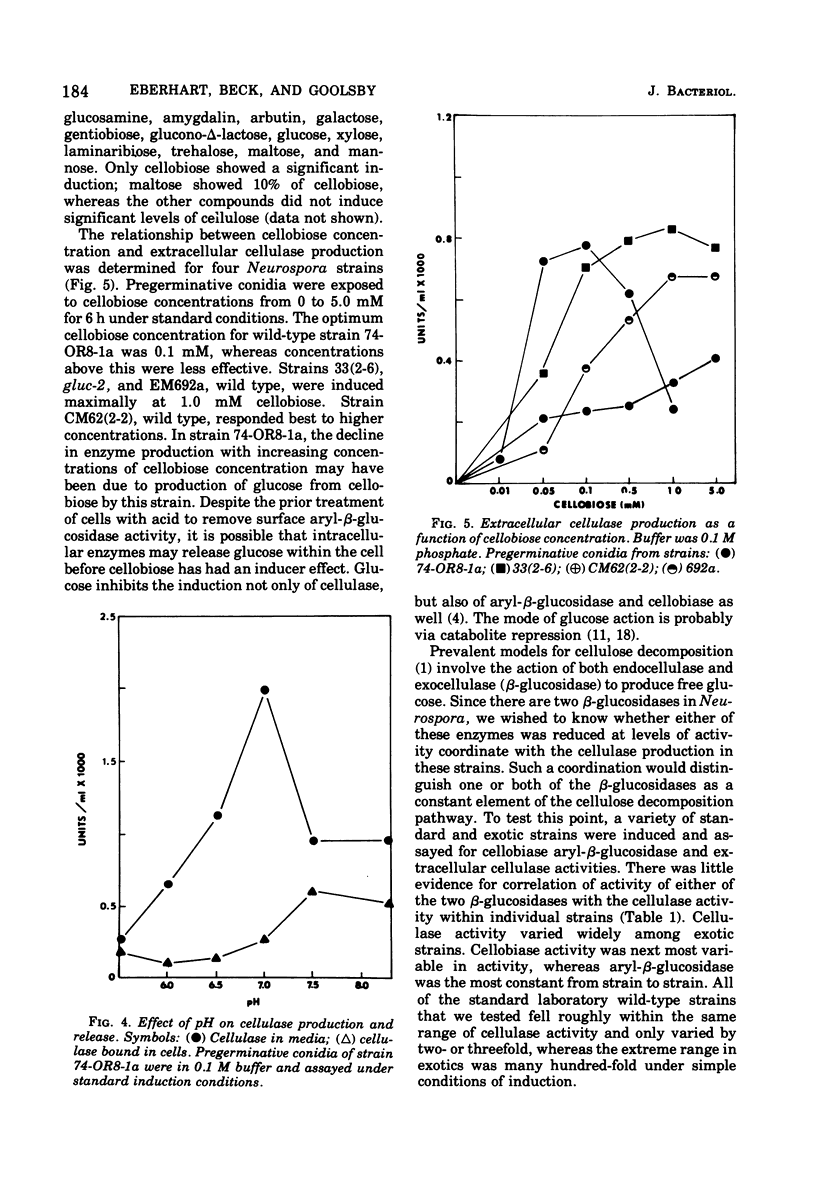
Mycelia and ungerminated conidia of Neurospora crassa were found to secrete extracellular endocellulase (EC 3.2.1.4). A simple induction system of potassium phosphate buffer (ph 6.0) plus inducer relied on the internal metabolic reserves of conicia or mycelia to provide energy and substrates for protein synthesis. Buffer concentration for optimum enzyme production was 100 mM, but at higher buffer concentrations enzyme production was inhibited. Cellobiose was clearly the best inducer, with an optimum effect from 0.05 to 1 mM. In deionized water, cellulase remained mostly associated with the cell, but a variety of salts stimulated the release of cellulase into the medium.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chang P. L., Trevithick J. R. How important is secretion of exoenzymes through apical cell walls of fungi? Arch Microbiol. 1974;101(4):281–293. doi: 10.1007/BF00455945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EBERHART B., CROSS D. F., CHASE L. R. BETA-GLUCOSIDASE SYSTEM OF NEUROSPORA CRASSA. I. BETA-GLUCOSIDASE AND CELLULASE ACTIVITIES OF MUTANT AND WILD-TYPE STRAINS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Apr;87:761–770. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.4.761-770.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberhart B. M., Beck R. S. Induction of beta-glucosidases in Neurospora crassa. J Bacteriol. 1973 Oct;116(1):295–303. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.1.295-303.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberhart B. M., Beck R. S. Localization of the beta-glucosidases in Neurospora crassa. J Bacteriol. 1970 Feb;101(2):408–417. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.2.408-417.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta D. P., Heale J. B. Induction of cellulase (Cx) in Verticillium albo-atrum. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Oct;63(2):163–173. doi: 10.1099/00221287-63-2-163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCH H. M. Temperature-dependent cellulase production by Neurospora crassa and its ecological implications. Experientia. 1954 Apr 15;10(4):180–182. doi: 10.1007/BF02157201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heppel L. A. Selective release of enzymes from bacteria. Science. 1967 Jun 16;156(3781):1451–1455. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3781.1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGASANIK B. Catabolite repression. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1961;26:249–256. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1961.026.01.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDELS M., REESE E. T. Induction of cellulase in fungi by cellobiose. J Bacteriol. 1960 Jun;79:816–826. doi: 10.1128/jb.79.6.816-826.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers M. G., Eberhart B. Regulation of cellulase and cellobiase in Neurospora crassa. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Sep 8;24(5):782–785. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90394-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville M. M., Suskind S. R., Roseman S. A derepressible active transport system for glucose in Neurospora crassa. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1294–1301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nisizawa T., Suzuki H., Nisizawa K. Catabolite repression of cellulase formation in Trichoderma viride. J Biochem. 1972 Jun;71(6):999–1007. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarborough G. A. Sugar transport in Neurospora crassa. J Biol Chem. 1970 Apr 10;245(7):1694–1698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R. P., Wiley W. R. Regulation of sugar transport in Neurospora crassa. J Bacteriol. 1971 May;106(2):487–492. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.2.487-492.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TONOMURA K., TANABE O. LOCALIZATION OF CELL-BOUND ALPHA-AMYLASE IN ASPERGILLUS ORYZAE DEMONSTRATED BY FLUORESCENT-ANTIBODY TECHNIQUE. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jan;87:226–227. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.1.226-227.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trevithick J. R., Metzenberg R. L. Genetic alteration of pore size and other properties of the Neurospora cell wall. J Bacteriol. 1966 Oct;92(4):1016–1020. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.4.1016-1020.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trevithick J. R., Metzenberg R. L. Molecular sieving by Neurospora cell walls during secretion of invertase isozymes. J Bacteriol. 1966 Oct;92(4):1010–1015. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.4.1010-1015.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weimberg R., Orton W. L. Elution of exocellular enzymes from Saccharomyces fragilis and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):1–13. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.1-13.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley W. R. Tryptophan transport in Neurospora crassa: a tryptophan-binding protein released by cold osmotic shock. J Bacteriol. 1970 Sep;103(3):656–662. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.3.656-662.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yabuki M., Fukui S. Presence of binding site for alpha-amylase and of masking protein for this site on mycelial cell wall of Aspergillus oryzae. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):138–144. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.138-144.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


