Abstract
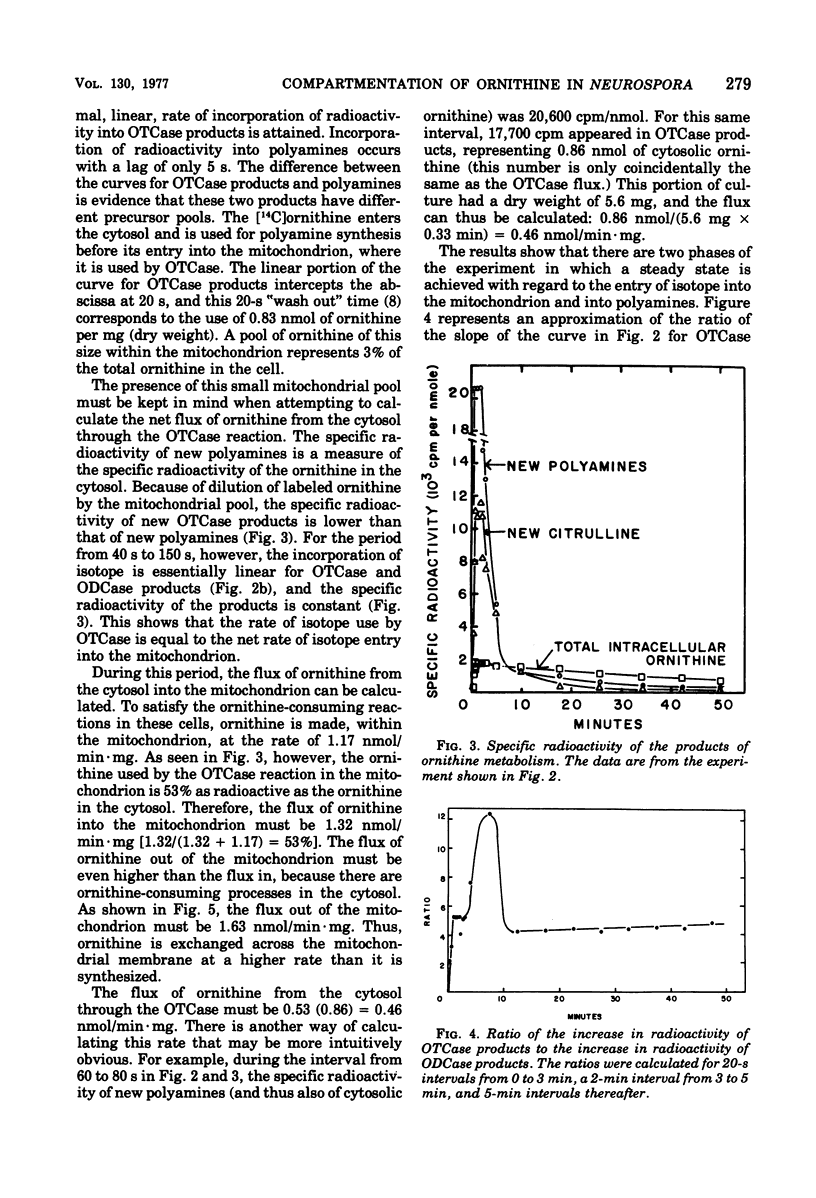
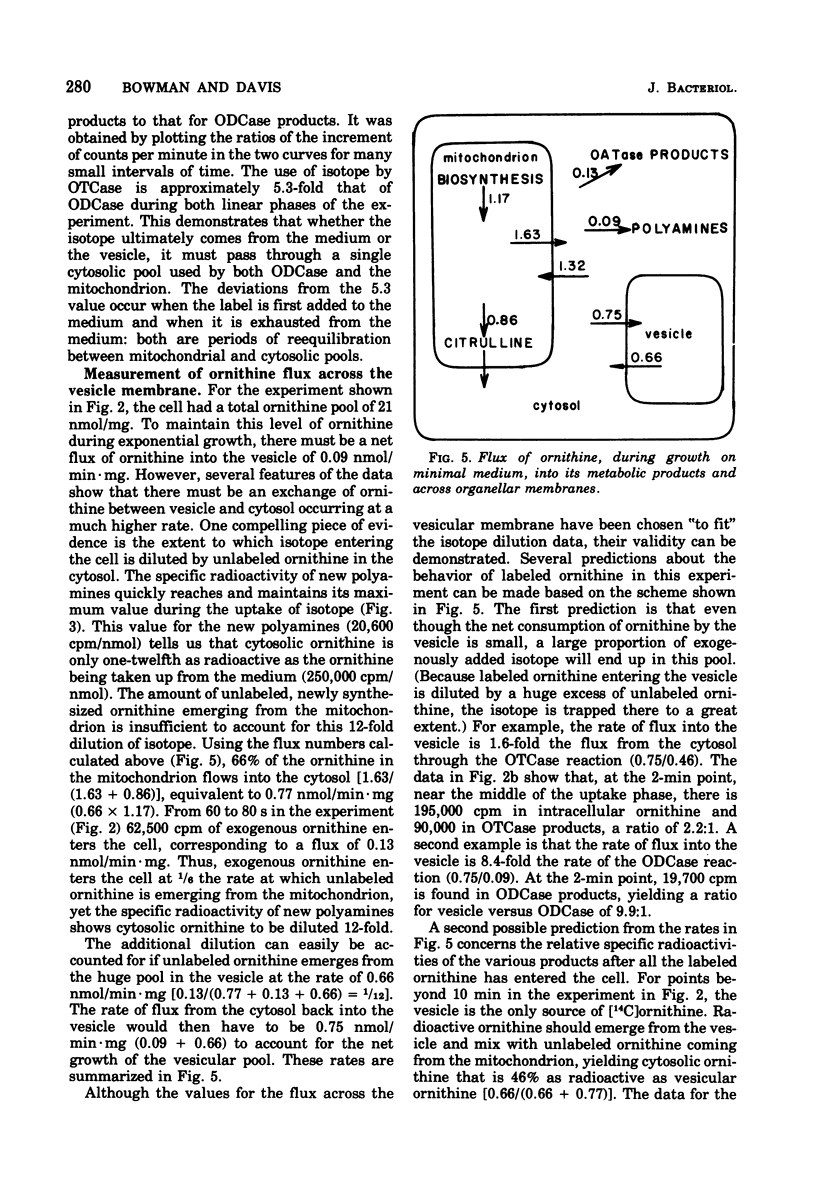
During growth on minimal medium, cells of Neurospora contain three pools of ornithine. Over 95% of the ornithine is in a metabolically inactive pool in vesicles, about 1% is in the cytosol, and about 3% is in the mitochondria. By using a ureaseless strain, we measured the rapid flux of ornithine across the membrane boundaries of these pools. High levels of ornithine and the catabolic enzyme ornithine aminotransferase coexist during growth on minimal medium but, due to the compartmentation of the ornithine, only 11% was catabolized. Most of the ornithine was used for the synthesis of arginine. Upon the addition of arginine to the medium, ornithine was produced catabolically via the enzyme arginasn early enzyme of ornithine synthesis. The biosynthesis of arginine itself, from ornithine and carbamyl phosphate, was halted after about three generations of growth on arginine via the repression of carbamyl phosphate synthetase A. The catabolism of arginine produced ornithine at a greater rate than it had been produced biosynthetically, but this ornithine was not stored; rather it was catabolized in turn to yield intermediates of the proline pathway. Thus, compartmentation, feedback inhibition, and genetic repression all play a role to minimize the simultaneous operation of anabolic and catabolic pathways for ornithine and arginine.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernhardt S. A., Davis R. H. Carbamoyl phosphate compartmentation in Neurospora: histochemical localization of aspartate and ornithine transcarbamoylases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1868–1872. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cybis J. J., Davis R. H. Acetylglutamate kinase: a feedback-sensitive enzyme of arginine biosynthesis in Neurospora. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Sep 23;60(2):629–634. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90287-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cybis J., Davis R. H. Organization and control in the arginine biosynthetic pathway of Neurospora. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jul;123(1):196–202. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.1.196-202.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. H., Lawless M. B., Port L. A. Arginaseless Neurospora: genetics, physiology, and polyamine synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1970 May;102(2):299–305. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.2.299-305.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. H., Mora J. Mutants of Neurospora crassa deficient in ornithine-delta-transmainase. J Bacteriol. 1968 Aug;96(2):383–388. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.2.383-388.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. H. Utilization of exogenous and endogenous ornithine by Neurospora crassa. J Bacteriol. 1968 Aug;96(2):389–395. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.2.389-395.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin J. N., Bowman B. J., Davis R. H. Compartmental behavior of ornithine in Neurospora crassa. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 10;251(13):3948–3955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIDDELHOVEN W. J. THE PATHWAY OF ARGININE BREAKDOWN IN SACCHAROMYCES CEREVISIAE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Dec 9;93:650–652. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90349-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middelhoven W. J. The derepression of arginase and of ornithine transaminase in nitrogen-starved baker's yeast. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 11;156(2):440–443. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(68)90284-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mora J., Salceda R., Sanchez S. Regulation of arginase activity by intermediates of the arginine biosynthetic pathway in Neurospora crassa. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jun;110(3):870–877. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.3.870-877.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner S. Enzymes of arginine and urea synthesis. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1973;39:1–90. doi: 10.1002/9780470122846.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian K. N., Weiss R. L., Davis R. H. Use of external, biosynthetic, and organellar arginine by Neurospora. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jul;115(1):284–290. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.1.284-290.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thwaites W. M. A mutation reducing feedback regulation by arginine in suppressed pyr-3 mutants in Neurospora. Genetics. 1967 Apr;55(4):769–781. doi: 10.1093/genetics/55.4.769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. L. Compartmentation and control of arginine metabolism in Neurospora. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jun;126(3):1173–1179. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.3.1173-1179.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. L., Davis R. H. Intracellular localization of enzymes of arginine metabolism in Neurospora. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 10;248(15):5403–5408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. L. Intracellular localization of ornithine and arginine pools in Neurospora. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 10;248(15):5409–5413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams L. G., Davis R. H. Pyrimidine-specific carbamyl phosphate synthetase in Neurospora crassa. J Bacteriol. 1970 Aug;103(2):335–341. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.2.335-341.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


